Advancing causal inference in clinical neuroscience research: a call for clarity
2023-07-13
(Press-News.org)
A Perspective published in Volume 3 of the journal Psychoradiology, researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University confronted these challenges and advocates for more clarity and transparency in causal analyses. The review distinguishes between traditional statistical analysis and causal inference, highlighting the need for specific causal assumptions, like the Stable Unit Treatment Value Assumption (SUTVA).
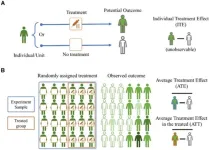
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are considered the gold standard for estimating causal effects. The authors stress the importance of imitating RCTs in observational studies through quasi-experimental techniques, given the constraints on RCT data availability due to ethical concerns. In observational studies, researchers grapple with controlling intervention assignments and justifying causal assumptions. Breaches of these assumptions could cause imbalanced covariates between treatment and control groups, needing statistical methods to create balance and replicate RCT results.
The definition of intervention in clinical neuroscience extends beyond medication administration to include brain stimulation or targeted surgery, demanding a multivariate mechanistic approach for causal inference. The authors advise researchers to provide detailed information about their causal formulation of research questions, including study type, causal effects, and observed outcomes. They emphasize the necessity of justifying causal assumptions and performing sensitivity analysis to evaluate results' robustness.
This review highlights the challenges and opportunities in advancing causal inference in clinical neuroscience research. By adopting clear and transparent practices in conducting and reporting causal analyses, researchers can improve the rigor and interpretability of their findings. This interdisciplinary effort will contribute to a better understanding of causal relationships in clinical neuroscience and facilitate evidence-based decision-making in the field.
###
References
DOI
10.1093/psyrad/kkad007
About Psychoradiology
Psychoradiology is an open-access journal co-published by Oxford University Press and West China Hospital of Sichuan University. It has been indexed by DOAJ and the APC is waived during its early stage.
We welcome interdisciplinary submissions in the fields of radiology, psychology, psychiatry, neurology and neuroscience, as well as medical imaging, interventional medicine, artificial intelligence, and computer science, etc. A fast-track production mode will be adopted to ensure the manuscript is published as soon as possible.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-13
Gero, an AI-driven biotech focused on aging and longevity, has demonstrated the feasibility of applying quantum computing for drug design and generative chemistry, which now offers significant promise for the future of healthcare. The research, published in Scientific Reports, outlines how a hybrid quantum-classical machine-learning model was used to interface between classical and quantum computational devices with the goal of generating novel chemical structures for potential drugs — an industry first.
The research paper follows ...
2023-07-13
A new study suggests eastern wild turkeys in five southern U.S. states are unlikely to make meaningful changes in the timing of when they begin nesting, even under significant future climate change.
The findings suggest eastern wild turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo silvestris) could be vulnerable to shifts in climate, which could threaten the availability of their food sources, the amount of vegetation cover available to protect them from predators, and other factors.
“There are implications here for turkey populations ...
2023-07-13
Although wheat was among the first domesticated food crops, it remains a global dietary staple several millennia later. Grown on every continent except Antarctica, wheat is the second highest produced grain worldwide, with nearly 800,000 metric tons grown each year (Food and Agriculture Organization). However, a fungal pathogen named Fusarium graminearum causes the devastating disease Fusarium head blight (FHB) on wheat and contaminates grains with harmful toxins called trichothecenes. One such trichothecene, called deoxynivalenol (DON), is produced by most F. graminearum strains in the United States, and it is an essential virulence factor that increases the pathogen’s spread ...
2023-07-13
Currently, there is no cure for amyloidosis, a life-threatening disease that can be present throughout the body, including the heart, kidneys, liver and brain. The most common localized form of amyloidosis, which is seen significantly more often, is in the brain. Cerebral amyloidosis, when symptomatic, usually manifests in one of two ways: in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias and in brain bleeds, which have consequences such as a stroke.
Because amyloidosis does not affect a specific organ, unraveling the underlying cause of amyloid fibril creation – a hallmark ...
2023-07-13
SAN FRANCISCO—Schmidt Marine Technology Partners, a program of the Schmidt Family Foundation, has awarded $3.5 million in grants to ten organizations and universities in seven countries for the development of new tools and innovations that will improve the sustainability of global fisheries, the program announced today.
“Tens of millions of jobs around the world depend on fisheries, and seafood is the primary protein source for 3 billion people,” said Wendy Schmidt, president and co-founder of the Schmidt Family Foundation. “The innovators chosen to receive these grants are ensuring that fishers and ...
2023-07-13
A University of Minnesota Twin Cities team has, for the first time, synthesized a thin film of a unique topological semimetal material that has the potential to generate more computing power and memory storage while using significantly less energy. The researchers were also able to closely study the material, leading to some important findings about the physics behind its unique properties.
The study is published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers the natural sciences and engineering.
As evidenced by the United States’ recent CHIPS and Science Act, there is a growing need to increase semiconductor manufacturing ...
2023-07-13
Researchers at University of Michigan developed a method to produce artificially grown miniature brains — called human brain organoids — free of animal cells that could greatly improve the way neurodegenerative conditions are studied and, eventually, treated.
Over the last decade of researching neurologic diseases, scientists have explored the use of human brain organoids as an alternative to mouse models. These self-assembled, 3D tissues derived from embryonic or pluripotent stem cells ...
2023-07-13
Averting our eyes from things that scare us may be due to a specific cluster of neurons in a visual region of the brain, according to new research at the University of Tokyo. Researchers found that in fruit fly brains, these neurons release a chemical called tachykinin which appears to control the fly’s movement to avoid facing a potential threat. Fruit fly brains can offer a useful analogy for larger mammals, so this research may help us better understand our own human reactions to scary situations and phobias. Next, the team want to find out how these ...
2023-07-13
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) – Rising ocean temperatures are sweeping the seas, breaking records and creating problematic conditions for marine life. Unlike heatwaves on land, periods of abrupt ocean warming can surge for months or years. Around the world these ‘marine heatwaves’ have led to mass species mortality and displacement events, economic declines and habitat loss. New research reveals that even areas of the ocean protected from fishing are still vulnerable to these extreme events fueled by climate change.
A study published today in Global Change Biology, led by researchers at UC Santa ...
2023-07-13
A collaboration of scientists from The University of Manchester and the University of Hong Kong have found a source for the mysterious alignment of stars near the Galactic Centre.
The alignment of planetary nebulae was discovered ten years ago by a Manchester PhD student, Bryan Rees, but has remained unexplained.
New data obtained with the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope in Chile and the Hubble Space Telescope, published in Astrophysical Journal Letters, has confirmed the alignment but also found a particular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Advancing causal inference in clinical neuroscience research: a call for clarity