(Press-News.org) Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Catherine Royer, Constellation Chair Professor of Bioinformatics and Biocomputation at the Shirley Ann Jackson, Ph.D. Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies (CBIS) and professor of biological sciences, has received a grant of over $400,000 from the National Science Foundation to investigate enzymes from organisms living in deep sea environments.
“Ultimately, I hope to better understand how these enzymes function under the high pressure that is present in the deep sea,” said Royer. “They also thrive in high or low temperatures. Biomolecules from the surface do not have the ability to survive these extreme conditions.”
Understanding the differences between deep sea enzymes and those at the surface could pave the way for the development of new enzymes with biotechnological applications. The deep sea is home to more than 80% of the Earth’s microbes. There are 15 times more viruses and bacteriophages than microbes in the world’s oceans, and they contribute to the deaths of 20% of those microbes on a daily basis. This releases 145 gigatons of carbon each year, which includes massive amounts of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
In this research, Royer will study Dnases, which break up DNA polymers. Many oceanic microbes exhibit extracellular Dnase activity, which shows the enzyme’s significance to oceanic biofilm dynamics and geobiochemical cycling, or the circulation of the essential elements of living matter.
“We have so much to learn from organisms living in the deep sea and other extreme environments,” said Curt Breneman, dean of Rensselaer’s School of Science. “Dr. Royer’s research on how biomolecules function under very high pressure will expand our understanding of fundamental biochemical mechanisms and may also provide new insights into new approaches towards drug development.”
About Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute:
Founded in 1824, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is America’s first technological research university. Rensselaer encompasses five schools, over 30 research centers, more than 140 academic programs including 25 new programs, and a dynamic community made up of over 6,800 students and 110,000 living alumni. Rensselaer faculty and alumni include upwards of 155 National Academy members, six members of the National Inventors Hall of Fame, six National Medal of Technology winners, five National Medal of Science winners, and a Nobel Prize winner in Physics. With nearly 200 years of experience advancing scientific and technological knowledge, Rensselaer remains focused on addressing global challenges with a spirit of ingenuity and collaboration. To learn more, please visit www.rpi.edu.
Contact:
Katie Malatino
Sr. Communications Specialist
malatk@rpi.edu
838-240-5691
For general inquiries: newsmedia@rpi.edu
Visit the Rensselaer research and discovery blog: https://everydaymatters.rpi.edu/
Follow us on Twitter: @RPINews
###
END
Rensselaer researcher receives grant to study enzymes in deep sea organisms
Catherine Royer to explore how enzymes function under high pressure
2023-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn State researchers receive $1M NSF award to develop hemp-based supply chain
2023-07-13
MIDDLETOWN, Pa. — An interdisciplinary team of researchers at Penn State is part of a project that recently received a $1 million National Science Foundation (NSF) Engines Development Award. The award will fund the development of the Pennsylvania Industrial Hemp Engine (PAIHE), which will support the manufacture and deployment of bio-based products for application in green building construction, packaging, fabrics, renewable energy and land remediation.
Launched by NSF’s new Directorate for Technology, Innovation ...
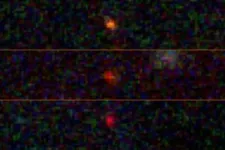
James Webb Telescope catches glimpse of possible first-ever ‘dark stars’
2023-07-13
Stars beam brightly out of the darkness of space thanks to fusion, atoms melding together and releasing energy. But what if there’s another way to power a star?
A team of three astrophysicists — Katherine Freese at The University of Texas at Austin, in collaboration with Cosmin Ilie and Jillian Paulin ’23 at Colgate University — analyzed images from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and found three bright objects that might be “dark stars,” theoretical objects much bigger and brighter than our sun, powered by particles of dark matter annihilating. If confirmed, dark stars could reveal the nature ...
Multidisciplinary team reduced hypothermia in NICU babies during and after surgery
2023-07-13
The percentage of infants from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) experiencing hypothermia upon operating room (OR) arrival and at any point during the operation decreased from 48.7% to 6.4% and 67.5% to 37.4%, respectively, after implementation of a multidisciplinary quality improvement project at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago. The project and its success were featured in the journal Pediatric Quality and Safety.
