(Press-News.org) Encouraging adolescents to feel capable and purposeful – rather than just happy – could improve their academic results as well as their mental health, according to new research which recommends changing how wellbeing is supported in schools.
The University of Cambridge study, involving over 600 teenagers from seven English schools, examined two separate aspects of their wellbeing: life satisfaction and ‘eudaimonia’. While life satisfaction roughly equates to how happy a person is, eudaimonia refers to how well that person feels they are functioning. It incorporates feelings of competence, motivation and self-esteem.
Researchers found that students with high levels of eudaimonia consistently outperformed their peers in GCSE-level assessments, especially Maths. On average, those achieving top Maths grades had eudaimonic wellbeing levels 1.5 times higher than those with the lowest grades.
No such link was found between academic performance and life satisfaction. Despite this, child wellbeing policy in England tends to focus on life satisfaction. The Government has, for example, recently added ‘happiness’ to national curricula as part of its Relationships, Sex and Health Education (RSHE) guidance, emphasising teaching adolescents how to feel happy and resilient while managing negative emotions.
Previous research has pointed to the importance of fostering adolescents’ eudaimonic wellbeing by nurturing their personal values, goals and sense of self-worth. The new study appears to strengthen that case by demonstrating a positive link between eudaimonia and academic performance.
Its lead author, Dr Tania Clarke, is a psychologist of education who now works for the Youth Endowment Fund, but undertook the study for her doctoral research at the Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge. The findings are published in School Psychology Review.
“Wellbeing education often focuses on teaching students about being happy and not being sad.” Clarke said. “That is over-simplistic and overlooks other vital qualities of wellbeing that are particularly salient during the formative period of adolescence.”
“Adolescents also need to develop self-awareness, confidence, and ideally a sense of meaning and purpose. Judging by our findings, an adolescent who is currently getting a 3 or 4 on their Maths GCSE could be helped to rise a couple of grades if schools emphasised these qualities for all students, rather than just promoting positivity and minimising negative emotions.”
The study involved 607 adolescents, aged 14-15. Participants completed an established psychological assessment called ‘How I feel about myself and school’, which measures both life satisfaction and eudaimonia, as well as feelings of interpersonal relatedness and negativity.
These measures were compared with their scores in mock English and Maths GCSEs. The research also assessed whether the students exhibited a ‘growth mindset’: a belief in their personal capacity for improvement. Many educators consider this essential for enhancing academic performance.
The students’ overall wellbeing – their eudaimonia and life satisfaction combined – clearly correlated positively with their exam results. Those attaining top Maths grades (Grades 8 or 9) had, on average, a wellbeing score of 32 out of a possible 50. This was nine points higher than those with a Grade 1, and three to four points higher than the average for all 607 students.
When they analysed the separate dimensions of wellbeing, however, the researchers found a positive relationship between eudaimonia and higher attainment, but no correlation with life satisfaction. In Maths, the average eudaimonic wellbeing score of Grade 9 students was 17.3 from a possible 25, while that of Grade 1 students was just 10.9. These results held true even when accounting for potentially confounding factors, such as school attended, gender, socio-economic status, or special educational needs.
The study also found that a growth mindset did not predict good academic results, although students with high eudaimonic wellbeing did tend to exhibit such a mindset. Other research has similarly struggled to draw a clear link between growth mindset and academic progress, but does link it more generally to positive mental health. This implies that eudaimonia, as well as supporting better attainment, may also underpin important aspects of self-belief, leading to broader mental health benefits.
Clarke’s wider research suggests that various constraints currently limit schools’ capacity to promote eudaimonic wellbeing. In an earlier Review of Education article she published the results of in-depth interviews with some of the same students, which highlighted concerns about a ‘performativity culture’ stemming from a heavy emphasis on high-stakes testing. These interviews indicated that many students associate ‘doing well’ with getting good grades, rather than with their own strengths, values and goals.
Students said they often felt worthless, inadequate or “dumb” if they failed to get high marks in tests. “You let your scores define you,” one student told Clarke. “Then you feel really low about… your worth and everything. You think it’s literally the end of the world.” Ironically, the new findings suggest that by limiting teachers’ capacity to support students’ personal growth, the heavy emphasis on exam results and testing may be undermining academic progress, at least in some cases.
Clarke suggested that eudaimonic therapy, which increasingly features in professional mental health psychology for adolescents, could be incorporated more into wellbeing education. In particular, her study underscores the need to help students understand their academic work and progress in the context of their personal motivations and goals.
“There is a link between better wellbeing and a more nuanced understanding of academic success,” Clarke said. “Because schools are under heavy pressure to deliver academic results, at the moment students seem to be measuring themselves against the exam system, rather than in terms of who they want to be or what they want to achieve.”
Dr Ros McLellan, from the Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge, who co-authored the study, said: “Wellbeing education needs to move beyond notions of ‘boosting’ happiness towards deeper engagement, helping adolescents to realise their unique talents and aspirations, and a sense of what happiness means for them, personally. This would not just improve wellbeing: it is also likely to mean better exam results, and perhaps fewer issues for students later on.”
END
Helping adolescents to feel competent and purposeful – not just happy – may improve grades
Study of 600 UK teenagers suggests that having stronger self-awareness and sense of purpose may raise GCSE Maths scores “by a couple of grades”.
2023-07-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unlocking the mystery of long-lasting cancer treatment
2023-07-06
New insights explaining why some children have a longer remission than others after having cutting-edge CAR T-cell therapy for leukaemia have been revealed by researchers at UCL, Great Ormond Street Hospital, and the Wellcome Sanger Institute.
