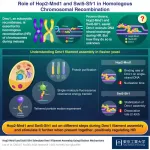
Unraveling the molecular basis of Dmc1 filament assembly in homologous recombination
2023-07-19
(Press-News.org)
Homologous recombination (HR) is an important process that plays multiple crucial roles during meiosis, a type of cell cycle dedicated to sexual reproduction. During HR, homologous DNA molecules exchange their genetic material. During the meiotic prophase, DNA are clipped throughout the genome, forming numerous DNA double-strand breaks. Such DNA breaks attract homologous recombination enzymes, which promote pairing of homologous chromosomes.
Dmc1 is one such meiosis-specific recombinase in eukaryotes (organisms that have a clearly defined nucleus), which along with the general recombinase Rad51, binds to the ssDNA regions formed at the end of broken DNA and facilitates the process of HR. Both Dmc1 and Rad51 preferentially bind ssDNA to form a helical filament structure called presynaptic filament. Critical for its efficient functioning, Swi5-Sfr1 and Hop2-Mnd1 are two accessory factors that help in assembling the Dmc1 filaments on ssDNA. While previous studies have shown that Swi5-Sfr1 and Hop2-Mnd1 make important contributions to the Dmc1-driven strand exchange during HR, the mechanisms underlying their molecular contributions have remained elusive.
Shedding light on their molecular functions, a research team led by Assistant Professor Hideo Tsubouchi from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan, and Professor Hung-Wen Li of the National Taiwan University, Taiwan, now reveal how the proteins Swi5-Sfr1 and Hop2-Mnd1 regulate Dmc1 filament assembly. Using single-molecule experiments, they performed this study with proteins from Schizosaccharomyces pombe, a fission yeast species used as a model organism. Their work was published in Nucleic Acids Research journal on 3 July, 2023.
To this end, the researchers first purified Dmc1, Hop2-Mnd1, and Swi5-Sfr1 from S. pombe. They then subjected these proteins to a specialized technique called single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer, which uses a laser beam and DNA substrates labeled with fluorescent chemicals to detect interactions between Dmc1 and DNA. Further, the researchers also conducted tethered particle motion experiments (to observe changes in the shape and configuration of polymers like DNA) to visualize the Dmc1 filament assembly in real time.
Based on these results, the researchers noted that both Swi5-Sfr1 and Hop2-Mnd1 promote the assembly of Dmc1 filament on ssDNA, but in two different ways. Hop2-Mnd1 binds to double/single-strand DNA junctions and initiates the binding of Dmc1 to itself. Swi5-Sfr1 binds to the assembled Dmc1 filament and prevents dissociation of Dmc1 from the presynaptic filament. Thus, they observed that the combination of these two factors contributes to efficient and stable Dmc1 filament formation.
In summary, these findings provide important insights into the mechanisms underlying Dmc1 filament assembly and functioning of its accessory proteins. Going ahead, this could contribute to advancing our understanding of HR in meiosis, a crucial biological phenomenon in eukaryotic reproduction. Although the proteins studied in this paper are from fission yeast, they are widely conserved throughout eukaryotes including humans. Given that homologous recombination is essential for faithful segregation of chromosomes during meiosis, the results obtained in this study are likely relevant to understanding human reproductive systems. They may shed light on understanding the cause of infertility and certain genetic disorders caused by chromosome mis-segregation, such as Down's syndrome.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-19
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are versatile materials composed of interconnected organic molecules held together by covalent bonds. These frameworks can be constructed in two-dimensional or three-dimensional (3D) forms which possess a unique combination of low density, high surface area, and easily tunable properties. Among the various types of COFs, imine-linked COFs have garnered considerable attention owing to their exceptional thermal and chemical stability as well as their broad scope of monomeric starting materials.
However, traditional bulk synthetic methods for COFs often yield powders that are insoluble ...