About one-third of infants admitted to children’s hospitals’ NICUs require surgery and ...
Argonne engineers to drive innovation with three GAIN funding awards
2023-07-13
Argonne is shaping the future of clean and reliable energy solutions.
Research into nuclear energy is gaining attention as a critical piece of the solution to climate change. As part of this trend, nuclear engineers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have received three new funding awards from the Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) initiative. These awards recognize the valuable contributions of Argonne’s world-class nuclear engineers and facilities in this field.
Among ...
C-Path and Vivpro formalize partnership to accelerate drug development
2023-07-13
TUCSON, Ariz., July 13, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path), a leading global nonprofit committed to expediting drug development through the acceleration of regulatory-endorsed solutions, today announced a newly formalized Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Vivpro, an industry-leading provider of a revolutionary biointelligence software platform and innovative services. The partnership will enhance C-Path’s core competencies in accelerating drug development, by utilizing advanced data analytics and deep machine learning insights offered by Vivpro to further revolutionize ...
Sanford health rare disease data registry partners with C-Path’s RDCA-DAP, cure Mito Foundation to aggregate rare disease data in platform
2023-07-13
TUCSON, Ariz., July 12, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) announced today that the Coordination of Rare Diseases based at Sanford Research (CoRDS), in partnership with Cure MITO, will contribute its mitochondrial disorders data from its international patient registry to the C-Path-managed Rare Disease Cures Accelerator-Data and Analytics Platform (RDCA-DAP®).
RDCA-DAP provides a centralized and standardized infrastructure to support and accelerate rare disease characterization targeted to accelerate clinical drug development. Additionally, the platform advances best practices to support the rigorous conduct of natural history ...
Scripps Research receives momentous award from NIH to lead key programs in national All of Us Research Program
2023-07-13
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research announced today that the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has renewed funding for its Translational Institute to continue its work enrolling and engaging participants in the All of Us Research Program. The initial funding of $54 million will support Scripps Research Translational Institute’s work with a nationwide consortium to help build one of the largest, most diverse health research resources of its kind. The project is expected to last five years, with anticipated total funding ...
Astronomers identify the coldest star yet that emits radio waves
2023-07-13
Astronomers at the University of Sydney have shown that a small, faint star is the coldest on record to produce emission at radio wavelength.
The ‘ultracool brown dwarf’ examined in the study is a ball of gas simmering at about 425 degrees centigrade – cooler than a typical campfire – without burning nuclear fuel.
By contrast, the surface temperature of the Sun, a nuclear inferno, is about 5600 degrees.
While not the coldest star ever found, it is the coolest so far analysed using radio astronomy. The findings are published today in The Astrophysical Journal.
Lead author and PhD student in the School of Physics, Kovi Rose, said: “It’s very rare ...
UT Health Science Center San Antonio develops tool that counts brain lesions in seconds
2023-07-13
SAN ANTONIO (July 13, 2023) — An artificial intelligence (AI) tool developed at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio accurately counts brain lesions on MRI scans within seconds. Once it is adapted to the clinic, the AI tool should help neuroradiologists to evaluate patients’ brain diseases at earlier stages.
“Certain kinds of brain lesions are tremendously difficult to quantify without AI,” said researcher Mohamad Habes, PhD, of the health science center’s Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative ...
New ways of getting to the heart of the matter
2023-07-13
Peter Keyel, an associate professor in Texas Tech University’s Department of Biological Sciences, has received an Innovative Project Award from the American Heart Association to study atherosclerosis, the condition that causes arteries to thicken and can trigger a variety of devastating health complications.
Statistics indicate diseases linked to atherosclerosis are the leading cause of death in the U.S. with as many as half of Americans between the ages of 45 and 84 having the condition but being unaware of its slow progression and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Rensselaer researcher receives grant to study enzymes in deep sea organismsCatherine Royer to explore how enzymes function under high pressure