(Press-News.org) As necessary as cooling technologies are, we’re still operating on an outdated technology that can be considered a significant contributor to global warming and greenhouse gas emissions. Currently, vapor compression cycle-based cooling (VCC) is the standard for reliable cooling of air conditioning and refrigeration, but by switching to electrocaloric cooling (EC) researchers are hoping to create a more environmentally friendly, scalable and compressor-free method of cooling to benefit businesses, families and the environment.
The researchers published their work in iEnergy on June 29. The study highlights the electrocaloric effect (ECE) and how it can work to produce a cleaner, high-efficiency way of cooling without all of the harmful greenhouse gas emissions that a standard VCC process would add to the atmosphere.
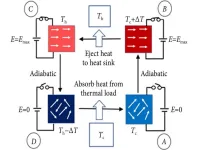
The ECE can be explained as a reversible change of a dielectric material when it’s been exposed to a controlled change in the applied electric field. A dielectric material, like ceramic which is used in this study, poorly conducts electricity but supports electrostatic fields, which is the catalyst for changing the polarization, or charge, of a field to induce the desired results of cooling. The reversible nature of this change allows for heat distribution and cooling to occur.
In order to have a large ECE the change in entropy needs to be sufficiently large, too. Entropy can be quantified as thermal energy that is ready to be made useful by converting it into mechanical work. This is where ferroelectric materials become advantageous to use. To have a high-efficiency product, the desired “operating window” where the largest change in the electrostatic field can be achieved, is just above the ferroelectric-paraelectric phase transition. Essentially, this transition phase consists of two oppositely “charged” polarized fields, yielding the large change in entropy, or disorder, needed.
“These EC materials and device research reveals the promise of ferroelectric materials in generating giant ECE at low electric fields and EC cooling devices achieving high performance,” said Q.M. Zhang, first author and researcher of the study.
Simply put, the EC material used is heated past the temperature of the heat sink, and when the two materials make contact, a temperature equilibrium is reached; this is achieved by putting the energy into the field around the objects, not the objects themselves. By using ferroelectric materials a large ECE can be seen under relatively low electric fields which can achieve a compressor-free system, lending to a cooling device that can be much more scalable to meet the needs of families and businesses alike.
“The electrocaloric cooling is attractive as an alternative to the VCC cooling. EC cooling is environmentally benign, compressor-free, highly scalable, and has the potential of achieving higher efficiency than VCC cooling” Zhang said.
While EC cooling is still being developed and researched as a practical way of cooling, a large portion of work that can be done on the EC coolers is developing lead-free materials, as currently the best-performing EC ceramics are lead-based. The lead-based ferroelectrics generate a higher amount of cooling in a shorter amount of time, but lead is a toxic substance, and generally, its use will not be well received by the public.
Another goal is to improve the thermal conductivity of the EC coolers. Since using lead isn’t the optimal choice, the performance of the ferroelectric component ideally would be improved to reduce heat loss and increase operating power. Achieving these goals and developing EC coolers that can be utilized in commercial and residential areas might aid in the global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and move forward with cleaner cooling technology.
Xin Chen of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Materials Research Institute at Pennsylvania State University, Wenyi Zhu and Q.M. Zhang of the Materials Research Institute and Department of Electrical Engineering at Pennsylvania State University contribute to this research.
The U.S. Office of Naval Research supported this research.
##
About iEnergy
iEnergy (Published by Tsinghua University Press), has multiple meanings, intelligent energy, innovation for energy, internet of energy, and electrical energy due to “i” is the symbol of current. iEnergy, publishing quarterly, is a cross disciplinary journal aimed at disseminating frontiers of technologies and solutions of power and energy. The journal publishes original research on exploring all aspects of power and energy, including any kind of technologies and applications from power generation, transmission, distribution, to conversion, utilization, and storage. iEnergy provides a platform for delivering cutting-edge advancements of sciences and technologies for the future-generation power and energy systems.
About Tsinghua University Press
Established in 1980, belonging to Tsinghua University, Tsinghua University Press (TUP) is a leading comprehensive higher education and professional publisher in China. Committed to building a top-level global cultural brand, after 42 years of development, TUP has established an outstanding managerial system and enterprise structure, and delivered multimedia and multi-dimensional publications covering books, audio, video, electronic products, journals and digital publications. In addition, TUP actively carries out its strategic transformation from educational publishing to content development and service for teaching & learning and was named First-class National Publisher for achieving remarkable results.
END
(Toronto July 19, 2023) Fully open access publisher JMIR Publications has acquired the Online Journal of Public Health Informatics (OJPHI), expanding its portfolio to 35 gold open access journals. This acquisition marks an open access milestone in JMIR Publications’ continued mission to keep openness at the heart of what it does.
