(Press-News.org) Peer-reviewed / Observational study / People
One of the largest observational studies to date of ‘superagers’ – people in their eighties with the memory function of people decades younger – suggests they also move more quickly and have better mental health than typical older adults.
MRI scans add to evidence that superagers have more grey matter in key regions linked to memory function.
No differences in biomarkers or genetic risk factors for neurodegenerative disease were detected between superagers and typical older adults, suggesting superagers are resistant to age-related processes that lead to memory decline.
People in their eighties who can recall everyday events and life experiences as well as someone 20 to 30 years younger – known as superagers – are also more likely to have greater movement speed than typical older adults. They also have lower rates of anxiety and depression, according to a new study published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity journal.
Most people’s memory function gradually declines as they age; however, superagers appear to be able to avoid this age-related deterioration.
First author Marta Garo-Pascual, of the Queen Sofia Foundation Alzheimer Centre, Madrid, said: “We are now closer to solving one of the biggest unanswered questions about superagers: whether they are truly resistant to age-related memory decline or they have coping mechanisms that help them overcome this decline better than their peers. Our findings suggest superagers are resistant to these processes, though the precise reasons for this are still unclear. By looking further into links between superageing and movement speed we may be able to gain important insights into the mechanisms behind the preservation of memory function deep into old age.”
While previous research has found differences in brain structure and certain lifestyle factors – such as stronger social connections – among superagers compared with typical older adults, most studies have had small sample sizes and did not track changes over time. As a result, in-depth understanding of demographic, lifestyle, or clinical factors that help to preserve memory function into old age is currently lacking.
To help address these knowledge gaps, the authors conducted one of the largest analyses of superagers to date. Superagers and typical older adults were discovered within an ongoing project designed to help identify early indicators of Alzheimer’s disease. The Vallecas Project cohort in Madrid is composed of people aged 69 to 86 years with no neurological or severe psychiatric disorders. Of the cohort’s 1,213 participants, recruited between 2011 and 2014, 64 superagers and 55 typical older adults, performing well on several cognitive tasks but not displaying superager memory ability, were identified and included in the new study.
Superagers and typical older adults were identified based on their performance in the Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test (FCSRT), which is used to assess people’s memory function. Superagers did at least as well as the average person around 30 years younger with the same education level. older adults performed within a normal range for their age and education. All typical superagers and normal older adults were 79.5 years or older. Most superagers were women (38/64, 59%), as were most typical older adults (35/55, 64%).
Participants had up to six annual follow-up visits, during which demographic and lifestyle factors were recorded. Participants also underwent MRI scans to measure grey matter volume and completed a range of clinical tests. Blood samples were taken to screen for biomarkers for neurodegenerative disease and a key genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. A machine learning computer model including 89 demographic, lifestyle, and clinical predictors was used to identify factors associated with superagers.
In line with previous studies, MRI scans showed superagers to have more grey matter – tissue vital for normal brain function – in key brain areas involved in memory, and also in a part of the brain involved in movement. Superagers’ overall level of grey matter in key areas also degenerated more slowly over five years than in typical older adults.
Using the machine learning computer model, the authors found faster movement speed and better mental health were the factors most often associated with superagers.
Superagers performed better in the Timed Up and Go Test – which gauges people’s mobility – and a finger tapping test that measures fine motor function, indicating they have better mobility, agility, and balance than do typical older adults. This observation was made despite no differences in self-reported exercise levels between superagers and typical older adults.
In clinical tests to measure levels of anxiety and depression, superagers scored lower than typical older adults. Previous research suggests depression and anxiety can impair performance on memory tests in people of all ages, and are risk factors for developing dementia.
Senior author Dr Bryan Strange, of the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, said: “Though superagers report similar activity levels to typical older people, it’s possible they do more physically demanding activities like gardening or stair climbing. From lower blood pressure and obesity levels to increased blood flow to the brain, there are many direct and indirect benefits of being physically active that may contribute to improved cognitive abilities in old age. We have shown before that when young adults make movements at the same time as seeing pictures, they are more likely to later remember the picture than if they don’t move. It’s also possible that having better brain health in the first place may be what’s responsible for superagers having faster movement speed.”
