(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO—Schmidt Marine Technology Partners, a program of the Schmidt Family Foundation, has awarded $3.5 million in grants to ten organizations and universities in seven countries for the development of new tools and innovations that will improve the sustainability of global fisheries, the program announced today.
“Tens of millions of jobs around the world depend on fisheries, and seafood is the primary protein source for 3 billion people,” said Wendy Schmidt, president and co-founder of the Schmidt Family Foundation. “The innovators chosen to receive these grants are ensuring that fishers and fisheries—and by extension all of us who rely on them—are secure and sustainable worldwide.”
Although more investors are funding ocean technology today than in years past, developers need considerable early-stage support to advance from an idea to wide use of a technology. The sustainable fisheries initiative—to which Schmidt Marine has committed $2 million in new funding, with partners Oceankind and Builders Initiative contributing the additional $1.5 million—aims to address that gap.
“Increasing the sustainability of fisheries is challenging, but we think that both technology and philanthropy have important roles to play,” said Mark Schrope, director of Schmidt Marine Technology Partners. “We try to take a realistic approach by focusing on solutions that offer significant benefits not just for the environment, but also for the fishers themselves.”
The 10 projects selected for grants—ranging from $150,000 to $500,000—seek to reduce bycatch, prevent illegal fishing, improve data collection on fisheries and fish populations, and increase the transparency of a fish’s journey from ocean to table. A team of seven expert advisers and additional tech reviewers from nonprofits, government, and industry helped evaluate proposals from a pool of 200 applications from 20 countries across six continents. Schmidt Marine selected grantees based on the environmental benefits of their proposed ideas, as well as their incorporation of sound fisheries science and management principles, and, where applicable, the practical appeal of the new technologies to fishers.
The funding recipients are:
Katchi Technologies (Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada): An alternative trawling net outfitted with a cable-mounted system that ensures the net stays open and is automatically controlled to prevent damaging contact with the seafloor. The system also reduces drag by an estimated 30%, which in turn further reduces carbon emissions, fuel costs and bycatch while also increasing fisher safety.
Trygg Mat Tracking (Oslo, Norway): Data-rich and easy-to-use software that enables countries to make quick and informed decisions on who can enter their ports and what to target in their inspections to stop illegal fish landings.
Abalobi (Cape Town, South Africa): Development and deployment of software that integrates fishing data with processing plant data to provide ocean-to-market tracking that helps prevent illegal fishing and connects small businesses to larger markets.
University of Haifa, work led by Roee Diamant, Ph.D. (Haifa, Israel): A “swarm” of low-cost underwater autonomous robots that coordinate for better acoustic detection and size estimation of fish populations.
Centro de Ciencas do Mar (Center for Marine Science) (Faro, Portugal): A redesigned fishing net, developed in partnership with fishers, that could reduce bycatch in certain squid and other fisheries by 40%, reducing net damage and protecting sensitive habitats.
Cornell University, work led by Aaron Rice, Ph.D., (Ithaca, N.Y.) in partnership with Marc Dantzker, Ph.D. of Fisheye Acoustics (Arlington, Va.): A new autonomous audio/video technology that allows researchers to identify fish species based on the specific unique sounds they emit. With this information, inexpensive passive acoustic monitoring techniques will be better able to track and estimate fish populations for conservation, sustainability and research.
Allen Institute for AI, in association with Ocean Aero (Gulfport, Miss.) and ThayerMahan (Groton, Conn.): Tools to improve the detection, interdiction and prosecution of illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing activities. The integration of Skylight AI and a modified ThayerMahan acoustic system into the TRITON—an environmentally powered Autonomous Underwater and Surface Vehicle (AUSV)—promises a revolutionary approach to securing our oceans against IUU fishing.
Arizona State University, work led by Jesse Senko, Ph.D., (Tempe, Ariz.): Low-cost lights, powered by solar energy, that easily hook on to fishing nets and reduce bycatch of threatened species including sea turtles and sharks.
Wildaid Marine (San Francisco, Calif.): An app that provides accurate fishing and vessel data to rangers to help them deter illegal fishing in marine areas and better protect marine wildlife and the coastal communities that depend on them.
Fishtek Marine (Devon, England): An evaluation of the effectiveness of multiple bycatch reduction tools such as a shark-repellent device for longline fishing.
About Schmidt Marine Technology Partners
Schmidt Marine Technology Partners supports scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs in developing technologies that restore ocean health. Schmidt Marine is one of two grant-making and investment programs of the Schmidt Family Foundation, founded by Eric and Wendy Schmidt. For more information, visit schmidtmarine.org.
About the Schmidt Family Foundation
Established in 2006 by Eric and Wendy Schmidt, the Schmidt Family Foundation works to restore a balanced relationship between people and planet. Through grantmaking and investments, the foundation partners with communities around the world in working for renewable energy, resilient food systems, healthy oceans and the protection of human rights. The foundation makes grants and impact investments through two programs: 11th Hour Project and Schmidt Marine Technology Partners.
