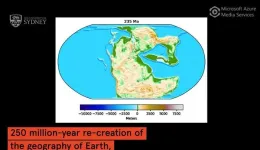
(Press-News.org) Movement in the Earth’s tectonic plates indirectly triggers bursts of biodiversity in 36‑million-year cycles by forcing sea levels to rise and fall, new research has shown.
Researchers including geoscientists at the University of Sydney believe these geologically driven cycles of sea level changes have a significant impact on the diversity of marine species, going back at least 250 million years.
As water levels rise and fall, different habitats on the continental shelves and in shallow seas expand and contract, providing opportunities for organisms to thrive or die. By studying the fossil record, the scientists have shown that these shifts trigger bursts of new life to emerge.
The research has been published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, led by Associate Professor Slah Boulila from Sorbonne University in Paris.
Study co-author Professor Dietmar Müller, from the School of Geosciences at the University of Sydney, said: “In terms of tectonics, the 36-million-year cycle marks alterations between faster and slower seafloor spreading, leading to cyclical depth changes in ocean basins and in the tectonic transfer of water into the deep Earth.
“These in turn have led to fluctuations in the flooding and drying up of continents, with periods of extensive shallow seas fostering biodiversity.
“This work was enabled by the GPlates plate tectonic software, developed by the EarthByte Group at the University of Sydney, supported by Australia’s National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy (NCRIS) via AuScope.”
The team based their findings on the discovery of strikingly similar cycles in sea-level variations, Earth's interior mechanisms and marine fossil records.
Scientists now have overwhelming evidence that tectonic cycles and global sea level change driven by Earth's dynamics have played a crucial role in shaping the biodiversity of marine life over millions of years.
“This research challenges previous ideas about why species have changed over long periods,” Professor Müller said.
“The cycles are 36 million years long because of regular patterns in how tectonic plates are recycled into the convecting mantle, the mobile part of the deep Earth, similar to hot, thick soup in a pot, that moves slowly.”
Professor Müller said the Cretaceous Winton Formation in Queensland serves as a prime example of how sea-level changes have shaped ecosystems and influenced biodiversity in Australia.
The formation, renowned for its collection of dinosaur fossils and precious opal, provides a valuable window into a time when much of the Australian continent was flooded.
As sea levels rose and fell, the flooding of the continent created expanding and contracting ecological recesses in shallow seas, providing unique habitats for a wide range of species.
“The Cretaceous Winton Formation stands as a testament to the profound impact of these sea-level changes, capturing a snapshot of a time when Australia's landscape was transformed and fascinating creatures roamed the land,” Professor Müller said.
END
Scientists discover 36-million-year geological cycle that drives biodiversity
Tectonic changes alter sea levels that can create breeding grounds for life
2023-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The sound of silence? Researchers prove people hear it
2023-07-10
Silence might not be deafening but it’s something that literally can be heard, concludes a team of philosophers and psychologists who used auditory illusions to reveal how moments of silence distort people’s perception of time.
The findings address the debate of whether people can hear more than sounds, which has puzzled philosophers for centuries.
“We typically think of our sense of hearing as being concerned with sounds. But silence, whatever it is, is not a sound — it’s the absence of sound,” said lead author Rui Zhe Goh, a Johns Hopkins University graduate student in philosophy and psychology. “Surprisingly, ...
Caterpillar venom study reveals toxins borrowed from bacteria
2023-07-10
Researchers at The University of Queensland have discovered the venom of a notorious caterpillar has a surprising ancestry and could be key to the delivery of lifesaving drugs.
A team led by Dr Andrew Walker and Professor Glenn King from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience found toxins in the venom of asp caterpillars punch holes in cells the same way as toxins produced by disease-causing bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella.
“We were surprised to find asp caterpillar venom was completely ...
Global cooling caused diversity of species in orchids, confirms study
2023-07-10
Research led by the Milner Centre for Evolution at the University of Bath looking at the evolution of terrestrial orchid species has found that global cooling of the climate appears to be the major driving factor in their diversity. The results help scientists understand the role of global climate on diversity of species, and how our current changing global climate might affect biodiversity in the future.
One of the largest families of plants, there are around 28,000 species of orchids growing across the world. These plants are known for their huge variety of different sized and shaped flowers, so why are there so many species
Climate change driving speciation
Charles ...
