(Press-News.org) New research published in the CABI journal Human-Animal Interactions has revealed that only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with a ban on the trimming of facial hair prior to its implementation in July 2022.
The research found that when asked if facial hair trimming should be banned in all equine competitions, most disciplines broadly agreed (60.5% to 84.6%) apart from showing with only 22.9% of respondents agreeing with a ban.
Indeed, some who took part in the research also believed that horses did not need muzzle or ear hairs for day-to-day living.
However, in response to the question on whether facial hair trimming should be banned only in elite sports, all disciplines disagreed strongly with this statement.
The study highlighted that those who entered horses into show competitions believed they were more likely to win if they trimmed their muzzle and ear hair and that the practice was normal and common place in their discipline.
Despite this, equine organizations from around the world – including Australia – banned the practice at competitions on welfare grounds.
This is because the hairs located around the muzzle and eyes have sensory functions that are important to horses.
The hairs are needed to help identify textures of grass and to aid spatial awareness and environmental navigation which is impeded by blind spots in front of their foreheads and below their noses.
Scientists from the University of Adelaide and the University of Newcastle, Australia, surveyed 422 horse owners from Australia of which 85% entered their horses into competitions with showing and dressage being the two most popular types.
Most respondents were female (96%) and lived in South Australia (56%) with a good spread of ages from 18-24 to 55-64, and fewer aged over 65 years.
The study sought to determine the proportions of horse owners trimming equine facial hairs (ear and muzzle hair) across different types of equestrian disciplines in Australia, the types of facial hairs trimmed, whether horses were restrained for trimming, and attitudes related to the practice.
Dr Kirrilly Thompson, a co-author on the paper, from the University of Newcastle, Australia, said, “The results of this study provide valuable insight into the widespread trimming of horse muzzle and ear hairs in some horse disciplines prior to the implementation of the ban in Australia in July 2022.
“The information gained may also be useful for the design and implementation of behaviour change interventions for other management and presentation practices used for horses and other animals.”
The German Equestrian Federation (FN) was the first federation to ban the trimming of whiskers and ear hairs in competitive horses – making it illegal in 1998.
The International Equestrian Federation (FEI) then passed a ban – except for where individual sensory hairs have been removed by a veterinarian to prevent pain or discomfort to the horse – in July 2020.
British Dressage in their 2022 rule changed banned the practice of trimming facial hairs stating: “Trimming of the horse’s sensory hairs around the mouth, nose, eyes, and ears is not permitted as this may reduce the horses’ sensory ability.”
The researchers highlighted that there has been limited studies into how people trim facial hair in horses and attitudes to this practice.
They add that their study provides preliminary results on how widespread the practice was in Australian equestrian sports prior to a ban being introduced, and the reasons and attitudes people in the equine industry have to the trimming of horse facial hairs.
Dr Susan Hazel, lead author of the research, from the University of Adelaide, said, “Further studies are needed to determine if and how the practice and attitudes to facial hair trimming in horses have changed with the enforcement of the ban.
“Findings from the present study, however, may also be useful for understanding and addressing other non-regulated horse presentation practices that can compromise welfare, such as clipping hair from the ear canal and ‘pulling’ manes and tails.”
Additional information
Full paper reference
Hazel, Susan; Holman, Carly; Thompson, Kirrilly, ‘What’s the fuzz: The frequency, practice and perceptions of equine facial hair trimming revealed in survey of horse owners in Australia,’ Human-Animal Interactions, 15 June (2023), DOI: 10.1079/hai.2023.0023
The paper can be read open access from 10:0hrs UK time 15 June, 2023, here: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/hai.2023.0023
Media enquiries
For more information and an advance copy of the paper contact:
Dr Kirrilly Thompson, Honorary Lecturer, School of Medicine and Public Health, The University of Newcastle, Australia – email: kirrilly.thompson@gmail.com
Wayne Coles, Senior PR Manager, CABI – email: w.coles@cabi.org
About Human—Animal Interactions
Human—Animal Interactions is an open access interdisciplinary journal devoted to the dissemination of research in all fields related to interactions between non-human animals and their human counterparts.
About CABI
CABI is an international not-for-profit organization that improves people’s lives by providing information and applying scientific expertise to solve problems in agriculture and the environment.
Through knowledge sharing and science, CABI helps address issues of global concern such as improving global food security and safeguarding the environment. We do this by helping farmers grow more and lose less of what they produce, combating threats to agriculture and the environment from pests and diseases, protecting biodiversity from invasive species, and improving access to agricultural and environmental scientific knowledge. Our 49-member countries guide and influence our core areas of work, which include development and research projects, scientific publishing and microbial services.
We gratefully acknowledge the core financial support from our member countries (and lead agencies) including the United Kingdom (Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office), China (Chinese Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs), Australia (Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research), Canada (Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada), Netherlands (Directorate-General for International Cooperation, and Switzerland (Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation). Other sources of funding include programme/project funding from development agencies, the fees paid by our member countries and profits from our publishing activities which enable CABI to support rural development and scientific research around the world.
END
Only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with facial hair trimming ban, new study reveals
New research published in the CABI journal Human-Animal Interactions has revealed that only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with a ban on the trimming of facial hair prior to its implementation in July 2022
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chronic wound healing using glass
2023-06-15
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have demonstrated that silver retains antimicrobial activity for longer when it is impregnated into ‘bioactive glass’, and shown for the first time how this promising combination delivers more long-lasting antimicrobial wound protection than conventional alternatives.
Bioactive glasses are a unique class of synthetic biomaterials made from silicone and have been used for some years in bone grafting.
