(Press-News.org) Researchers at University of Michigan developed a method to produce artificially grown miniature brains — called human brain organoids — free of animal cells that could greatly improve the way neurodegenerative conditions are studied and, eventually, treated.
Over the last decade of researching neurologic diseases, scientists have explored the use of human brain organoids as an alternative to mouse models. These self-assembled, 3D tissues derived from embryonic or pluripotent stem cells more closely model the complex brain structure compared to conventional two-dimensional cultures.
Until now, the engineered network of proteins and molecules that give structure to the cells in brain organoids, known as extracellular matrices, often used a substance derived from mouse sarcomas called Matrigel. That method suffers significant disadvantages, with a relatively undefined composition and batch-to-batch variability.
The latest U-M research, published in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, offers a solution to overcome Matrigel’s weaknesses. Investigators created a novel culture method that uses an engineered extracellular matrix for human brain organoids — without the presence of animal components – and enhanced the neurogenesis of brain organoids compared to previous studies.
“This advancement in the development of human brain organoids free of animal components will allow for significant strides in the understanding of neurodevelopmental biology,” said senior author Joerg Lahann, Ph.D., director of the U-M Biointerfaces Institute and Wolfgang Pauli Collegiate Professor of Chemical Engineering at U-M.
“Scientists have long struggled to translate animal research into the clinical world, and this novel method will make it easier for translational research to make its way from the lab to the clinic.”
The foundational extracellular matrices of the research team’s brain organoids were comprised of human fibronectin, a protein that serves as a native structure for stem cells to adhere, differentiate and mature. They were supported by a highly porous polymer scaffold.
The organoids were cultured for months, while lab staff was unable to enter the building due to the COVID 19-pandemic.
Using proteomics, researchers found their brain organoids developed cerebral spinal fluid, a clear liquid that flows around healthy brain and spinal cords. This fluid more closely matched human adult CSF compared to a landmark study of human brain organoids developed in Matrigel.
“When our brains are naturally developing in utero, they are of course not growing on a bed of extracellular matrix produced by mouse cancer cells,” said first author Ayşe Muñiz, Ph.D., who was a graduate student in the U-M Macromolecular Science and Engineering Program at the time of the work.
“By putting cells in an engineered niche that more closely resembles their natural environment, we predicted we would observe differences in organoid development that more faithfully mimics what we see in nature.”
The success of these xenogeneic-free human brain organoids opens the door for reprogramming with cells from patients with neurodegenerative diseases, says co-author Eva Feldman, M.D., Ph.D., director of the ALS Center of Excellence at U-M and James W. Albers Distinguished Professor of Neurology at U-M Medical School.
“There is a possibility to take the stem cells from a patient with a condition such as ALS or Alzheimer’s and, essentially, build an avatar mini brain of that patients to investigate possible treatments or model how their disease will progress,” Feldman said. “These models would create another avenue to predict disease and study treatment on a personalized level for conditions that often vary greatly from person to person.”
Additional authors include Tuğba Topal, Ph.D., Michael D. Brooks, Ph.D., Angela Sze, Do Hoon Kim, Jacob Jordahl, Ph.D., Joe Nguyen, Ph.D., Paul H. Krebsbach, D.D.S., Ph.D., Masha G. Savelieff, all of University of Michigan.
A.J.M. is funded by the National Science Foundation with grant no. DGE 1256260. E.L.F. thanks the Robert and Katherine Jacobs Health Environmental Initiative Fund, the Andrea and Lawrence A. Wolfe Brain Health Initiative Fund, Robert E. Nederlander Sr. Program for Alzheimer's Research, and NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies. We acknowledge funding from the University of Michigan Biointerfaces Institute (E.L.F. and J.L.).
Paper Cited: “Engineered extracellular matrices facilitate brain organoids from human pluripotent stem cells,” Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology. DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51820
END
Artificially grown ‘mini-brains’ without animal components bring opportunities for neuroscience
Novel method will make it easier for translational research to leap from the lab to the clinic, researchers say
2023-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fear is in the eye of the beholder
2023-07-13
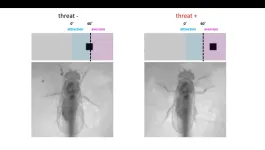
Averting our eyes from things that scare us may be due to a specific cluster of neurons in a visual region of the brain, according to new research at the University of Tokyo. Researchers found that in fruit fly brains, these neurons release a chemical called tachykinin which appears to control the fly’s movement to avoid facing a potential threat. Fruit fly brains can offer a useful analogy for larger mammals, so this research may help us better understand our own human reactions to scary situations and phobias. Next, the team want to find out how these ...
Multiple ecosystems in hot water after marine heatwave surges across the Pacific
2023-07-13
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) – Rising ocean temperatures are sweeping the seas, breaking records and creating problematic conditions for marine life. Unlike heatwaves on land, periods of abrupt ocean warming can surge for months or years. Around the world these ‘marine heatwaves’ have led to mass species mortality and displacement events, economic declines and habitat loss. New research reveals that even areas of the ocean protected from fishing are still vulnerable to these extreme events fueled by climate change.