Real-world context increases capacity for remembering colors
2023-07-10
Human memory is fundamental to everything we do. From remembering the faces of someone you just met to finding your cell phone that you just left on a table, one's "visual working memory"— the core cognitive system that retains visual information in an active state for a short period of time, plays a vital role. Prior work has found that visual working memory capacity is well correlated with other important cognitive abilities such as academic performance, and fluid intelligence, which includes general reasoning and problem solving, so understanding its limits is integral to understanding how human cognition works.
In the past, theories have proposed that an individual’s ...
Argonne scientist Shirley Meng recognized for contributions to battery science
2023-07-10
The Electrochemical Society (ECS) has selected scientist Shirley Meng of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory as the recipient of the 2023 Battery Division Research Award for innovative research on interfacial science, which has led to improved battery technologies.
A pioneer in discovering and designing better materials for energy storage, Meng serves as chief scientist of the Argonne Collaborative Center for Energy Storage Science (ACCESS) and as a professor at the Pritzker School of Molecular ...
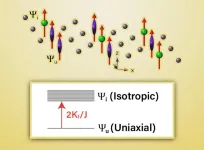
Researchers make a surprising discovery about the magnetic interactions in a Kagome layered topological magnet
2023-07-10
A team from Ames National Laboratory conducted an in-depth investigation of the magnetism of TbMn6Sn6, a Kagome layered topological magnet. They were surprised to find that the magnetic spin reorientation in TbMn6Sn6 occurs by generating increasing numbers of magnetically isotropic ions as the temperature increases.
Rob McQueeney, a scientist at Ames Lab and project lead, explained that TbMn6Sn6has two different magnetic ions in the material, terbium and manganese. The direction of the manganese moments controls the topological state, “But ...
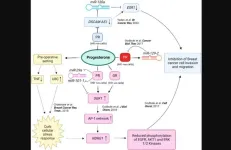
Deciphering progesterone’s mechanisms of action in breast cancer
2023-07-10
“The mechanisms underlying the observed effects of progesterone on breast cancer outcomes are unclear.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 1, 2023, entitled, “Deciphering the mechanisms of action of progesterone in breast cancer.”
A practice-changing, randomized, controlled clinical study established that preoperative hydroxyprogesterone administration improves disease-free and overall survival in patients with node-positive breast cancer. In this new perspective, researchers Gaurav Chakravorty, Suhail Ahmad, Mukul S. Godbole, Sudeep Gupta, Rajendra A. Badwe, ...
More data needed on lifestyle interventions for postpartum blood pressure control
2023-07-10
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy such as preeclampsia and gestational hypertension occur in up to 10% of pregnancies and are associated with a three-fold increased risk of chronic hypertension and up to two-fold increased risk of cardiovascular disease when compared with healthy pregnancies. While the year after pregnancy is a critical time to address hypertension risk with lifestyle changes (healthy diet and exercise), the effects of lifestyle interventions on postpartum blood pressures are not well documented.
A new Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine study has found that there are few relevant studies on the ...
New biodegradable plastics are compostable in your backyard
2023-07-10
We use plastics in almost every aspect of our lives. These materials are cheap to make and incredibly stable. The problem comes when we're done using something plastic — it can persist in the environment for years. Over time, plastic will break down into smaller fragments, called microplastics, that can pose significant environmental and health concerns.
The best-case solution would be to use bio-based plastics that biodegrade instead, but many of those bioplastics are not designed to degrade in backyard composting conditions. They must be processed in commercial composting facilities, which are not accessible in all regions of the ...
Canned, frozen corn industry struggling across US growing regions
2023-07-10
URBANA, Ill. — For those whose primary experience with corn is the butter-drenched cob variety, it might come as a surprise that other forms of sweet corn are in trouble. A new University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign analysis shows sweet corn production for frozen and canned products has been steadily shrinking in the U.S. over the past 27 years, particularly in rainfed portions of the Midwest.
“The processing sweet corn industry [corn grown for canned and frozen products] was thriving in the U.S. throughout the 20th century. This type of production, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
SwRI to create advanced Product Lifecycle Management system for the Air Force
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
A new vascularized tissueoid-on-a-chip model for liver regeneration and transplant rejection
Augmented reality menus may help restaurants attract more customers, improve brand perceptions
Power grids to epidemics: study shows small patterns trigger systemic failures
Computational insights into the interactions of andrographolide derivative SRJ09 with histone deacetylase for the management of beta thalassemia
A genetic brake that forms our muscles
CHEST announces first class of certified critical care advanced practice providers awarded CCAPP Designation
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
[Press-News.org] Scientists discover 36-million-year geological cycle that drives biodiversityTectonic changes alter sea levels that can create breeding grounds for life