(Press-News.org) Animals using the most of efficient methods of searching for resources may well pay with their lives, scientists at the University of Bristol have discovered.
The findings, published today in Behavioural Ecology, reveal why animals may not always use a searching strategy that maximises results.
How animals move through their habitat, particularly in search for food, is a major question in biology, and has application in how animals will respond to environmental change.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that a special kind of movement, known as Lévy motion, increases the ability to find resources because it includes long-distance moves between areas being searched, as well as periods of concentrated searching in one area. It has also been shown that a range of animals use this kind of movement.
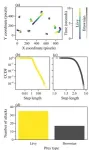
This study is the first to demonstrate a potential cost of Lévy motion in an experiment, showing prey using Lévy motion are targeted twice as often as prey using Brownian motion – the movement observed in molecules in a gas, and thus a baseline expectation.
Professor Christos Ioannou from Bristol’s School of Biological Sciences explained: “We show that this is because the predators prefer to target prey that are moving with straighter paths of motion, possibly because this makes the future position of the prey more predictable.”
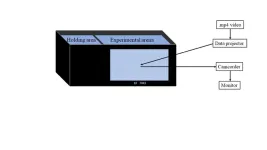
Professor Ioannou and his team used a virtual prey approach. They developed a computer simulation of the prey which are identical in size, colour, speed etc but differ in how they turn.
The video was then played to stickleback fish in a tank by projecting the video onto a translucent screen. This allowed the fish to see the prey, and for researchers to capture and record their choices.
“By using an experimental design that presents virtual prey on a screen to real predators, we can control everything about the prey and isolate the variable we're interested in - here, movement - while also using real animals,” continued Professor Ioannou.
This study demonstrates that prey animals might not always use a searching strategy that maximises finding a resource because there might be costs that were, previous to the study, unknown. This might explain why some studies have found animals use different kinds of searches other than Lévy motion.
He added: “Our study shows, for the first time, that animals using a common and very effective way of searching for resources may actually pay a cost of being more susceptible to predators.
“Going forward, we want to look at whether the prey of sticklebacks show Levy or Brownian motion.
“More broadly, our study predicts that prey animals should be less likely to demonstrate Lévy motion than apex predators.”
Paper:
‘Virtual prey with Lévy motion are preferentially attacked by predatory fish’ by Christos Ioannou et al in Behavioural Ecology.
END
Most effective ways of foraging can attract predators, scientists find
2023-05-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Heavy drinkers risk muscle loss, new study finds
2023-05-25
EMBARGO: 00.01 BST (London time) on THURSDAY, MAY 25, 2023 / 19.01 US EDT on WEDNESDAY, MAY 24, 2023
Heavy drinkers risk muscle loss, new study finds
Peer reviewed – observational study - humans
Heavy drinkers could be putting themselves at risk of muscle loss and frailty in later life, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today shows with statistical modelling that people with the lowest amount of muscle were drinking 10 units or more a day – about ...
Plant-based diets are better for your health – as well as for the climate
2023-05-25
Vegetarian and vegan diets are linked to lower levels of cholesterol and fats in your blood, according to an analysis of all the evidence from randomised trials published since 1982.
The authors of the study, which is published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Thursday), say this means that plant-based diets can play a significant role in reducing blocked arteries, thereby lowering the risk of heart and blood vessel diseases, such as stroke and heart attacks.
The researchers looked at 30 randomised trials with a total of 2,372 participants, published between 1982 and 2022, that quantified the effect of vegetarian or vegan diets versus omnivorous diets on levels ...
Successful terahertz wireless communication using a micro-resonator soliton comb: Expectations for next-generation mobile communications based on photonic technology
2023-05-25
Key points
Wireless electronics that have been used thus far in next-generation mobile communications using terahertz waves may reach their technical limit (namely, upper limit of frequency for wireless electronics).
Terahertz wireless communication in the 560-GHz band was achieved by optical-to-electrical conversion of ultra-high-frequency photonic RF signals in near-infrared micro-resonator soliton comb.
Adding the low-phase noise that is characteristic of micro-resonator soliton comb to terahertz waves makes it possible to achieve ultra-high-speed ...
Sudden infant death syndrome may have biologic cause
2023-05-25
Sudden infant death syndrome is a case where the death of an apparently healthy infant before their first birthday remains unexplained even after thorough investigation. Death generally seems to occur when infants are sleeping. While rare, it is the leading post-neonatal infant death in the United States today, occurring in 103 out of 100,000 live births a year. Despite the initial success of national public health campaigns promoting safe sleep environments and healthier sleep positions in infants in the 1990s in the ...
Risk of death from liver disease is twice as high in lower-income countries, new research suggests
2023-05-24
Richmond, Va. (May 23, 2023) — New research is shedding light on global disparities in mortality rates from late-stage liver disease, also called cirrhosis. The study, published Monday in Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, revealed that the risk of death for hospitalized cirrhosis patients was more than twice as high in lower-or lower-middle income countries compared to high-income countries, largely because of limited access to diagnostic and therapeutic resources.
Liver disease occurs when a person’s liver experiences chronic inflammation, often due to obesity, excessive alcohol use, viral hepatitis or a combination. ...
Unlocking restful nights: unveiling teen-friendly social media habits for optimal sleep
2023-05-24
Toronto, ON - The US Surgeon General issued an advisory on social media and youth mental health a week after the American Psychological Association issued a health advisory on social media use in adolescence. Both advisories note potential links between social media use and poor sleep quality in teens. Given these concerns, what specific actions can teens and parents take to optimize sleep?
A new national study, published in Sleep Health, offers insights into screen habits linked with better sleep.
“Getting enough sleep is crucial ...
Researchers map the brain during blood sugar changes
2023-05-24
EL PASO, Texas (May 24, 2023) – Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso have successfully mapped specific regions in the brain that are activated in association with changes in blood sugar — also known as glucose — providing fundamental location information that could ultimately lead to more targeted therapies for people who struggle with conditions like diabetes.
The landmark 13-year study, published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, describes how the team used careful microscopic analysis to pinpoint specific cell populations ...
External factors shape genetic predisposition to lipids, Alzheimer’s and heart disease in MLXIPL gene
2023-05-24
“Recent findings suggest that neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases may have overlapping etiologies [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- May 24, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 9, entitled, “Exogenous exposures shape genetic predisposition to lipids, Alzheimer’s, and coronary heart disease in the MLXIPL gene locus.”
In this new study, researchers Yury Loika, Elena Loiko, Fan ...
A student’s poor eating habits can lead to a lifetime of illness
2023-05-24
A UBC Okanagan researcher is cautioning that a person’s poor eating habits established during post-secondary studies can contribute to future health issues including obesity, respiratory illnesses and depression.
Dr. Joan Bottorff, a Professor with UBCO’s School of Nursing, is one of several international researchers who published a multi-site study looking at the eating habits of university students. Almost 12,000 medical students from 31 universities in China participated in the study that aimed to determine the association between eating behaviours, obesity and various diseases.
The point, ...
Recent UCLA computer grad constructs “Crown Jewel of Cryptography”
2023-05-24
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today announced that Aayush Jain receives the 2022 ACM Doctoral Dissertation Award for his dissertation “Indistinguishability Obfuscation from Well-Studied Assumptions,” which established the feasibility of mathematically rigorous software obfuscation from well-studied hardness conjectures.
The central goal of software obfuscation is to transform source code to make it unintelligible without altering what it computes. Additional conditions may be added, such as requiring the transformed code to perform ...