Our favorite vintages and their precarious mountainside homes are at risk due to climate change, environmental scientists warn
2023-07-14
(Press-News.org) Tucked into the hillsides of Italy, Portugal, and Spain, some of the world’s most famous—and most difficult to maintain—vineyards are heralded for their unique flavor profiles and centuries of tradition. But as extreme weather and changing socioeconomic conditions make this so-called “heroic viticulture” even more challenging, scientists worry these grapes and their cultural histories are at risk. In a Backstory publishing on July 14 in the journal iScience, researchers argue that farmers and scientists must work together to protect some of the world’s most celebrated wines.
“The risk is not only losing an agricultural product or seeing a landscape change, negatively impacting the local economy,” write the authors from the University of Padova. “The risk is losing entire communities' history and their cultural roots.”
Vineyards are considered “heroic viticulture” sites if they have a slope steeper than 30 percent, are located on small islands or at an altitude higher than 500 meters above sea level, or if they incorporate vines grown on terraces. The name “heroic” originated from the inherent difficulty of cultivating and harvesting crops in these landscapes. Some of the most famous, centuries-old examples of heroic viticulture include the Prosecco Hills of Conegliano and Valdobbiadene and the traditional vineyards of Pantelleria Island, both of which are protected by UNESCO.
“The great effort required to manage these areas reinforces the specific human-environment connection,” write the authors. “This is why they are recognized as cultural uniquenesses of primary historical and social importance, where traditional knowledge is still the determining element.”
In the Backstory, the authors list soil degradation and drought as the biggest climate change-related risks to heroic viticulture. They also argue that the vineyards face several significant socioeconomic barriers.
“The last half past century has been characterized by rural exodus and a gradual abandonment of mountain landscapes,” the authors write. “The new generation is unwilling to continue working under extreme conditions if economic benefits are insignificant.”
In order to protect heroic viticulture sites, the authors suggest several forms of potential solutions, from strategic communications designed to unite scientists, farmers, and consumers to onsite solutions like small water storage systems integrated into the vineyard landscapes that prevent runoff and retain water for future usage. They also underline the importance of education, including “educating the new generation about the benefits of rural reality, the need to preserve cultural heritage, live in equilibrium with the environment, and to have a sustainable approach to agriculture.”
“The key to success lies in combining the traditional knowledge of winemakers with innovation and scientific rigor,” write the authors. “In this way, farms can work closely with scientists to optimize investments for a more functional, sustainable, and safe agricultural landscape—a winning alliance to face these diverse natural and anthropogenic challenges.”
###
iScience, Tarolli et al. “Heroic viticulture: Environmental and socioeconomic challenges of unique heritage landscapes” https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(23)01202-6
iScience (@iScience_CP) is an open-access journal from Cell Press that provides a platform for original research and interdisciplinary thinking in the life, physical, and earth sciences. The primary criterion for publication in iScience is a significant contribution to a relevant field combined with robust results and underlying methodology. Visit: http://www.cell.com/iscience. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-14
In the animal world, you don't need to learn a numeral system – such as the ten-digit Indo-Arabic system we commonly use – to be able to count. Animals constantly use numerical information from their environment to make decisions. Estimating the number of conspecifics in a competing group before engaging in conflict, the amount of food available in a difficult-to-reach location, or the number of potential sexual partners in a new territory is essential for survival and reproduction. This skill can reach an astonishing level of refinement; for example, certain species of ants orient themselves ...
2023-07-14
About The Study: In this secondary analysis of an 18-month randomized trial that included 135 older adults, meditation and non-native language training did not confer salutary cognitive effects. Although further analyses are needed to explore the effects of these interventions on other relevant outcomes related to aging and well-being, these findings did not support the use of these interventions for enhancing cognition in cognitively healthy older adults.
Authors: Natalie L. Marchant, Ph.D., of University College London, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.17848)
Editor’s ...
2023-07-14
About The Study: This nationwide cross-sectional study demonstrated that residing in a highly segregated neighborhood was associated with a statistically significantly lower life expectancy by four years, which was partially mediated by neighborhood-level socioeconomic factors. These findings help to quantify the contribution of residential segregation as a key structural driver of racial inequities.
Authors: Sadiya S. Khan, M.D., M.Sc., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1805)
Editor’s ...
2023-07-14
About The Study: In this study of 10,000 older individuals in Australia, more frequent participation in adult literacy activities (taking education classes, using a computer, and writing letters or journals) and in active mental activities (playing games, cards, or chess and doing crosswords or puzzles) was associated with reduced dementia risk over 10 years. However, social outings and interactions were not associated with dementia risk.
Authors: Joanne Ryan, Ph.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is ...
2023-07-14
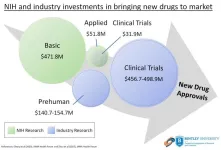
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) contributed $8.1 billion in project funding for phased clinical trials involving drugs approved by the FDA from 2010-2019, according to a new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry. The study, published in JAMA Health Forum, shows that NIH funding for clinical trials represents <3.5% of total NIH spending for basic or applied research related to these products and was significantly less than reported industry spending on clinical development. ...
2023-07-14
The electric grids of the future will need to handle much bigger loads due to electrification of transportation and other sectors. This could mean expensive infrastructure upgrades to ensure their reliable operation, but a new study from Stanford University says most of those upgrades may be unnecessary.
Better grid reliability could be achieved instead by installing software in homes and businesses that coordinates various consumer demands and resources. Such coordination not only improves reliability of the electric grid, but also ...
2023-07-14
Over the past two decades, conditional cash transfer programmes have led to a 24% reduction in child mortality in Brazil, Mexico and Ecuador, equivalent to more than 700,000 child deaths averted, according to an impact evaluation study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The results, published in JAMA Network Open, also show that expanding these programmes could save more than 150,ooo lives by mitigating the effects of the ...
2023-07-14
New nationwide study is first to examine implications of racial segregation on life expectancy by neighborhood
Findings quantify how neighborhood segregation contributes to racial inequities in life expectancy
Black residents living in heavily segregated areas experienced higher rates of poverty and unemployment and less education
CHICAGO --- Black residents living in highly segregated neighborhoods have significantly shortened life expectancies, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Compared to residents living in less segregated predominantly ...
2023-07-14
Antibodies are crucial, not only for treating tumors and infections. Sometimes, however, the immune reaction they trigger can be too strong and end up causing more damage, for example in the case of people infected with Covid-19. Problems such as these can often be avoided by finetuning antibodies, as Prof. Dr. Falk Nimmerjahn from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and two of his colleagues in the Netherlands and in the UK have now reported in the journal Nature Immunology.
In his laboratories, the FAU researcher is carrying out research into immunoglobulin ...
2023-07-14
The real-time monitoring of facilities, particularly large facilities (such as rail transit systems, large bridges, and buildings), can provide information regarding their surrounding environment and allow their health conditions to be assessed, which is essential for establishing the current concept of smart cities based on the Internet of Things. As a precise real-time monitoring technique, distributed fiber-optic sensing (DFOS) systems, which require long-distance simultaneous measurements along a sensing fiber, are in high demand for various industrial applications. However, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Our favorite vintages and their precarious mountainside homes are at risk due to climate change, environmental scientists warn