(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS – People with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are more likely to have a stroke than people without the disease, according to a study published in the June 14, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that IBD causes stroke; it only shows an association.
Inflammatory bowel disease causes chronic inflammation of the intestines. It includes Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and unclassified inflammatory bowel disease.
The study found that people with IBD were 13% more likely to have a stroke up to 25 years after their diagnosis than people without IBD.
“These results show that people with inflammatory bowel disease and their doctors should be aware of this long-term increased risk,” said study author Jiangwei Sun, PhD, of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. “Screening and management of stroke risk factors may be more urgent in people with IBD.”
The study involved 85,006 people with IBD confirmed with a biopsy. They were each matched with up to five people of the same birth year, sex and county of residence who did not have IBD, for a total of 406,987 people.
During an average follow-up of 12 years, 3,720 of the people with IBD had a stroke, compared with 15,599 of the people who did not have IBD, which is a rate of 32.6 per 10,000 person years for those with IBD compared to 27.7 for those without IBD. Person-years represent both the number of people in the study and the amount of time each person spends in the study.
When researchers accounted for other factors that could affect stroke risk, such as heart disease, high blood pressure and obesity, they found that people with IBD were 13% more likely to have a stroke than those without IBD. Researchers found that the increased risk was mainly due to ischemic stroke, which is caused by a blockage of blood flow to the brain, rather than hemorrhagic stroke, a stroke caused by bleeding in the brain.
Because both IBD and stroke have some genetic components predisposing people to the disease, researchers also included in the study full siblings of the people with IBD. The 101,082 siblings had no history of IBD or stroke at the beginning of the study. Consistent with the main results, people with IBD had a higher risk of stroke than their siblings without IBD. Their overall risk was 11% higher.
“The elevated risk for people with IBD remained even 25 years after they were first diagnosed, corresponding to one additional stroke case for every 93 people with IBD until that point,” Sun said.
A limitation of the study was that the criteria for diagnosing inflammatory bowel disease and stroke have changed over the study period, which could affect the results. Also, researchers did not have complete information on all factors that could affect stroke risk, such as diet, smoking and alcohol consumption.
The study was supported by Forte.
Learn more about stroke at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Inflammatory bowel disease linked to increased risk of stroke
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCF researcher’s innovative approach could redefine allergy treatment
2023-06-14
For years, research and therapies for allergic asthma have been focused largely on targeting the inflammatory cytokines in the body that react to allergens and cause overproduction of mucus, wheezing and difficulty breathing. Commonly prescribed drugs like Omalizumab, Dupilumab, Mepolizumab and Reslizumab lower or block the various cytokines and antibodies responsible for the asthmatic response, but they work after a patient’s airway inflammation is well underway.
Dr. Tigno-Aranjuez wanted to ...
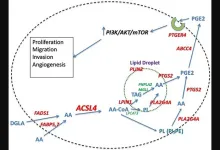
ACSL4: Biomarker, mediator and target in quadruple negative breast cancer
2023-06-14
“ACSL4 has been demonstrated to play a pivotal role in both normal physiology as well as in a variety of disease states, including breast and other cancers.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 14, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 12, 2023, entitled, “ACSL4: biomarker, mediator and target in quadruple negative breast cancer.”
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease for which effective treatment depends on correct categorization of its molecular subtype. ...
UTIA researchers find high risk to amphibians if fungal pathogen invades North America
2023-06-14
New research indicates the fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans (Bsal) could be devastating to amphibian biodiversity if introduced to North America. Nature Communications published the findings June 5 from a group of researchers at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, the University of Massachusetts-Boston and Washington State University.
“We could see over 80 species of salamanders in the United States and 140 species in North America experience population declines if Bsal is introduced,” said Matt Gray, the lead author and professor of ...
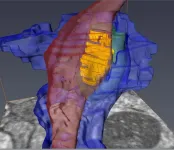
New images capture unseen details of the synapse
2023-06-14
Scientists have created one of the most detailed 3D images of the synapse, the important juncture where neurons communicate with each other through an exchange of chemical signals. These nanometer scale models will help scientists better understand and study neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington’s disease and schizophrenia.
The new study appears in the journal PNAS and was authored by a team led by Steve Goldman, MD, PhD, co-director of the Center for Translational Neuromedicine at the University of Rochester and the University of Copenhagen. The findings represent a significant technical achievement ...
New UCF project launched to engage a diverse, new generation of researchers to aid aging populations
2023-06-14
ORLANDO, June 14, 2023 — The number of older adults in the U.S. population is growing, expecting to nearly double by 2060, and becoming more diverse with racial and ethnic minority populations projected to increase by 105% by 2040.
“As a society, we’re not ready for that,” says Norma Conner, a professor in the University of Central Florida’s College of Nursing. “We need to be cognizant of the large population of older adults that is going to be ours to care for, and we need to have a better understanding that reflects them.”
To ...
Stanford Medicine and Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence announce RAISE-Health, a responsible AI initiative
2023-06-14
Responding to rapid advances in artificial intelligence and the urgent need to define its responsible use in health and medicine, Stanford Medicine and the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) today announced the launch of RAISE-Health (Responsible AI for Safe and Equitable Health). This pioneering initiative seeks to address critical ethical and safety issues surrounding AI innovation and help others navigate this complex and evolving field.
Co-led by Stanford School ...
Scientists discover small RNA that regulates bacterial infection
2023-06-14
People with weakened immune systems are at constant risk of infection. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a common environmental bacterium, can colonize different body parts, such as the lungs, leading to persistent, chronic infections that can last a lifetime – a common occurrence in people with cystic fibrosis.
But the bacteria can sometimes change their behavior and enter the bloodstream, causing chronic localized infections to become acute and potentially fatal. Despite decades of studying the transition in lab environments, how and why the switch happens in humans has remained unknown.
However, researchers ...
Making immunotherapy safer
2023-06-14
Researchers at the University of Houston are working to make T-cell immunotherapy safer, developing a tool called CrossDome, which uses a combination of genetic and biochemical information to predict if T-cell immunotherapies might mistakenly attack healthy cells.
T-cell based immunotherapies hold tremendous potential in the fight against cancer and infectious diseases, thanks to their capacity to specifically target diseased cells, including cancer metastasis. Nevertheless, this potential has been tempered with safety concerns regarding ...
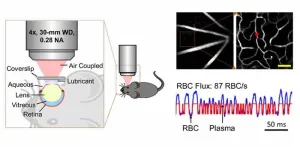
Eyeing the brain: Predicting cerebrovascular diseases with retinal imaging
2023-06-14
The brain is one of the most metabolically active organs in the human body. Although it represents only about 2 percent of the human body’s weight, it receives 15 to 20 percent of the body’s total blood supply. Disrupted blood flow to the brain over a long period of time, a condition known as “chronic cerebral hypoperfusion” (CCH), can lead to serious cerebrovascular diseases such as white matter disease.
CCH manifests as lesions in the white matter, a brain region vulnerable to problems with blood supply. Unfortunately, CCH has no available cure. An early diagnosis by visualizing the microvascular changes in the brain that occur prior to lesion ...
Phone Menu Test Detects Who May Be at Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease
2023-06-14
A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham has found that a brief, simulated task of navigating a phone menu can detect the earliest changes in daily functioning in people at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Investigators found that an older adult’s performance on the test, which can be completed in a matter of minutes, was associated with the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease pathology, including amyloid and tau depositions in the brain. The findings, which were published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, could help inform prevention trials testing treatments for Alzheimer’s disease before ...