(Press-News.org) With almost 250 million cases a year, 621,000 of them fatal, malaria remains a major public health problem, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. Malaria is a parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes and caused by a microbe of the genus Plasmodium. On its journey from mosquito to human, Plasmodium must adapt to the specificities of the many organs and cells it parasitizes. Microbes do not have sensory organs; instead, they have sensors made of proteins to detect molecules specific to the environments they colonize. While most living organisms share the same types of sensors, Plasmodium is an exception. Biologists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have identified a new type of sensor that enables Plasmodium to know precisely where it is and what to do. This work, published in the journal Science Advances, opens up the possibility of scrambling the signals perceived by this sensor to disorientate the parasite and thus prevent its replication and transmission.
When a human is bitten by a Plasmodium-infected mosquito, the parasite enters the bloodstream and travels to the liver, where it thrives for around ten days without causing any symptoms. After this period, Plasmodium re-enters the bloodstream, where it parasitizes red blood cells. Once inside the red blood cells, the parasites multiply in a synchronized 48-hour cycle. At the end of each multiplication cycle, the newly-formed parasites leave their host red blood cells, destroying them and infecting new ones. It is this destruction of red blood cells that causes the waves of fever associated with malaria. Severe forms of malaria are linked to the obstruction of blood vessels by infected red blood cells.
When a mosquito bites a human whose blood is infected with Plasmodium, the parasite changes its development program to colonize the intestine of its new host. After a further period of multiplication, Plasmodium returns to the mosquito’s salivary glands, ready to infect a new human.
Unknown communication channels
From the warmth of the red blood cell to the depths of the mosquito’s intestine via the liver, how does Plasmodium perceive changes in its environment in order to change its development program? "Understanding this very specific biological mechanism is an important step towards countering the parasite," explains Mathieu Brochet, Associate Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Molecular Medicine at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine, who led this project. "At each stage of its life cycle, the parasite must logically pick up signals that enable it to react correctly, but which ones and how?"
There are small molecules absent in the blood but present in the mosquito that the parasite is able to detect. "Starting from this single known element, we have identified a sensor that enables the parasite to detect the presence of these molecules when it is ingested by a mosquito", explain Ronja Kühnel and Emma Ganga, PhD students in Mathieu Brochet’s laboratory and first authors of this study. "This sensor is made up of five proteins. In its absence, the parasite does not realize that it has left the bloodstream for the mosquito, and is therefore unable to continue its development".
Surprisingly, this sensor is also present at other stages of the parasite lifecycle, notably when the parasite has to leave the red blood cell. "We then observe exactly the same mechanism: without this sensor, Plasmodium is trapped in the red blood cells, unable to continue its infection cycle." However, scientists have not identified the human molecules detected by the parasite; identifying them could provide a better understanding of how waves of fever are caused by Plasmodium.
Other parasites also involved
The protein complex discovered here is absent in humans, but is found in the entire family of apicomplexan parasites to which Plasmodium belongs, as well as Toxoplasma, the agent of toxoplasmosis. By identifying this sensor, scientists can now imagine how to scramble the signals perceived by the parasite at different stages of its development, thus disorienting it and blocking its multiplication and transmission.
END
Disorient the malaria parasite to prevent it from causing harm
UNIGE scientists have identified a new type of molecular sensor that enables the malaria parasite to infect human cells or mosquitoes at just the right moment
2023-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Growing number of hypothyroidism patients receiving treatment other than levothyroxine
2023-06-16
The use of thyroid hormones other than the commonly prescribed hormone medicine levothyroxine to treat hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, is increasing, according to a study being presented Friday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
“This is significant because the long-term health outcomes of these treatments are not as well known as levothyroxine,” said researcher Matthew Ettleson, M.D., of the University of Chicago in Chicago, Ill.
The thyroid makes the hormones triiodothyronine ...
Prevalence of metabolic associated fatty liver disease is increasing
2023-06-16
CHICAGO—The percent of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), the leading global cause of liver disease, is increasing in U.S. adults, according to a study presented Friday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
Mexican Americans consistently had the highest percentage of MAFLD, especially in 2018, although the prevalence of increase was higher among Whites, the study found.
MAFLD, previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is fast becoming the most common indication ...