2023-07-19
As necessary as cooling technologies are, we’re still operating on an outdated technology that can be considered a significant contributor to global warming and greenhouse gas emissions. Currently, vapor compression cycle-based cooling (VCC) is the standard for reliable cooling of air conditioning and refrigeration, but by switching to electrocaloric cooling (EC) researchers are hoping to create a more environmentally friendly, scalable and compressor-free method of cooling to benefit businesses, families and the environment.
The researchers published their work in iEnergy on ...
2023-07-19
(Toronto July 19, 2023) Fully open access publisher JMIR Publications has acquired the Online Journal of Public Health Informatics (OJPHI), expanding its portfolio to 35 gold open access journals. This acquisition marks an open access milestone in JMIR Publications’ continued mission to keep openness at the heart of what it does.
Indexed in PubMed Central, OJPHI has been delivering the latest developments in the emerging field of public health informatics since 2009. The journal publishes research articles, book reviews, technology reviews, working papers, interviews, commentaries, and handpicked student capstone projects.
All ...
2023-07-19
JMIR Medical Education (2023 Impact Factor 5.2) and Guest Editors: Amir Tal, PhD, and Oren Asman, LLD welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Responsible Design, Integration, and Use of Generative AI in Mental Health"
This special theme issue aims to unite various stakeholders in exploring the responsible use of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) within the mental health domain. The goal is to curate a collection of articles that examine the advantages, challenges, and potential risks associated with deploying GAI models ...
2023-07-19
Prof Sei-ichi Tsujimura of the Nagoya City University and Prof Su-Ling Yeh of National Taiwan University and Kagoshima University, have discovered that our visual acuity (contrast sensitivity) can be improved by using a light with a special spectrum that can selectively stimulate melanopsin cells in the retina.
Background
The retina of our eye contains cone photoreceptor cells, which identify colors in bright environment, and rod photoreceptor cells, which work in the dark. It has long been thought that humans see and identify objects by these two types of photoreceptor cells alone. ...
2023-07-19
Intermittent rivers and ephemeral streams are the world's dominant river ecosystem, yet monitoring and management typically focus on rivers that flow year round. Writing in BioScience, Amélie Truchy of the French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food, and the Environment (INRAE) and colleagues describe the problem, as well as a potential solution: citizen science.
The authors discuss the results from a new app, DRYRivERS, which allows scientist and nonscientist users alike to record data on ephemeral streams and intermittent ...
2023-07-19
For millions of Americans who have heart surgery or experience cardiovascular complications, like heart attack or heart failure, they may be encouraged to participate in cardiac rehabilitation. The medically supervised program combines lifestyle changes, education and physical activity to help patients recover and reduce their risk of future problems.
A Michigan Medicine study now finds that people who participate in cardiac rehabilitation have a decreased risk of death years after surgery, with a trend towards better outcomes in patients who attend more sessions.
“Time and time again, cardiac rehabilitation has been shown to ...
2023-07-19
As life expectancy increases worldwide, age-associated diseases such as osteoporosis are having an increasing impact. Although early detection could help physicians intervene as soon as possible — when treatment might offer the greatest benefit — this type of detection is not yet possible with current osteoporosis diagnostic tests. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a biosensor that could someday help identify those most at risk for osteoporosis using less than a drop of blood.
Early intervention is critical to reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with osteoporosis, a condition characterized by an elevated ...
2023-07-19
Whether enjoyed on its own or mixed into a latte, Americano or even a martini, espresso provides an ultra-concentrated jolt of caffeine to coffee lovers. But it might do more than just wake you up. Research now published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows that, in preliminary in vitro laboratory tests, espresso compounds can inhibit tau protein aggregation — a process that is believed to be involved in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Roughly half of all Americans drink coffee every day, and espresso is a popular way to consume ...
2023-07-19
Almost everyone has a bag of veggies shoved into the dark recesses of their freezer that’s now essentially an unrecognizable block of ice crystals. And when thawed, foods damaged by excessive ice lose their texture and become mushy. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have shown that broken-down soy proteins can prevent ice crystal growth and could be especially useful for preserving frozen vegan foods or biological samples.
Some animals that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Unraveling the molecular basis of Dmc1 filament assembly in homologous recombination