(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, June 13, 2023 – Cognitive deficits accompany mood disorders and other psychiatric conditions, often with debilitating effects. Limited treatments currently exist, but studies in animals and humans have pointed to drugs such as the laxative prucalopride that activate serotonin receptors as a potential therapeutic for the symptoms. It has remained unclear, however, how the medication affects resting brain activity. Now, a new study in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier, examines the drug’s effects in healthy human adults.
Serotonin receptors and the 5-HT4-type receptors in particular are found in areas throughout the brain, including the frontal cortex, basal ganglia, and hippocampus, that are known to mediate cognitive function and regulate mood. Serotonin receptors are the primary targets of antidepressant medications, but resolving mood disturbances often does not resolve cognitive symptoms.
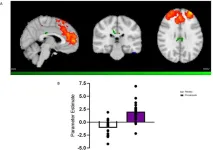
The researchers enlisted 50 healthy volunteers, half of whom received a six-day course of prucalopride, a highly selective agonist of the 5-HT4 type serotonin receptor, whereas the other half of the participants received a placebo. Participants underwent scanning with functional magnetic resonance imaging, including a “resting scan,” in which they relaxed in the scanner.
Lead author Angharad de Cates, PhD, MRCPsych, at the University of Oxford, said of the work, “Our previous studies on prucalopride demonstrated that even at low clinical doses it can improve cognition and memory in healthy volunteers. This latest research provides a neurological mechanism by which this might occur.”
Participants who received the medication displayed more functional connectivity in their resting-state (rsFC) between major cognitive networks. This included more rsFC between the central executive network, a brain network used for processing thoughts, and the posterior and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), brain areas that regulate information processing and attention in the brain. There was also more rsFC between regions of the ACC and the lateral occipital cortex, a region that helps us pay attention to objects that matter. In addition, medicated participants compared to placebo controls showed decreased rsFC in the default mode network, a brain network that is activated during mind wandering.
Dr. de Cates added, “This provides further evidence that prucalopride is having an effect in areas of the brain that improve cognitive function – both by increasing and reducing connectivity between specific brain regions as required.”
Susannah Murphy, PhD, Associate Professor and joint senior author of the study, said, “Appropriate connectivity between and within these brain networks is needed to think properly, and this connectivity has been shown to be abnormal in depression. Here, the participants taking prucalopride had better scores on cognitive tests the day of the scan compared to the placebo participants. That suggests that the changes in rsFC that we saw with prucalopride may serve as a ‘signature’ of a drug that improves cognition.”
Dr. Murphy continued, “Untreated cognitive problems have a significant impact on the quality of life of people with depression. This study adds to the growing evidence base that drugs affecting the 5-HT4 serotonin receptor hold promise as a novel way to treat depression and cognitive impairment.”
Catherine Harmer, PhD, Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience and joint senior author of the study, said, “This study adds to the evidence base that the common laxative treatment prucalopride can have important effects in the brain, particularly affecting circuits which are important for learning and memory. Together with previous data, this suggests that this drug might be useful as a pro-cognitive treatment in disorders such as depression.”
Cameron Carter, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, said of the work, “These data, showing modulation of resting state connectivity in the brain by the 5HT4 receptor agonist and putative cognitive enhancer prucalopride, add to previous evidence that the agent modulates brain systems that are engaged during focused, higher cognitive activity and might have therapeutic potential.”
END
Serotonin booster leads to increased functional brain connectivity
Pro-cognitive agent could have therapeutic use, according to a new study in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
2023-06-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Positive parenting buffers stress’s effects on the brain
2023-06-13
Positive parenting—as reported by children and teenagers— protects young people from the deleterious effects of stressors like financial hardship or serious illness, according to a study. Jamie Hanson and colleagues examined magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data along with survey data for 482 participants in an ongoing study, the Healthy Brain Network, who were between the ages of 10–17 at the time of data collection. Previous work has found associations between stress and small hippocampal volumes as well as between stress and behavioral problems—associations confirmed ...
DESI early data release holds nearly two million objects
2023-06-13
The universe is big, and it’s getting bigger. To study dark energy, the mysterious force behind the accelerating expansion of our universe, scientists are using the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) to map more than 40 million galaxies, quasars, and stars. Today, the collaboration publicly released its first batch of data, with nearly 2 million objects for researchers to explore.
The 80-terabyte data set comes from 2,480 exposures taken over six months during the experiment’s “survey validation” phase in 2020 and 2021. In this period ...