Silver has long been known to prevent or reduce the growth ...
Finding out you’re autistic in later life can be a positive experience
2023-06-15
Receiving an autism diagnosis in your 20, 30s, 40s, 50s or even 60s may seem daunting, but a new study from psychologists in Bath and London finds that the link between the age at which someone gets diagnosed has little bearing on their quality of life.
So-called ‘late diagnosis’ for autism has hit the headlines recently thanks to autism campaigner Christine McGuiness. Whereas autism is usually diagnosed in childhood, it is increasing being diagnosed in adults and especially among women.
Parents often wonder if their child finding out they are autistic earlier or later will have an impact on their lives in the long term. Whilst many people who discover they are autistic as adults ...
Rising rates of benzodiazepine toxicity among young people spark concern
2023-06-15
Toronto, ON, June 15, 2023 – The rate of hospital encounters for benzodiazepine-related toxicity rose by 67 per cent for young adults (aged 19 to 24) and 44 per cent for youth (aged 18 or below) in Ontario between 2013 and 2020, according to a new study from ICES and Unity Health Toronto.
Though there was an overall decline of 7 per cent in the provincial rate of benzodiazepine toxicity, this was largely driven by reductions in rates among people aged 35 years and older.
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety ...
How antelopes under threat from the climate crisis have responded to rising temperatures
2023-06-15
The climate crisis is turning the temperature up all over the world, but in southern Africa, the rise has been particularly concerning. Wild animals dependent on delicate ecosystems which are already dry, so that food and water scarcity limits their ability to cope with increased heat, are at serious risk. Scientists studied the behavior of three different species of antelope with overlapping ranges in Namibia to try to understand how animals of different sizes and behaviors adapt to the heat.
“Even the indigenous wildlife, adapted to hot and arid conditions, shows sensitivity to extreme heat,” said Paul Berry of the University of Potsdam, lead author of the study in ...
Dialogues across language and culture
2023-06-15
Teacher talk seems intuitive – the expert imparts knowledge onto novices, who passively receive expertise like a car or machine receives parts at every station on an assembly line. In reality, an effective teacher in an era of dynamic and higher literacies is less of a factory worker and more of an active negotiator who tries to understand where their students are coming from in order to reach them. The language classroom amplifies this challenge where the negotiation not only centers on the knowledge itself but the means of communication for that knowledge. ...
Access to financial services linked to lower COVID mortality rates
2023-06-15
New research shows that some of the best tools to decrease COVID-19 mortality rates weren’t found in the ER, but rather at the bank.
A study of COVID-19 mortality rates across 142 nations has demonstrated a surprisingly strong link between access to formal financial services and lower COVID-19 mortality rates. In fact, it’s proved to be as strong a predictor of lower COVID-19 death rates as several comorbidities are of higher COVID-19 death rates.
“The reduction is surprisingly large, similar in magnitude to, but opposite in direction from, the mortality risks associated with higher rates of lung cancer and hypertension,” says Todd Watkins, ...
Men died of overdose at 2-3 times greater a rate than women in the U.S. in 2020-2021
2023-06-15
Men were significantly more vulnerable than women to overdose deaths involving opioid and stimulant drugs in 2020-2021, according to a new study analyzing death records data from across the United States. The study found that men had a 2–3 times greater rate of overdose mortality from opioids (like fentanyl and heroin) and psychostimulants (like methamphetamine and cocaine). While it has been known that men use drugs at higher rates than women, the researchers found that this alone does not explain the gap in overdose deaths, noting that biological, behavioral, and social factors likely ...
A marine mystery: Discovering the link between climate change and sea sponge loss
2023-06-15
Sea sponges are essential to marine ecosystems. They play critical roles in the ocean, as they provide shelter and food to a plethora of marine creatures, recycle nutrients by filtering thousands of litres of sea water daily, and are hosts to microbes that may be the key to some of the most pressing medical challenges we face today.
Now, scientists from UNSW have discovered that when a tropical sea sponge is exposed to warmer temperatures, it loses an important microbe, which could explain why the sponge tissue dies. The latest study, published today in ISME Communications, has revealed that by exposing sea sponges ...
International expert panel revises management of concussion in sport for optimal care of athletes at all levels of participation
2023-06-15
Journals from BMJ Press Release:
Embargoed 23:30 hours UK (BST) time Wednesday 14 June 2023
Please click on links for full articles and contact authors direct for further comment - details can be found under Notes for Editors. Please remember to credit the relevant journal - this assures your audience it is from a reputable source.
BRITISH JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE
Externally peer reviewed? Yes
Evidence type: Consensus Statement
Subjects: People
Latest Consensus Statement on Concussion in Sport includes:
-New and updated age appropriate tools to aid identification ...
Machine-learning method used for self-driving cars could improve lives of type-1 diabetes patients
2023-06-15
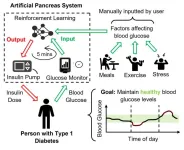
The same type of machine learning methods used to pilot self-driving cars and beat top chess players could help type-1 diabetes sufferers keep their blood glucose levels in a safe range.
Scientists at the University of Bristol have shown that reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning in which a computer program learns to make decisions by trying different actions, significantly outperforms commercial blood glucose controllers in terms of safety and effectiveness. By using offline reinforcement learning, where the algorithm learns from patient records, the researchers improve ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
[Press-News.org] Only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with facial hair trimming ban, new study revealsNew research published in the CABI journal Human-Animal Interactions has revealed that only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with a ban on the trimming of facial hair prior to its implementation in July 2022