(Press-News.org)
“This evidence strengthens the relevance of the findings by Pietrobono et al., shedding light on the potential application of SMO inhibitors in concert with BRD4 inhibitors.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 19, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 26, 2023, entitled, “Combined targeting of HEDGEHOG signaling and BRD4 as a novel therapeutic option against melanoma.”
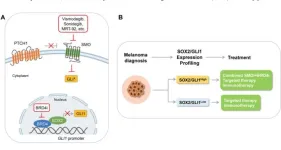
The Hedgehog-GLI (HH/GLI) pathway is aberrantly activated in several types of cancer. Canonical HH/ GLI pathway is triggered by binding of HH ligands to the twelve-pass transmembrane receptor Patched 1 (PTCH1), which retrieves its inhibition on the seven-pass transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor Smoothened (SMO), leading to the activation of the GLI transcription factors. Small molecules inhibitors targeting the essential pathway transducer SMO (e.g., vismodegib, sonidegib) have demonstrated therapeutic efficacy in HH-dependent tumors, such as basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and medulloblastoma (MB).
However, the therapeutic efficacy of these SMO antagonists is limited by the development of acquired resistance and recurrence after drug withdrawal, and by additional oncogenic signals responsible for noncanonical activation of GLI transcription factors [1]. In this new editorial, researchers Silvia Pietrobono and Barbara Stecca from the University of Verona and the Institute for Cancer Research and Prevention (CRL-ISPRO) state that they subscribe to the idea that targeting non-canonical HH/GLI signaling will improve the response rate and durability of therapeutic effects exerted by SMO inhibition. Therefore, they propose that the identification of novel targetable regulators that function downstream of SMO, especially those acting at the transcriptional level, is of critical importance to effectively inhibit the HH pathway and prevent tumor relapse.
“Collectively, the findings presented by Pietrobono et al. pave the path for the development of a novel therapeutic strategy in tumors having both canonical and non-canonical HH/GLI signaling activation, such as melanoma.”
Read the full editorial: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28441
Correspondence to: Silvia Pietrobono, Barbara Stecca
Emails: silvia.pietrobono@univr.it, b.stecca@ispro.toscana.it
Keywords: melanoma, hedgehog signaling, BRD4, SOX2, GLI1
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28441
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
A study of data from about 500,000 people in the UK Biobank has uncovered small but statistically significant associations between signs of systemic inflammation and later risk of dementia. Dr. Krisztina Mekli of The University of Manchester, UK, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 19, 2023.
Millions of people around the world have Alzheimer’s disease or other types of dementia, and researchers are working to tease out the complex mechanisms behind these conditions. Prior research has suggested that inflammation—activation of the body’s innate immune system—may ...
Women working as STEM instructors are more likely than men in the same profession to disclose to their undergraduate students identities which could carry stigma, such as depression or growing up in a low-income household. In the new study, published July 19, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, Carly Busch of Arizona State University, USA, and colleagues suggest that these decisions to disclose may be in order to act as role models for students.
Concealable stigmatized identities (CSIs) are identities that ...
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283134
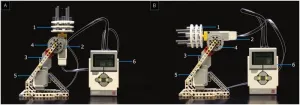
Article Title: Gradient-mixing LEGO robots for purifying DNA origami nanostructures of multiple components by rate-zonal centrifugation
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The research in Hariadi lab was supported by the National Institutes of Health Director’s New Innovator Award (1DP2AI144247), National Science Foundation SemiSynBio II (2027215), and Arizona Biomedical Research Consortium (ADHS17-00007401). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. END ...
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287719
Article Title: A double-pointed wooden throwing stick from Schöningen, Germany: Results and new insights from a multianalytical study
Author Countries: UK, Germany
Funding: T.T. and this project are funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – project number 447423357. https://www.dfg.de/. The project is further funded by the Lower Saxony Ministry for Science and Culture, with funds from the Future Lower Saxony Programme of the Volkswagen Foundation – project ...
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285372
Article Title: Ear health and quality of life in pet rabbits of differing ear conformations: A UK survey of owner-reported signalment risk factors and effects on rabbit welfare and behaviour
Author Countries: UK
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. M.R.D.K included some of this questionnaire in part-fulfilment of her Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine at Royal Veterinary College. ...
Philadelphia, July 19, 2023—Why do nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) exacerbate gastrointestinal infections by Clostridioides difficile, the leading cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea worldwide? In a new paperpublished in Science Advances, researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have begun to answer that question, showing that NSAIDs disrupt the mitochondria of cells lining the colon, sensitizing them to damage by pathogenic toxins.
Clostridioides ...
A 300,000-year-old hunting weapon has shone a new light on early humans as woodworking masters, according to a new study.
State-of-the-art analysis of a double-pointed wooden throwing stick, found in Schöningen in Germany three decades ago, shows it was scraped, seasoned and sanded before being used to kill animals. The research indicates early humans’ woodworking techniques were more developed and sophisticated than previously understood.
The findings, published today (Wednesday, 19 July) in PLOS ONE, also suggest the ...
· Contacts between lysosomes and mitochondria are broken due to Parkinson’s mutation
· Lysosomes cannot ‘feed’ mitochondria with essential metabolites
CHICAGO --- Northwestern Medicine scientists have uncovered a new mechanism by which mutations in a gene parkin contribute to familial forms of Parkinson's disease. The discovery opens a new avenue for Parkinson’s therapeutics, scientists report in a new study.
The Northwestern scientists discovered that mutations in parkin result in a breakdown ...
A research group in Carnegie Mellon University's Robotics Institute is creating the next generation of explorers — robots.
The Autonomous Exploration Research Team has developed a suite of robotic systems and planners enabling robots to explore more quickly, probe the darkest corners of unknown environments, and create more accurate and detailed maps. The systems allow robots to do all this autonomously, finding their way and creating a map without human intervention.
"You can set it in any environment, like a department store or a residential building after a disaster, and off it goes," ...
What determines whether we become overweight? Aside from lifestyle, predisposition plays a role, but genes cannot fully explain the inherited propensity to accumulate excess weight. A new study by Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Science Translational Medicine* shows that a kind of formatting of the DNA code in one gene that is associated with satiety is implicated in a slightly elevated risk of excess body weight – at least in women. This “epigenetic marking” is established early on during the embryonic stage.
People who are overweight, especially those who ...