Indexed in PubMed Central, OJPHI has been delivering the latest developments in the emerging field of public health informatics since 2009. The journal publishes research articles, book reviews, technology reviews, working papers, interviews, commentaries, and handpicked student capstone projects.
All ...
JMIR Medical Education (2023 Impact Factor 5.2) and Guest Editors: Amir Tal, PhD, and Oren Asman, LLD welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Responsible Design, Integration, and Use of Generative AI in Mental Health"
This special theme issue aims to unite various stakeholders in exploring the responsible use of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) within the mental health domain. The goal is to curate a collection of articles that examine the advantages, challenges, and potential risks associated with deploying GAI models ...
Prof Sei-ichi Tsujimura of the Nagoya City University and Prof Su-Ling Yeh of National Taiwan University and Kagoshima University, have discovered that our visual acuity (contrast sensitivity) can be improved by using a light with a special spectrum that can selectively stimulate melanopsin cells in the retina.
Background
The retina of our eye contains cone photoreceptor cells, which identify colors in bright environment, and rod photoreceptor cells, which work in the dark. It has long been thought that humans see and identify objects by these two types of photoreceptor cells alone. ...
Intermittent rivers and ephemeral streams are the world's dominant river ecosystem, yet monitoring and management typically focus on rivers that flow year round. Writing in BioScience, Amélie Truchy of the French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food, and the Environment (INRAE) and colleagues describe the problem, as well as a potential solution: citizen science.
The authors discuss the results from a new app, DRYRivERS, which allows scientist and nonscientist users alike to record data on ephemeral streams and intermittent ...
For millions of Americans who have heart surgery or experience cardiovascular complications, like heart attack or heart failure, they may be encouraged to participate in cardiac rehabilitation. The medically supervised program combines lifestyle changes, education and physical activity to help patients recover and reduce their risk of future problems.
A Michigan Medicine study now finds that people who participate in cardiac rehabilitation have a decreased risk of death years after surgery, with a trend towards better outcomes in patients who attend more sessions.
“Time and time again, cardiac rehabilitation has been shown to ...
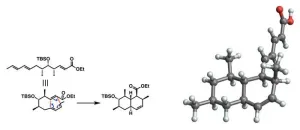
As life expectancy increases worldwide, age-associated diseases such as osteoporosis are having an increasing impact. Although early detection could help physicians intervene as soon as possible — when treatment might offer the greatest benefit — this type of detection is not yet possible with current osteoporosis diagnostic tests. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a biosensor that could someday help identify those most at risk for osteoporosis using less than a drop of blood.
Early intervention is critical to reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with osteoporosis, a condition characterized by an elevated ...
Whether enjoyed on its own or mixed into a latte, Americano or even a martini, espresso provides an ultra-concentrated jolt of caffeine to coffee lovers. But it might do more than just wake you up. Research now published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows that, in preliminary in vitro laboratory tests, espresso compounds can inhibit tau protein aggregation — a process that is believed to be involved in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Roughly half of all Americans drink coffee every day, and espresso is a popular way to consume ...
Almost everyone has a bag of veggies shoved into the dark recesses of their freezer that’s now essentially an unrecognizable block of ice crystals. And when thawed, foods damaged by excessive ice lose their texture and become mushy. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have shown that broken-down soy proteins can prevent ice crystal growth and could be especially useful for preserving frozen vegan foods or biological samples.
Some animals that ...
The discovery of antibiotics in 1928 was a major turning point in the history of medicine. For the first time since the dawn of human civilization, doctors had gained access to an extremely powerful and effective tool to fight against a wide variety of bacterial infections. Today, bacterial diseases that were previously a death sentence can be cured, and infections following surgery or chemotherapy can be prevented or treated more effectively.
Unfortunately, the worldwide use (and abuse) of antibiotics led to the emergence of drug-resistant bacterial strains. Over time, bacteria that could normally be killed by ...
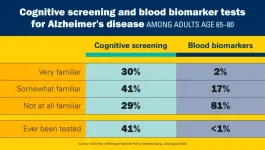
Eighty percent of older adults see the benefit of tests that can give an early warning that a person’s memory and thinking abilities have started to decline, a new poll of people age 65 to 80 finds. And 60% think that health care providers should offer cognitive screening, in the form of brief memory tests, to all older adults every year.
If they had a cognitive screening test and it showed signs of trouble, the vast majority of those polled said it would spur them to take action to protect their brain health (96%) and adjust their financial and health ...