(Press-News.org) Oxidative stress – characterized by elevated levels of unstable molecules called reactive oxygen species– is associated with neurodegeneration and cardiovascular disease. However, until recently it has not been possible to demonstrate a causal relationship between oxidative stress and disease states. A new study used “chemogenetics” to activate a recombinant yeast protein expressed in mouse tissues to manipulate levels of oxidative stress in living mice. Researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research applied chemogenetic approaches in a new transgenic mouse model to introduce oxidative stress into blood vessels and neurons.
The researchers initially set out to use this new transgenic mouse model to identify pathways through which oxidative stress might cause dysfunction of blood vessels and lead to diseases like hypertension and aortic aneurysms. But they were surprised to find that these mice rapidly developed profound ataxia, characterized by an inability to walk. Probing further, they found that specific sets of sensory neurons in peripheral nerve cells had undergone degeneration from oxidative stress caused by the transgene. And when the researchers looked at the hearts of these animals, they found that heart muscle had developed cardiac hypertrophy. This combination of sensory neuron degeneration and cardiac hypertrophy is associated with Friedreich’s ataxia (FA), a progressive neurodegenerative disease that is the most common form of hereditary ataxia found in patients. Researchers also characterized specific inflammatory cell types involved in these responses, offering a more complete understanding of the mechanisms through which FA causes cardiac hypertrophy.
“Our team followed up on an unexpected phenotype that we uncovered in a new transgenic mouse line and found surprising new connections between peripheral nerves and the heart,” said Thomas M. Michel, MD, PhD of the Brigham Division of Cardiovascular Medicine. “Our findings may help us understand the cardiac remodeling seen in the hearts of patients with neurodegenerative diseases.”
in Nature Communications.
END
New model offers insights into how stress in neurons connects to cardiovascular disease
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New data demonstrates potential role of probiotic supplementation in adults with Major Depressive Disorder
2023-06-14
Study shows improvements in depression and anxiety scores among individuals supplementing with probiotics alongside standard antidepressant medication
Data from a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pilot trial published today in JAMA Psychiatry
A new study published today (14 June) in JAMA Psychiatry has found evidence that supplementing the diet with a probiotic blend containing 14 strains of bacteria can help individuals who are being treated for major depressive disorder with antidepressants. The research, led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) ...
Racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic differences in food allergies
2023-06-14
About The Study: This survey study of a nationally representative sample suggests that the prevalence of food allergies was highest among Asian, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Black individuals compared with non-Hispanic white individuals in the U.S. Further assessment of socioeconomic factors and corresponding environmental exposures may better explain the causes of food allergy and inform targeted management and interventions to reduce the burden of food allergies and disparities in outcomes.
Authors: Ruchi S. Gupta, M.D., M.P.H., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding ...
Physician, biomedical scientist harassment on social media during pandemic
2023-06-14
About The Study: Many physicians and scientists in this survey study reported being harassed on social media during the COVID-19 pandemic, often due to their advocacy and on the basis of gender, race, sexual orientation, or disability. Many reported sexual harassment and sharing of their private information.
Authors: Regina Royan, M.D., M.P.H., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18315)
Editor’s ...
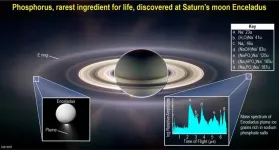
Key building block for life found at Saturn’s moon Enceladus
2023-06-14
SAN ANTONIO —Wednesday, June 14, 2023 —The search for extraterrestrial life in our solar system just got more exciting. A team of scientists including Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Christopher Glein has discovered new evidence that the subsurface ocean of Saturn’s moon Enceladus contains a key building block for life. The team directly detected phosphorus in the form of phosphates originating from the moon’s ice-covered global ocean using data from NASA’s Cassini mission. Cassini explored Saturn and its system of rings and moons for over ...
Study shows psychedelic drugs reopen ‘critical periods’ for social learning
2023-06-14
Neuroscientists have long searched for ways to reopen “critical periods” in the brain, when mammals are more sensitive to signals from their surroundings that can influence periods of brain development. Now, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine say a new study in mice shows that psychedelic drugs are linked by their common ability to reopen such critical periods, but differ in the length of time the critical period is open — from two days to four weeks with a single dose.
The findings, published June 16 in the journal Nature, provide a new explanation for how psychedelic drugs work, say the scientists, and suggest potential to treat a wider ...
Building a new vaccine arsenal to eradicate polio
2023-06-14
Despite some of the most successful international vaccination campaigns in history, the poliovirus continues to circulate around the world, posing a threat of neurological damage and even paralysis to anyone who is not vaccinated.
While the original polio strains, called wildtype, have largely been eliminated, new strains can develop from the oral polio vaccine (OPV), which is the one most used in the developing world. Oral vaccines use live, weakened virus that occasionally mutates to an active form, leading to outbreaks even in countries believed to have eliminated polio.
Scientists at UCSF and the UK’s National Institute of Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) have developed ...
Food allergy is highest among Hispanic, Black and Asian individuals
2023-06-14
· Many racial and ethnic groups not well aware of food allergies
· Lack of food allergy research in racial and ethnic communities
· ‘These individuals need to be aware so they can be diagnosed and treated’
CHICAGO --- Food allergy has not been on the radar of most racial and ethnic communities. But a new Northwestern Medicine study — the first population-based food allergy study in the U.S. to explore racial and ethnic differences in all age groups — shows why it should be.
The new study found the prevalence of food allergy is highest among Hispanic, non-Hispanic Black and ...
World’s first transgenic ants reveal how colonies respond to an alarm
2023-06-14
Ants navigate their richly aromatic world using an array of odor receptors and chemical signals called pheromones. Whether foraging or defending the nest, mating or tending to their young, ants both send and receive chemical signals throughout their lives. The importance of this system is underscored by how well equipped the ant brain is to process the abundance of scents: The olfactory processing center in the ant’s brain has 10 times as many subdivisions as fruit flies do, for example, even though their brains are about the same size.
And yet how the ant olfactory system encodes scent data has remained largely unknown. To whittle ...
For experimental physicists, quantum frustration leads to fundamental discovery
2023-06-14
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of physicists, including University of Massachusetts assistant professor Tigran Sedrakyan, recently announced in the journal Nature that they have discovered a new phase of matter. Called the “chiral bose-liquid state,” the discovery opens a new path in the age-old effort to understand the nature of the physical world.
Under everyday conditions, matter can be a solid, liquid or gas. But once you venture beyond the everyday—into temperatures approaching absolute zero, things smaller than a fraction ...
Metamaterials with built-in frustration have mechanical memory
2023-06-14
Researchers from the UvA Institute of Physics and ENS de Lyon have discovered how to design materials that necessarily have a point or line where the material doesn’t deform under stress, and that even remember how they have been poked or squeezed in the past. These results could be used in robotics and mechanical computers, while similar design principles could be used in quantum computers.
The outcome is a breakthrough in the field of metamaterials: designer materials whose responses are determined by their structure rather than their chemical composition. To construct a metamaterial with mechanical memory, physicists ...