(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO — PLOS today is announcing that it has extended the scope of its “Accessible Data” experiment, which was first launched in March 2022, with support from a Wellcome Trust grant. The experimental “Accessible Data” feature is designed to increase research data sharing and reuse by highlighting links to select repositories with an eye-catching icon on the article page. We are now expanding from the original three repositories to nine, which together host about three quarters of the outputs linked to from PLOS articles.
PLOS began its Accessible Data experiment with two overarching goals. First, to increase reuse of datasets linked to PLOS articles and second, to increase authors’ use of data repositories by visually acknowledging and rewarding repository use on articles. Through analysis of 543 Figshare datasets linked to PLOS articles, we observed a 20% relative increase in the average number of views received per month.
PLOS now has a third goal, which is to understand if there are meaningful differences in how readers engage with different types of data, and different types of research output. To achieve this, PLOS is increasing the number of articles that will qualify for the icon on an article by diversifying the repository and output types that are included. In this next phase, articles will display an icon if they:
Were published from 2016 onwards
Include a link to a research output in a repository in their Data Availability Statement, and
The link directs to a unique record in Dryad, Figshare, Open Science Framework (OSF), Github, Zenodo, Gene Expression Omnibus, Sequence Read Archive, BioProject, or Demographic and Health Surveys
Extending the icon achieves two things. First, it increases the number of articles that qualify for the feature threefold, to more than 15,000 articles, rewarding more researchers and increasing our potential to promote discovery of research data and code. Second, by adding different types of repositories, PLOS is increasing its potential for learning. We've added repositories specializing in life sciences, social sciences, and medicine to better understand where readers engage differently in domain-specific repositories vs generalist repositories.
The results of the next phase of the experiment will inform future strategies to support discovery and reuse of research outputs produced by PLOS authors. For more information on this experiment, a summary is available as a poster in Figshare, along with the supporting data from our surveys.
###
About the Public Library of Science
PLOS is a nonprofit, Open Access publisher empowering researchers to accelerate progress in science and medicine by leading a transformation in research communication. Since our founding in 2001, PLOS journals have helped break boundaries in research communication to provide more opportunities, choice, and context for researchers and readers. For more information, visit http://www.plos.org.
END
PLOS to extend accessible data to more articles and repositories
2023-07-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Big robot bugs reveal force-sensing secrets of insect locomotion
2023-07-06
Researchers have combined research with real and robotic insects to better understand how they sense forces in their limbs while walking, providing new insights into the biomechanics and neural dynamics of insects and informing new applications for large legged robots.
Campaniform sensilla (CS) are force receptors found in the limbs of insects that respond to stress and strain, providing important information for controlling locomotion. Similar force receptors exist in mammals known as Golgi tendon organs, suggesting that understanding the role ...
How dietary restraint could significantly reduce effects of genetic risk of obesity
2023-07-06
Obesity risk genes make people feel hungrier and lose control over their eating, but practicing dietary restraint could counteract this.
New research by University of Exeter, Exeter Clinical Research Facility, and University of Bristol – funded by the Medical Research Council Doctoral Training Partnership and published in the International Journal of Epidemiology - found that those with higher genetic risk of obesity can reduce the effects that are transmitted via hunger and uncontrolled eating by up to half through dietary restraint.
Psychology PhD student, Shahina Begum, from the University of Exeter is lead author and said: “At a time when high ...
Webb Telescope detects most distant active supermassive black hole
2023-07-06
Researchers have discovered the most distant active supermassive black hole to date with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The galaxy, CEERS 1019, existed about 570 million years after the big bang, and its black hole is less massive than any other yet identified in the early universe.
In addition to the black hole in CEERS 1019, the researchers identified two more black holes that are on the smaller side and existed 1 billion and 1.1 billion years after the big bang. JWST also identified eleven galaxies that existed when the universe was 470 million to 675 million years old. The evidence was provided ...
Unveiling the secret of viruses-bacteria interactions in man-made environments
2023-07-06
Viruses in man-made environments cause public health concerns, but they are generally less studied than bacteria. A recent study led by environmental scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) provided the first evidence of frequent interactions between viruses and bacteria in man-made environments. It found that viruses can potentially help host bacteria adapt and survive in nutrient-depleted man-made environments through a unique gene insertion.
By understanding these virus–bacteria interactions and identifying the possible spread of antibiotic ...
ASBMB weighs in on changes to NIH fellowship review
2023-07-06
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent feedback in June to the National Institutes of Health about its proposed changes to the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award fellowship application and review process.
The proposed changes indicate that the NIH adopted nearly all of the ASBMB’s earlier recommendations (here and here) to reduce institutional and investigator bias and refocus the evaluation on an applicant’s potential and the impact of the ...
Wastewater monitoring could act as pandemic early warning system
2023-07-06
Wastewater monitoring could act as an early warning system to help countries better prepare for future pandemics, according to a new study.
An international collaboration involving Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, The Rockefeller Foundation, Mathematica and the United Kingdom’s Health Security Agency has shed light on how different countries monitor wastewater during infectious diseases outbreaks and where improvements could be made.
For the study, samples from treatment plants, rivers, wetlands and open drains were reported ...
T cells require healthy “power plants”
2023-07-06
All cells have their own power plants, called mitochondria. There are often more than 100 mitochondria per cell and each possesses their own genome, which in turn contains genes responsible for energy production. If errors creep into these genes, this can cause problems in the cell and result in diseases. Scientists from the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH) and the Max Delbrück Center have now discovered that the T cells of the immune system are especially sensitive to genetic disturbances within their mitochondrial power plants. They have published their findings ...
Sweat it out: Novel wearable biosensor for monitoring sweat electrolytes for use in healthcare and sports
2023-07-06
The remarkable level of miniaturization possible in modern electronics has paved the way for realizing healthcare devices previously confined to the realm of science fiction. Wearable sensors are a prominent example of this. As the name suggests, these devices are worn on the body, usually directly on the skin. They can monitor important bodily parameters, including heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle activity.
Some wearable sensors can also detect chemicals in bodily fluids. For instance, sweat biosensors ...
New teaching method can even out children's reading skills
2023-07-06
How well do children know letters and their corresponding sounds? In Norway, the gender difference on these tasks when children start school is significant. The girls have a clear head start.
“We see these differences in all categories – for upper case and lower case letters, for the names of the letters and for their corresponding sounds,” says Hermundur Sigmundsson, a professor at Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Psychology.
Girls’ letter-sound knowledge is clearly better than that of boys,’ and girls remain far better readers than boys at age 15. Since reading is key for so many ...
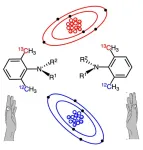
Scientists synthesize isotopic atropisomers based on carbon isotope discrimination
2023-07-06
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is said to be chiral if it cannot be superposed on to its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, or conformational changes. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two forms, called enantiomers, that are mirror images of each other; they are often distinguished as either ‘right-handed’ or ‘left-handed’ by their absolute configuration. Enantiomers exhibit similar physical and chemical properties, except when interacting with polarized light and reacting with other chiral compounds, ...