A study published today in Global Change Biology, led by researchers at UC Santa ...
When the stars align: Astronomers find answers to mysterious action of ghost stars in our Galaxy
2023-07-13
A collaboration of scientists from The University of Manchester and the University of Hong Kong have found a source for the mysterious alignment of stars near the Galactic Centre.
The alignment of planetary nebulae was discovered ten years ago by a Manchester PhD student, Bryan Rees, but has remained unexplained.
New data obtained with the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope in Chile and the Hubble Space Telescope, published in Astrophysical Journal Letters, has confirmed the alignment but also found a particular ...
Skin lightening products can be dangerous, but users don’t know risks
2023-07-13
· Colorism – system of inequality that views lighter skin as more beautiful and advantageous – motivates skin lightening
· Users aren’t aware of adulterated ingredients in over-the-counter products such as mercury and steroids
· Products are purchased from chain grocery stores or online, used without medical advice
CHICAGO --- Skin lightening is prevalent in the U.S. among skin of color individuals – particularly women – but the people who use those products don’t know the risks, reports a new Northwestern ...
Small-winged and lighter colored butterflies likely to be at greatest threat from climate change
2023-07-13
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 05:01 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON THURSDAY 13 JULY 2023
Images and paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18XRYP9dHcC1Z8lc3B86j3k6BzgIesqUS?usp=sharing
Small-winged and lighter coloured butterflies likely to be at greatest threat from climate change
The family, wing length and wing colour of tropical butterflies all influence their ability to withstand rising temperatures, say a team led by ecologists at the University of Cambridge. The researchers believe this could help identify species whose survival is under threat from climate change.
Butterflies with smaller or lighter coloured wings are likely to ...
Unexpected coupling with leaky mode unveils new path for dense photonic integration
2023-07-13
Defying conventional wisdom, researchers have uncovered a novel coupling mechanism involving leaky mode, previously has been considered unsuitable for high-density integration in photonic circuits. This unexpected finding opens new possibilities for dense photonic integration, revolutionizing the scalability and application of photonic chips in optical computing, quantum communication, light detection and ranging (LiDAR), optical metrology, and biochemical sensing.
In a recent Light Science & Application publication, Sangsik Kim, associate professor of electrical engineering ...
Unemployment and underemployment significant drivers of suicide: Analysis
2023-07-13
A study examining unemployment and underemployment figures and suicide rates in Australia has found both were significant drivers of suicide mortality between 2004-2016.
The researchers say the findings indicate that economic policies such as a Job Guarantee, which prioritise full employment, should be a core part of any comprehensive national suicide prevention strategy.
Predictive modelling also revealed an estimated 9.5 percent of suicides reported during that time resulted directly from unemployment ...
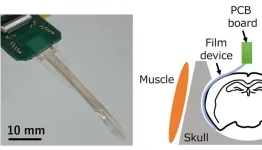
Multisensory information detection by using multi-channel electrocorticography film that can place over a wide area of the cerebral cortex
2023-07-13
Overview
Associate Professor Hiroto Sekiguchi (Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) and Assistant Professor Susumu Setogawa and Associate Professor Noriaki Ohkawa (Comprehensive Research Facilities for Advanced Medical Science, Dokkyo Medical University; Assistant Professor Setogawa is currently a Specially Appointed Assistant Professor at University Public Corporation Osaka) have developed a flexible electrocorticography (Note 1) film for simultaneous detection of multisensory information (Note 2) from multiple regions of the cerebral cortex by placing neural ...
Fungi blaze a trail to fireproof cladding
2023-07-13
Mycelium, an incredible network of fungal strands that can thrive on organic waste and in darkness, could be a basis for sustainable fireproofing. RMIT researchers are chemically manipulating its composition to harness its fire-retardant properties.
Associate Professor Tien Huynh, an expert in biotechnology and mycology, said they’ve shown that mycelium can be grown from renewable organic waste.
“Fungi are usually found in a composite form mixed with residual feed material, but we found a way to grow pure mycelium sheets that can be layered and engineered into different uses – from flat panels for the building industry to a leather-like material for ...
Investigating interactions at molecular junctions for novel electronic devices
2023-07-13
The structure of a molecular junction with noncovalent interaction plays a key role in electron transport, reveals a recent study conducted by researchers at Tokyo Tech. Through simultaneous surface-enhanced Raman scattering and current–voltage measurements, they found that a single dimer junction of naphthalenethiol molecule shows three different bondings, namely π–π intermolecular and through-π and through-space molecule–electrode interactions.
The π–π interaction is a type of noncovalent interaction that occurs when the electron clouds in the π orbitals ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Artificially grown ‘mini-brains’ without animal components bring opportunities for neuroscienceNovel method will make it easier for translational research to leap from the lab to the clinic, researchers say