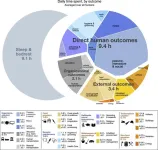
The global human day – A bird’s eye perspective
2023-06-16
Everyone has 24 hours per day. Across the global population of 8 billion people this adds up to approximately 190 billion human hours per day. How those hours are spent determines the impacts we have on our surroundings as well as how we experience life. To find out how people around the world use their time, a research team led by McGill University has gathered and analyzed information about both economic and non-economic activities in order to estimate, for the first time, what a day in the life of the world looks like.
“At present, we are struggling to come to terms with global challenges, and that calls for fresh perspectives on how the world ...
Planned reform of EU pharmaceutical legislation: early market access and robust evidence need not be a contradiction
2023-06-16
The European Commission's stated aim is to improve access to innovative drugs at the national level throughout the EU. Firstly, according to the proposal for the reform of EU pharmaceutical legislation, there are still considerable differences in access between countries. Secondly, drug development has so far only been geared to a limited extent to the actual needs of patients. According to the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), the latter point is in line with the perspective of the ...
Dads are key in supporting breastfeeding, safe infant sleep
2023-06-16
Findings highlight racial disparities in sudden unexpected infant death in the U.S.
Only 16% fathers followed all three AAP-recommended infant sleep practices
Rates of breastfeeding initiation and breastfeeding at eight weeks were much higher among fathers who wanted their infant’s mother to breastfeed than those who did not or had no opinion
CHICAGO --- Fathers can make a huge difference in whether an infant is breastfed and placed to sleep safely, according to a recent survey of new fathers led by scientists at Northwestern University and the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
The study included 250 fathers who ...
AI could replace humans in social science research
2023-06-16
In an article published yesterday in the prestigious journal Science, leading researchers from the University of Waterloo, University of Toronto, Yale University and the University of Pennsylvania look at how AI (large language models or LLMs in particular) could change the nature of their work.
“What we wanted to explore in this article is how social science research practices can be adapted, even reinvented, to harness the power of AI,” said Igor Grossmann, professor of psychology at Waterloo.
Grossmann and colleagues note ...
Research hints at how fungus farming ants keep their gardens healthy
2023-06-16
‘Weed early and often’ is the key to a productive garden. Interestingly, certain species of ants are also avid gardeners, a practice they’ve refined over 50 million years. They too weed their underground fungus gardens, but how they know what to weed out has been a mystery. Now, a multidisciplinary team of scientists report in PNAS on June 15 how ants distinguish the good fungus from the bad.
People rely on sight to identify weeds but ants grow fungus underground in the dark and must have other ways to sense undesirable garden denizens. A team led by Jonathan Klassen, Ph.D., at the ...
Impacts of elevated salinity on microbial interactions within activated sludge microbial community: RMT-based network analysis
2023-06-16
Biological treatment processes are critical for sewage purification, wherein microbial interactions are tightly associated with treatment performance. Previous studies have focused on assessing how environmental factors (such as salinity) affect the diversity and composition of the microbial community but ignore the connections among microorganisms. To fill this gap, an international team of researchers conducted an in-depth analysis of microbial interactions at elevated salinity in activated sludge systems.
Biological ...
Rice University chemist leverages heterogeneity for insight into catalysis, cancer initiation
2023-06-16
HOUSTON – (June 16, 2023) – Rice University chemist Anatoly Kolomeisky has won an award from the National Science Foundation to investigate how heterogeneity affects chemical and biological processes. The goal of his project is to develop analytical models that quantify the role of heterogeneity in various phenomena including catalytic reactions, antimicrobial peptides, early cancer development and lysis, a process describing cellular membrane breakdown.
“We live in a world of heterogeneity,” ...
Significant correlation found between vitreous human biomarkers and Alzheimer’s disease
2023-06-16
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center found a significant correlation between biomarkers in the vitreous humor of the eye and pathologically confirmed cases of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) in post-mortem brain and eye tissue. Published in IOS Press, this exploratory study indicates that biomarkers in the vitreous humor may serve as a proxy for neuropathological disease.
The incidence of dementias like AD continues to rise. As of 2021, 6.2 million North Americans above 65 years of age are suffering from AD, and this number is projected to reach 13.2 million by 2060. Diagnosis of both AD and CTE is based on symptoms, clinical exam ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
[Press-News.org] Disorient the malaria parasite to prevent it from causing harmUNIGE scientists have identified a new type of molecular sensor that enables the malaria parasite to infect human cells or mosquitoes at just the right moment