Treating wastewater using passive processes
2023-06-13
Human activities have a significant impact on natural waters, aquatic biodiversity and the quality of drinking water resources. For Professor Mathieu Lapointe of the Department of Construction Engineering at École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS), it is possible to treat certain types of wastewater—not currently treated—globally using more sustainable and affordable in situ methods.
In a study carried out by Professor Lapointe and published in the Nature journal, the rate of discharge into the environment of certain ...
Scholastica announces CRediT Taxonomy support across its journal publishing solutions
2023-06-13
CHICAGO, IL (June 13, 2023) — Scholastica, a leading academic journal publishing software provider, has announced CRediT Taxonomy support across its products and services in line with ANSI/NISO guidelines. The CRediT Taxonomy, which consists of 14 research contributor roles, helps facilitate transparency around research development processes and ensure proper acknowledgment of all contributors.
With the new CRediT implementation, journals using Scholastica's peer review system can request to have CRediT fields added to their submission form, ...
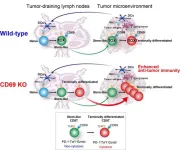
The benefits of Anti-CD69 antibodies for future cancer therapies
2023-06-13
CD8+ T cells, a vital component of the immune system that provides immunity against cancer, have been the focal point of anti-cancer therapies. Recent studies have identified two major subpopulations of these cells present within the tumor—the stem-like cells that do not have anti-tumor activity, and the terminally differentiated CD8+ T cells, which are generated from the stem-like cells and have cytotoxic function on tumor cells. Tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs) have been found to be the primary site for the presence of these cells. However, the molecular mechanisms responsible for the generation of stem-like cells into terminally differentiated ...
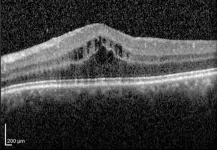
Intraocular corticosteroids best for treating complications of chronic inflammatory eye condition
2023-06-13
Repeat treatment with corticosteroid injections improved vision in people with persistent or recurrent uveitis-related macular edema better than two other therapies, according to results from a clinical trial funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI). Compared with methotrexate or ranibizumab intravitreal (in-the-eye) injections, the corticosteroid treatment achieved greater reductions in retinal swelling and was the only therapy in the study that improved vision. The report was published today in the journal Ophthalmology. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
“Prior to this study, we didn’t know the best treatment for persistent or recurrent macular edema, a major ...
Binghamton University and six HBCUs forge New Educational and Research Alliance
2023-06-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- In collaboration with the Thurgood Marshall College Fund, Binghamton University has announced a New Educational and Research Alliance (New ERA) with six historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs): Alabama A&M University, Central State University, Tuskegee University, Prairie-View A&M University, the University of the District of Columbia and Virginia State University.
The groundbreaking partnership is built on the shared missions of education, research and service, aiming to foster holistic, equitable and sustainable collaborations that will shape the future of academia and beyond.
The strategic alliances formed through this partnership will ...
PFAS, PFAS everywhere: how pristine are laboratory materials?
2023-06-13
How do you study the effects of exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), when it is in everything?! To study the effect of a chemical, toxicologists typically expose animals to various doses of the chemical over a period of time so that they could then study the dose versus effect relationship. Such toxicology studies often employee several types of “blanks” for quality control. Blanks are experiments where the test animals are not given any dose of the chemical being studied (sort of like a placebo in human drug ...
Groundbreaking study reveals new insights into human gut-brain connection
2023-06-13
Tulsa, Okla. – A pioneering study conducted by researchers at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR) in Tulsa, Okla., has made significant strides in understanding the elusive gut-brain connection, a complex relationship that has long puzzled scientists due to the difficulty of accessing the body's interior. The study, “Parieto-occipital ERP indicators of gut mechanosensation in humans,” appears in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Nature Communications.
The research team successfully had ...
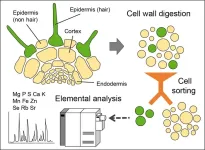
New approach opens avenue to investigate element distribution and transport pathways in plants
2023-06-13
Plant roots play a critical role in taking up, selecting, enriching and retaining a range of different mineral elements thereby supplying distant plant tissues with nutrients while sequestering excessive amounts of metals. To execute such element-specific functions, a range of ion transporters present at roots mediate the uptake, efflux and intracellular compartmentalization of different mineral elements. Most ion transporters show characteristic tissue and cell type-specific localization patterns, which can be altered in response to internal signalling or external cues. To fully ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
[Press-News.org] Serotonin booster leads to increased functional brain connectivityPro-cognitive agent could have therapeutic use, according to a new study in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging