(Press-News.org) Researchers have finally settled a decades-long dispute about the evolutionary origins of the pygmy right whale.
The smallest of the living baleen whales, it’s tank-like skeleton is unique, and its ecology and behaviour remain virtually unknown.
Because it is so unusual, the evolutionary relationships of the pygmy right whale (Caperea marginata) have long been a bone of contention.
In a study that solves the debate, just published in Marine Mammal Science, an international group of researchers sequenced the complete genome of Caperea, combining their findings with morphology and palaeontology.
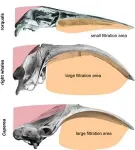
Co-author Dr Felix Marx, curator of marine mammals at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa explains the skull shape of the pygmy right whale seems to be adapted for skim-feeding, where a whale will swim at the water’s surface with its mouth open to food.
“This is very similar to the larger true right whale, leading some scientists to believe the two whales are closely related, hence their similar names. However, others believe the pygmy right whale is more closely related to species like the blue whale, which take big gulps of water to collect food instead of skimming,” he says.
He was pleased to be able to exploit the power of genomics to elucidate the history of life.
“After 150 years of anatomical orthodoxy and decades of dispute, genomics now shows beyond reasonable doubt that Caperea is a distinct lineage and not related to right whales.
“Like river dolphins and sperm whales, Caperea is the sole guardian of a unique piece of evolutionary heritage. It’s not just another weird right whale – it truly is the last survivor of an otherwise lost family that once played a much bigger role in Earth’s history,” he says.
Co-lead author Dr Kieren Mitchell, of Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research, says new genetic information often prompts scientists to reconsider why different animals appear more similar or different to each other.
"When DNA and anatomy seem to be at odds about the relationship between species, usually that means there's an even deeper and more interesting story to be discovered about their evolution,” he says.
Co-author Dr Nic Rawlence, Otago Palaeogenetics Laboratory Director, describes Caperea as a “wonderful case of convergent evolution”, which occurs when two unrelated species end up appearing more and more alike as they adapt to similar selective pressures.
“Caperea has historically been aligned with right whales because they look the same due to similar feeding strategies, when, in fact, it’s probable that Caperea is the last surviving member of an ancient group of whales called cetotheres,” he says.
Co-lead author Dr Ludo Dutoit, of Otago’s Department of Zoology, says now its position in the family tree of whales has been confirmed, researchers can start to explore what the Caperea lineage looks like, and what kind of past events were significant in driving its evolution.
Dr Marx agrees, adding that Caperea may be another example of how being ‘unusual’ helped save a lineage from extinction.
“River dolphins likely survived the demise of their marine relatives because they invaded freshwater habitats; sperm whales persisted when their toothed relatives disappeared because they were deep-diving suction specialists; and Caperea survived because it adapted to be a skim filter feeder, when most of its relatives presumably didn’t.”
END
Whale of a debate put to rest
2023-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Acute kidney injury not associated with worsening kidney function in persons with CKD
2023-07-10
1. Acute kidney injury not associated with worsening kidney function in persons with CKD
Findings suggest kidney disease observed after AKI often present before injury
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M22-3617
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A study of hospitalized persons with chronic kidney disease (CKD) fournd that acute kidney injury (AKI) did not predict worsening of kidney function trajectory once difference in pre-hospitalization characteristically were fully accounted for. Instead, the authors suggest that much of determinants of faster ...
New fish species discovered after decades of popularity in the aquarium trade
2023-07-10
With just a few clicks of a mouse, you can purchase your very own redtail garra, a type of fish that feeds on algae. Information about the fish’s biology, however, is much less easily obtained. That’s because redtail garra, although popular in the aquarium trade since the early 2000s, has until now been unknown to science.
Researchers were peripherally aware of the fish’s existence, but “discovering” a new species requires scientific description based on specimens collected in their natural ...
Hospital understaffing and poor work conditions associated with physician and nurse burnout and intent to leave
2023-07-10
PHILADELPHIA (July 10, 2023) – A unique collaborative study on hospital clinician wellbeing by teams at 60 of the nation’s best hospitals, defined by Magnet Hospital Recognition, was published today in JAMA Health Forum. The study found that physicians and nurses, even at hospitals known to be good places to work, experienced adverse outcomes during the pandemic and want hospital management to make significant improvements in their work environments and in patient safety. The solutions to high hospital clinician burnout and turnover, they say, are not resilience training ...
Anti-inflammatory drugs did not speed COVID-19 recovery but prevented deaths
2023-07-10
Two drugs commonly used to treat inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis did not shorten recovery time for patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 but did reduce the likelihood of death when compared with standard care alone, according to a national study led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The study was funded by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The study was coordinated by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) of the National Institutes of Health ...
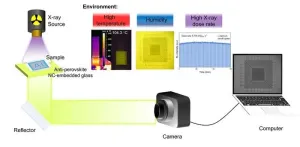
Illuminating the future of X-ray imaging: High-resolution and ultrastable solutions with lead-free anti-perovskite nanocrystals
2023-07-10
In the realms of material inspection, medical diagnostics, astronomical discovery, and scientific research, the demand for high-resolution and ultrastable X-ray imaging methods has ignited a fervent pursuit of innovative X-ray-responsive materials. These sought-after materials must possess exceptional qualities such as high X-ray attenuation, efficient scintillation, rapid light decay, and robust durability. Among them, lead-halide-based perovskites have emerged as a compelling contender due to their remarkable luminescence efficiency, superior X-ray attenuation capabilities, and short ...
DOE announces $72 million for small business research and development grants
2023-07-10
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $72 million in funding for small businesses to pursue scientific, clean energy, and climate research, development, and demonstration projects. The funding will support 296 projects across 44 states and addresses multiple topic areas, such as renewable energy, nuclear energy, cybersecurity, advanced materials and manufacturing, microelectronics, and artificial intelligence. Today’s announcement underscores the Biden-Harris Administration's deep commitment to advancing innovative climate solutions and strengthening America’s ...
Personalized oral cancer survival calculator to estimate risk of death from oral cancer or other causes
2023-07-10
About The Study: The models developed for the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Oral Cancer Survival Calculator demonstrate that survival estimates that exclude the effects of coexisting conditions can lead to underestimates or overestimates of survival.
Authors: Louise Davies, M.D., M.S., of the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center in White River Junction, Vermont, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2023.1975)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Key points for clinicians about the SEER oral cancer survival calculator
2023-07-10
About The Article: This article describes the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Oral Cancer Survival Calculator, which is designed to provide patient-specific survival estimates based on the severity of an index cancer as well as the competing risk of death of other comorbid ailments.
Authors: Louise Davies, M.D., M.S., of the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center in White River Junction, Vermont, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2023.1977)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Global study finds while humans sheltered in place, wildlife roamed
2023-07-10
MISSOULA – While humans sheltered in place during the COVID-19 pandemic, wild animals took the opportunity to roam spaces typically avoided by wildlife, according to a study published last month in Science. Photos quickly emerged of wild goats spotted on the city streets of Wales and coyotes touring downtown San Francisco, yet evidence explaining this phenomenon was sparse.
Dr. Mark Hebblewhite, professor of ungulate habitat ecology at the University of Montana, joined an international research team of 175, led by Dr. Marlee Tucker – an ecologist at Radboud University in the Netherlands – in analyzing ...
Curious compound: Tin selenide may hold the key for thermoelectric solutions
2023-07-10
Researchers at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory discovered that atomic-level structural changes occur when the compound tin selenide heats up — changes that help it to conduct electricity but not heat.
The study, funded by the National Science Foundation and Department of Energy, provides information that could lead to new technologies for applications such as refrigeration or waste heat recovery from cars or nuclear power plants. The research was published by Nature Communications.
“Tin selenide is a curious compound,” ...