“Further research in these areas may ultimately reveal ways to help preserve memory function in more older people. What we have, however, discovered is that there is an overlap between risk or protective factors for dementia and those associated with superaging (such as blood pressure, glucose control and mental health). This raises a possibility that some putative risk factors for dementia are, in fact, contributing to age-related decline in memory-related brain activity that may act in parallel or additively with dementia pathophysiology to amplify memory impairment.”
Other self-reported differences were also observed, including that superagers’ lifestyles in midlife were generally more active, were satisfied with their sleep duration, and were more likely to have a musical background – either taught or amateur – than did typical older adults. Superagers also demonstrated greater independence in their day-to-day living and scored higher in intelligence tests.
Blood sample analysis indicated that superagers have lower levels of biomarkers for neurodegeneration than do typical older adults. There were also no differences found between them based on the presence of a major genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, called APOE e4.
The authors acknowledge some limitations to their study. As with any observational study, it is not possible to say whether the factors reported have any direct effect on superageing. Despite using 89 variables, the machine learning model was only able to distinguish superagers from typical older adults around 66% of the time, indicating that additional factors – possibly genetic – are linked with superageing. Further research into overlap between genetic links with superageing and genes associated with fast muscle movements among the elderly could help to narrow the search.
Writing in a linked Comment, Alexandra Touroutoglou, Bonnie Wong, and Joseph M Andreano, of Harvard University, who were not involved in the study, said: “The findings of Garo-Pascual and colleagues study are consistent with reports of resilience to Alzheimer’s disease in superageing, although the mechanisms underlying this resilience remain unknown. More efforts are needed to refine and harmonise definitions of superageing in multisite studies using large and diverse cohorts. Large-scale studies will allow further exploration of resilience factors in superagers, which could lead to new insights in the prevention of age-related memory decline.”
NOTES TO EDITORS
This study was funded by the Queen Sofia Foundation, Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, Alzheimer’s Association, European Research Council and MAPFRE foundation-. It was conducted by researchers from the , Queen Sofia Foundation Alzheimer Centre, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria del Hospital Clínico San Carlos (IdISSC), , Jena University Hospital, German Centre for Mental Health (DZPG), Centre for Intervention and Research on adaptive and maladaptive brain Circuits underlying mental health (C-I-R-C), University of Eastern Finland, and Network Centre for Biomedical Research in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
[1] Quote direct from author and cannot be found in the text of the Article.
The labels have been added to this press release as part of a project run by the Academy of Medical Sciences seeking to improve the communication of evidence. For more information, please see: http://www.sciencemediacentre.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/AMS-press-release-labelling-system-GUIDANCE.pdf if you have any questions or feedback, please contact The Lancet press office pressoffice@lancet.com
IF YOU WISH TO PROVIDE A LINK FOR YOUR READERS, PLEASE USE THE FOLLOWING, WHICH WILL GO LIVE AT THE TIME THE EMBARGO LIFTS: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanhl/article/PIIS2666-7568(23)00079-X/fulltext
END
THE LANCET HEALTHY LONGEVITY: Razor-sharp memory function in older adults linked to faster movement and better mental health, study suggests
2023-07-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
App helps identify autistic children in India – study
2023-07-14
Children with autism and related neurodevelopmental disorders in India can be successfully identified by community healthcare workers using a low-cost app, a study has found.
The results, published today (Friday 14 July) in Autism, could open the door to help millions of children with autism spectrum conditions to get earlier screening quickly and inexpensively, leading to life-changing support.
Researchers from India, the UK and US tested the app with 131 two- to seven-year-olds living in low-resource neighbourhoods of Delhi, India.
The tests were carried out at the homes of the children, by non-specialist ...
Geological Society of America announces 2023–2024 Officers and Councilors
2023-07-14
13 July 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release no. 23-26
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For Immediate Release
Geological Society of America Announces 2023–2024 Officers and Councilors
Boulder, Colo., USA: Christopher (Chuck) M. Bailey, College of William & Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia, takes over the role of president of The Geological Society of America as of 1 July 2023. The incoming president-elect is Carmala N. Garzione, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona.
Rounding ...