# # # # #
END
A University of Minnesota Twin Cities team has, for the first time, synthesized a thin film of a unique topological semimetal material that has the potential to generate more computing power and memory storage while using significantly less energy. The researchers were also able to closely study the material, leading to some important findings about the physics behind its unique properties.
The study is published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers the natural sciences and engineering.
As evidenced by the United States’ recent CHIPS and Science Act, there is a growing need to increase semiconductor manufacturing ...
Researchers at University of Michigan developed a method to produce artificially grown miniature brains — called human brain organoids — free of animal cells that could greatly improve the way neurodegenerative conditions are studied and, eventually, treated.
Over the last decade of researching neurologic diseases, scientists have explored the use of human brain organoids as an alternative to mouse models. These self-assembled, 3D tissues derived from embryonic or pluripotent stem cells ...
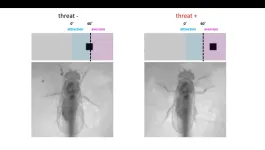
Averting our eyes from things that scare us may be due to a specific cluster of neurons in a visual region of the brain, according to new research at the University of Tokyo. Researchers found that in fruit fly brains, these neurons release a chemical called tachykinin which appears to control the fly’s movement to avoid facing a potential threat. Fruit fly brains can offer a useful analogy for larger mammals, so this research may help us better understand our own human reactions to scary situations and phobias. Next, the team want to find out how these ...
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) – Rising ocean temperatures are sweeping the seas, breaking records and creating problematic conditions for marine life. Unlike heatwaves on land, periods of abrupt ocean warming can surge for months or years. Around the world these ‘marine heatwaves’ have led to mass species mortality and displacement events, economic declines and habitat loss. New research reveals that even areas of the ocean protected from fishing are still vulnerable to these extreme events fueled by climate change.
A study published today in Global Change Biology, led by researchers at UC Santa ...
A collaboration of scientists from The University of Manchester and the University of Hong Kong have found a source for the mysterious alignment of stars near the Galactic Centre.
The alignment of planetary nebulae was discovered ten years ago by a Manchester PhD student, Bryan Rees, but has remained unexplained.
New data obtained with the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope in Chile and the Hubble Space Telescope, published in Astrophysical Journal Letters, has confirmed the alignment but also found a particular ...
· Colorism – system of inequality that views lighter skin as more beautiful and advantageous – motivates skin lightening
· Users aren’t aware of adulterated ingredients in over-the-counter products such as mercury and steroids
· Products are purchased from chain grocery stores or online, used without medical advice
CHICAGO --- Skin lightening is prevalent in the U.S. among skin of color individuals – particularly women – but the people who use those products don’t know the risks, reports a new Northwestern ...
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 05:01 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON THURSDAY 13 JULY 2023
Images and paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18XRYP9dHcC1Z8lc3B86j3k6BzgIesqUS?usp=sharing
Small-winged and lighter coloured butterflies likely to be at greatest threat from climate change
The family, wing length and wing colour of tropical butterflies all influence their ability to withstand rising temperatures, say a team led by ecologists at the University of Cambridge. The researchers believe this could help identify species whose survival is under threat from climate change.
Butterflies with smaller or lighter coloured wings are likely to ...
Defying conventional wisdom, researchers have uncovered a novel coupling mechanism involving leaky mode, previously has been considered unsuitable for high-density integration in photonic circuits. This unexpected finding opens new possibilities for dense photonic integration, revolutionizing the scalability and application of photonic chips in optical computing, quantum communication, light detection and ranging (LiDAR), optical metrology, and biochemical sensing.
In a recent Light Science & Application publication, Sangsik Kim, associate professor of electrical engineering ...
A study examining unemployment and underemployment figures and suicide rates in Australia has found both were significant drivers of suicide mortality between 2004-2016.
The researchers say the findings indicate that economic policies such as a Job Guarantee, which prioritise full employment, should be a core part of any comprehensive national suicide prevention strategy.
Predictive modelling also revealed an estimated 9.5 percent of suicides reported during that time resulted directly from unemployment ...
Overview
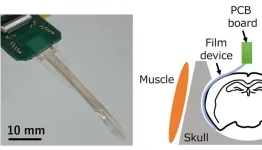
Associate Professor Hiroto Sekiguchi (Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) and Assistant Professor Susumu Setogawa and Associate Professor Noriaki Ohkawa (Comprehensive Research Facilities for Advanced Medical Science, Dokkyo Medical University; Assistant Professor Setogawa is currently a Specially Appointed Assistant Professor at University Public Corporation Osaka) have developed a flexible electrocorticography (Note 1) film for simultaneous detection of multisensory information (Note 2) from multiple regions of the cerebral cortex by placing neural ...