The collaborative research project, published today in Nature Medicine, combines expertise in novel immune therapy design and state-of-the-art computational analysis to identify a genetic signature of CAR T-cells that will be the most effective in the long term.
In recent years, CAR T-cells – genetically engineered ...
Astronomers identify the earliest strands of the cosmic web
2023-07-06
Using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, a team of scientists led by University of Arizona astronomers has discovered a threadlike arrangement of 10 galaxies that existed just 830 million years after the Big Bang.
Lined up like pearls on an invisible string, the 3-million-light-year-long structure is anchored by a luminous quasar – a galaxy with an active, supermassive black hole at its core. The team believes the filament will eventually evolve into a massive cluster of galaxies, much like the well-known Coma Cluster in the "nearby" universe. The results are published in two papers in The Astrophysical Journal ...
Professor spreads the gospel of ‘good fire’ through eco-cultural lens
2023-07-06
LAWRENCE – A pyromaniac is someone unhealthily obsessed with the destructive power of fire. Melinda Adams instead is pulled toward the term pyromantic – a lover of “good fire” for the benefits it can bring to people, communities and the environment as a whole.
The Langston Hughes Assistant Professor in Indigenous Studies and Geography & Atmospheric Science at the University of Kansas, Adams extols the benefits of cultural or ceremonial fire in a new paper she has co-authored ...
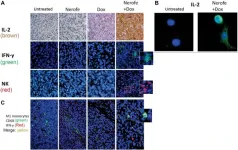
Transformation of immunosuppressive mtKRAS tumors into immunostimulatory tumors by Nerofe and Doxorubicin
2023-07-05
“[...] we demonstrated that the combination of Nerofe and DOX exerts a synergistic effect during mCRC treatment [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 1, 2023, entitled, “Transformation of immunosuppressive mtKRAS tumors into immunostimulatory tumors by Nerofe and Doxorubicin.”
Members of the rat sarcoma viral oncogene (RAS) subfamily KRAS are frequently mutated oncogenes in human cancers and have been identified ...
Bar-Ilan University study reveals disparity in quality of life among COVID-19 survivors from different ethnic groups
2023-07-05
A new study conducted by researchers at Bar-Ilan University in Israel has shed light on the long-term impact of COVID-19 on the quality of life among different ethnic groups in the country. The study, part of a larger cohort project, highlights a significant discrepancy between Arabs and Druze, and Jews, with the two former groups experiencing a more pronounced decline in quality of life one year after infection.
In this cohort study, researchers regularly followed up with individuals who had been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus to assess various aspects of their health. The findings, published in the International ...
Fossils reveal how ancient birds molted their feathers— which could help explain why ancestors of modern birds survived when all the other dinosaurs died
2023-07-05
Every bird you’ve ever seen— every robin, every pigeon, every penguin at the zoo— is a living dinosaur. Birds are the only group of dinosaurs that survived the asteroid-induced mass extinction 66 million years ago. But not all the birds alive at the time made it. Why the ancestors of modern birds lived while so many of their relatives died has been a mystery that paleontologists have been trying to solve for decades. Two new studies point to one possible factor: the differences between how modern birds and their ancient cousins molt their feathers.
Feathers are one of the key traits that all birds share. They're made of a protein called keratin, the same material ...
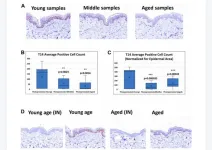
A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin
2023-07-05
“[...] the results suggest a possible novel approach [for] exploring skin disorders [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin.”
T14 is a 14mer peptide derived from the C-terminus of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Once cleaved, it is independently bioactive of the parent molecule and enhances calcium influx in different cell types, in a range of scenarios: it binds to an allosteric site selectively ...
Tracking ships’ icy paths amidst climate change
2023-07-05
There has been much buzz about the warming planet’s melting Arctic region opening shipping routes and lengthening travel seasons in ocean passageways that ice once blocked. Expanded fishing, trade and tourism is envisioned.
Operative word: Envisioned.
Scientists at Michigan State University (MSU), University of Waterloo, and University of Alaska Fairbanks report in Climatic Change where vessels are traveling in the ice-covered waters of the Arctic between Alaska and Russia, and what those reports may mean for important wildlife and communities in the region.
“Even with climate change, sea ice is still a substantial barrier to Arctic vessel traffic,” said Kelly Kapsar, ...
Study shines light on why companies use a variety of dark money strategies
2023-07-05
AUSTIN, Texas — As public concerns mount over lack of transparency in political giving, a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin is the first to illuminate how and why corporations choose to legally conceal their lobbying and campaign contributions.
U.S. companies are required to disclose the total amount they spend on political activity, but beyond that, the disclosure is incredibly vague, according to Tim Werner, associate professor of business, government and society at the McCombs ...
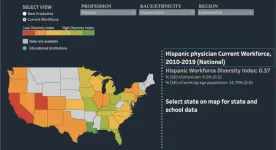
Health professions requiring advanced degrees have few Latinos
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON (July 5, 2023)--Although the situation is improving, Latinos and especially Mexican Americans, remain very underrepresented in U.S. health professions that require advanced degrees, according to a study published today in the journal Health Affairs. The study by George Washington University researchers is the first to examine the representation of the four largest Latino populations in the U.S. health workforce and the findings raise concerns about the lack of diversity in the U.S. health workforce.
The study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Helping adolescents to feel competent and purposeful – not just happy – may improve gradesStudy of 600 UK teenagers suggests that having stronger self-awareness and sense of purpose may raise GCSE Maths scores “by a couple of grades”.