Awareness of racial, ethnic bias and potential solutions to address bias with use of health care algorithms
JAMA Health Forum
2023-06-02
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: This qualitative study found that participants perceived widespread and increasing use of algorithms in health care and lack of oversight, potentially exacerbating racial and ethnic inequities. Increasing awareness for clinicians and patients and standardized, transparent approaches for algorithm development and implementation may be needed to address racial and ethnic biases related to algorithms.
Authors: Peter Treitler, M.S.W., of Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1197)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1197?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=060223
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-02
Contrary to expectations, the risk for relapses, overdoses and deaths related to substance use disorder didn’t increase after a large-scale prison release in New Jersey, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in JAMA Health Forum, examined whether post-release overdose deaths and drug-related hospital and emergency department visits increased after more than 2,000 individuals were released from prison in late 2020 as the result of a pandemic-era policy.
“Risk of relapse and adverse health events is high following prison release, with risk of fatal overdose ...
2023-06-02
Our skin contains specialised long-lived killer cells that protect against intruders. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have now identified how these cells are formed, and shown that high levels of memory killer cells in cancer tissue correlate with a better survival rate in people with melanoma. The study is published in the journal Immunity.
Certain immune T cells called tissue-resident memory cells are formed locally in the skin and other tissue, and protect against infections that they have encountered before. Some of ...
2023-06-02
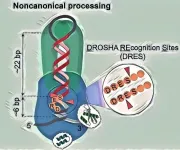
To discover and thoroughly demonstrate the newly identified noncanonical cleavage mechanism, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) research team, led by Prof. Tuan Anh Nguyen, Assistant Professor of the Division of Life Science, used several sophisticated techniques, such as miRNA sequencing, pri-miRNA structure analysis, and high-throughput pri-miRNA cleavage assays for approximately 260,000 pri-miRNA sequences. In contrast to the canonical mechanism, the noncanonical mechanism does not rely on several essential protein and RNA elements ...
2023-06-02
New research suggests that the immune system’s ability to respond to spinal cord injuries diminishes with age – and identifies potential avenues to improve that response and help patients heal.
The new findings offer important insights into how the immune system responds to spinal-cord injuries, and why that response becomes blunted with the passing years. Further, it reveals an important role for the membranes surrounding the spinal cord in mounting the immune response to spinal-cord injury. With this information, doctors one day may be able to bolster the body’s natural immune response to improve patient outcomes, particularly among older adults.
“Recently, ...
2023-06-02
Researchers from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center have made a foundational discovery about chromosome biology through their work on the first-ever human pangenome reference.
Published recently by the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium in the journal Nature, the draft pangenome uses complete genome assemblies to provide a diverse look at the genetic makeup of humans. Researchers in the UTHSC Department of Genetics, Genomics and Informatics created the technical tools to build the pangenome, and then used the tools to understand variation in parts of the genome that could not be seen before.
The pangenome ...
2023-06-02
New radio telescope images reveal hundreds of filaments along the galactic plane, each measuring 5 to 10 light-years in length
These structures likely originated a few million years ago when outflow from our supermassive black hole interacted with surrounding materials
Researcher: ‘I was actually stunned when I saw these’
EVANSTON, Ill. — An international team of astrophysicists has discovered something wholly new, hidden in the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
In the early 1980s, Northwestern University’s Farhad Yusef-Zadeh discovered gigantic, one-dimensional filaments dangling vertically near Sagittarius A*, our ...
2023-06-02
A study involving UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers found when ribociclib, a targeted therapy drug, is added to hormone therapy there are a significant invasive disease-free survival benefit in patients with early hormone-receptor (HR) positive/HER2 negative breast cancer.
Researchers found that patients who took the combination therapy had substantially longer invasive disease-free survival compared to those who were treated with the hormone therapy alone, regardless of whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The addition of the targeted therapy reduced the risk of recurrence by 25%.
The results were shared today during the American Society of Clinical ...
2023-06-02
The world is getting hotter, causing shifts in seasonal patterns and increasing the amount of extreme weather such as severe droughts and heat waves, which can affect crop yields and food supplies. A recent study led by a researcher at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University found that the likelihood of extreme temperatures that could affect crop yields has increased significantly in wheat-producing regions of the U.S. and China.
The findings predict heat waves that happened approximately ...
2023-06-02
New theoretical research by Michael Wondrak, Walter van Suijlekom and Heino Falcke of Radboud University has shown that Stephen Hawking was right about black holes, although not completely. Due to Hawking radiation, black holes will eventually evaporate, but the event horizon is not as crucial as had been believed. Gravity and the curvature of spacetime cause this radiation too. This means that all large objects in the universe, like the remnants of stars, will eventually evaporate.
Using a clever combination of quantum physics and Einstein’s theory of gravity, Stephen Hawking argued that the spontaneous creation and annihilation ...
2023-06-02
Human activity has degraded ecosystems and damaged biodiversity around the world, but ecosystem restoration offers hope for the future. Scientists studying the restoration of underwater seaweed forests which provide other species with food and shelter have found that 10 years of restoration efforts have helped a damaged forest regrow to richness and strength comparable to forests that have never been disturbed.
“Macroalgal forests are found along over one-third of the world’s coastlines and underpin ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Awareness of racial, ethnic bias and potential solutions to address bias with use of health care algorithms
JAMA Health Forum