Multimillion dollar consortium to address southwest water concerns
2023-07-14
The Colorado River, which provides drinking water to tens of millions of people and irrigation water to more than 5 million acres of farmland, has dropped by one-third in recent years. Arizona recently limited housing construction in the Phoenix area based on projections that groundwater will be unable to meet growing demand.
The University of Arizona has received $4 million for phase one of a project to improve water security and water reuse methods in the arid southwestern United States. Phase two will be awarded an ...
Media Tip Sheet: Ecology of the Pacific Northwest and the Cascadia Bioregion
2023-07-14
Dozens of sessions at the Ecological Society of America’s upcoming Annual Meeting in Portland, Oregon, Aug. 6-11, will feature research on the ecology of the geographic and environmental region surrounding the conference venue: the Pacific Northwest and Cascadia Bioregion, which encompass a vast area stretching from northern California to southern Alaska.
The Pacific Northwest’s temperate rainforests are home to old-growth conifers and multiple threatened and endangered species. Its diverse marine and coastal environments host whales, puffins and vibrant kelp forests. The annual salmon runs in the region’s ...
Researchers’ sweeping discovery shows how kidney cells self-renew
2023-07-13
University of Texas at Dallas scientists have discovered a previously unknown “housekeeping” process in kidney cells that ejects unwanted content, resulting in cells that rejuvenate themselves and remain functioning and healthy.
The self-renewal process, which is fundamentally different from how other bodily tissues are thought to regenerate, helps explain how, barring injury or disease, the kidneys can remain healthy for a lifetime. The researchers described the mechanism in a study published April 17 in Nature Nanotechnology.
Unlike ...
Rensselaer researcher receives grant to study enzymes in deep sea organisms
2023-07-13
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Catherine Royer, Constellation Chair Professor of Bioinformatics and Biocomputation at the Shirley Ann Jackson, Ph.D. Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies (CBIS) and professor of biological sciences, has received a grant of over $400,000 from the National Science Foundation to investigate enzymes from organisms living in deep sea environments.
“Ultimately, I hope to better understand how these enzymes function under the high pressure that is present in the deep sea,” said Royer. “They also thrive in high or low temperatures. Biomolecules from the surface do not have the ability to survive these extreme ...
Penn State researchers receive $1M NSF award to develop hemp-based supply chain
2023-07-13
MIDDLETOWN, Pa. — An interdisciplinary team of researchers at Penn State is part of a project that recently received a $1 million National Science Foundation (NSF) Engines Development Award. The award will fund the development of the Pennsylvania Industrial Hemp Engine (PAIHE), which will support the manufacture and deployment of bio-based products for application in green building construction, packaging, fabrics, renewable energy and land remediation.
Launched by NSF’s new Directorate for Technology, Innovation ...
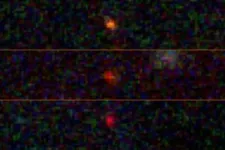
James Webb Telescope catches glimpse of possible first-ever ‘dark stars’
2023-07-13
Stars beam brightly out of the darkness of space thanks to fusion, atoms melding together and releasing energy. But what if there’s another way to power a star?
A team of three astrophysicists — Katherine Freese at The University of Texas at Austin, in collaboration with Cosmin Ilie and Jillian Paulin ’23 at Colgate University — analyzed images from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and found three bright objects that might be “dark stars,” theoretical objects much bigger and brighter than our sun, powered by particles of dark matter annihilating. If confirmed, dark stars could reveal the nature ...
Multidisciplinary team reduced hypothermia in NICU babies during and after surgery
2023-07-13
The percentage of infants from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) experiencing hypothermia upon operating room (OR) arrival and at any point during the operation decreased from 48.7% to 6.4% and 67.5% to 37.4%, respectively, after implementation of a multidisciplinary quality improvement project at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago. The project and its success were featured in the journal Pediatric Quality and Safety.
About one-third of infants admitted to children’s hospitals’ NICUs require surgery and ...
Argonne engineers to drive innovation with three GAIN funding awards
2023-07-13
Argonne is shaping the future of clean and reliable energy solutions.
Research into nuclear energy is gaining attention as a critical piece of the solution to climate change. As part of this trend, nuclear engineers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have received three new funding awards from the Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) initiative. These awards recognize the valuable contributions of Argonne’s world-class nuclear engineers and facilities in this field.
Among ...