(Press-News.org) NASA’s Parker Solar Probe accomplished a milestone on June 27, 2023 – its 16th orbit of the Sun. This included a close approach to the Sun (known as perihelion) on June 22, 2023, where the spacecraft came within 5.3 million miles of the solar surface while moving at 364,610 miles per hour. The spacecraft emerged from the solar flyby healthy and operating normally.
On Aug. 21, 2023, Parker Solar Probe will swing past Venus for its sixth flyby of the planet. To prepare for a smooth course, the mission team at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) applied a small trajectory correction maneuver on June 7, 2023, the first course correction since March 2022. This flyby will be the sixth of seven planned flybys of Venus during Parker’s primary mission. Parker uses Venus’ gravity to tighten its orbit around the Sun and set up a future perihelion at just 4.5 million miles from the Sun’s surface. As the Sun becomes increasingly active, this perihelion will be especially important to learning more about heliophysics.
Parker Solar Probe was developed as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program to explore aspects of the Sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. The Living With a Star program is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. APL designed, built, and operates the spacecraft and manages the mission for NASA.
END
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe completes 16th close approach to the Sun
2023-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify a new mechanism, cancer hijacks enzyme substrate motif mutations
2023-07-03
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Cancer spreads throughout the human body in cunning, almost militaristic, ways. For example, it can manipulate our genetic make-up, take over specific cell-to-cell signaling processes, and mutate key enzymes to promote tumor growth, resist therapies, and hasten its spread from the original site to the bloodstream or other organs.
Enzyme mutations have been of great interest to scientists who study cancer. Scientists in the Liu and Tan labs at UNC’s Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center have been studying mutations of enzyme recognition motifs in substrates, ...
Researchers develop tool that could improve liquid biopsy
2023-07-03
A research team led by Xianghong Jasmine Zhou, PhD, professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, has made an important advancement to address one of the major challenges in cell-free DNA (cfDNA) testing, also known as liquid biopsy. They’ve identified specific methylation patterns unique to each tissue, potentially helping to Identify the specific tissue or organ associated with cfDNA alterations picked up by testing, a critical challenge for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of diseases.
Cell-free DNA has significant potential in disease detection and monitoring. However, accurately quantifying tissue-derived ...
Cigarette smoke and HPV have synergistic effects on cells, heightening the risk of head and neck cancer
2023-07-03
Tobacco smoking and human papillomavirus (HPV) are both well-known risk factors for head and neck cancer, but there is ample evidence to show they can interact to increase still further the risk of contracting the disease, according to a study by scientists at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil and the University of Chile. An article on the study is published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
The results of the study clarify aspects of the molecular mechanisms ...
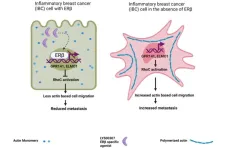
ERβ as a mediator of estrogen signaling in inflammatory breast cancer
2023-07-03
“The mechanism of the anti-metastatic activity of ERβ was investigated [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 3, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 12, 2023, entitled, “ERβ as a mediator of estrogen signaling in inflammatory breast cancer.”
In this new editorial, researchers Harika Nagandla and Christoforos Thomas from Houston Methodist Neal Cancer Center discuss inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)—a rare and aggressive form of breast ...
Pathogenic bacteria use a sugar in the intestinal mucus layer to infect the gut, study shows
2023-07-03
A new study by researchers at the University of British Columbia (UBC) and BC Children’s Hospital shows the sugar sialic acid, which makes up part of the protective intestinal mucus layer, fuels disease-causing bacteria in the gut.
The findings, published in PNAS, suggest a potential treatment target for intestinal bacterial infections and a range of chronic diseases linked to gut bacteria, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, irritable bowel syndrome and short bowel syndrome.
“Bacteria need to find a place in our intestines to take hold, establish and expand, and then they need to overcome all the different defences that normally protect our ...
Birds raise fewer young when spring arrives earlier in a warming world
2023-07-03
Rising global temperatures are making it harder for birds to know when it’s spring and time to breed according to a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
A large collaboration led by scientists at UCLA and Michigan State University has found that birds produce fewer young if they start breeding too early or late in the season. With climate change resulting in earlier springlike weather, the researchers report, birds have been unable to keep pace.
And, the authors write, the mismatch between the ...
Chemists discover why photosynthetic light-harvesting is so efficient
2023-07-03
When photosynthetic cells absorb light from the sun, packets of energy called photons leap between a series of light-harvesting proteins until they reach the photosynthetic reaction center. There, cells convert the energy into electrons, which eventually power the production of sugar molecules.
This transfer of energy through the light-harvesting complex occurs with extremely high efficiency: Nearly every photon of light absorbed generates an electron, a phenomenon known as near-unity quantum efficiency.
A new study from MIT chemists offers a potential explanation for how proteins of the light-harvesting complex, also called the antenna, achieve that ...
Planting seeds: FSU researchers dig into how chemical gardens grow
2023-07-03
EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 3 AT 3 P.M. ET
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
CONTACT: Kathleen Haughney, University Communications
(850) 644-1489; khaughney@fsu.edu
July 2023
PLANTING SEEDS: FSU RESEARCHERS DIG INTO HOW CHEMICAL GARDENS GROW
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Since the mid-1600s, chemists have been fascinated with brightly colored, coral-like structures that form by mixing metal salts in a small bottle.
Until now, researchers have been unable to model how these deceptively simple tubular structures —called chemical gardens — work and the patterns and rules that ...
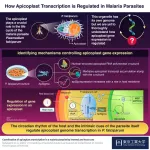
Understanding the regulation of apicoplast gene expression in the malaria parasite
2023-07-03
Gene expression within the apicoplast, an organelle in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum, is regulated by melatonin (the circadian signaling hormone) in host blood, and intrinsic parasite cues, via a factor called ApSigma, as identified by a recent study aided by Tokyo Tech’s World Research Hub Initiative. The regulatory system highlighted in this study might be a future target for malaria treatment.
Malaria is one of the biggest public health risks, with around 240 million people from across the globe contracting it every year. However, this life-threatening disease is ...
Study suggests resistance training can prevent or delay Alzheimer’s disease
2023-07-03
Regular physical exercise, such as resistance training, can prevent Alzheimer’s disease, or at least delay the appearance of symptoms, and serves as a simple and affordable therapy for Alzheimer’s patients. This is the conclusion of an article published in Frontiers in Neuroscience by Brazilian researchers affiliated with the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) and the University of São Paulo (USP).
Although older people and dementia patients are unlikely to be able to do long daily runs or perform other high-intensity aerobic exercises, these activities are the focus for most scientific studies on ...