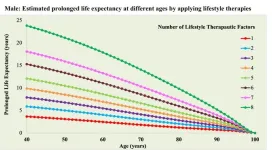
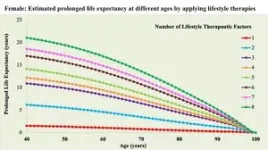
(Press-News.org) A new study involving over 700,000 U.S. veterans reports that people who adopt eight healthy lifestyle habits by middle age can expect to live substantially longer than those with few or none of these habits. The eight habits are: being physically active, being free from opioid addiction, not smoking, managing stress, having a good diet, not regularly binge drinking, having good sleep hygiene, and having positive social relationships.
According to the results, men who have all eight habits at age 40 would be predicted to live an average of 24 years longer than men with none of these habits. For women, having all eight healthy lifestyle factors in middle age was associated with a predicted 21 additional years of life compared to women with none of these habits.
“We were really surprised by just how much could be gained with the adoption of one, two, three, or all eight lifestyle factors,” said Xuan-Mai T. Nguyen, health science specialist at the Department of Veterans Affairs and rising fourth-year medical student at Carle Illinois College of Medicine. “Our research findings suggest that adopting a healthy lifestyle is important for both public health and personal wellness. The earlier the better, but even if you only make a small change in your 40s, 50s, or 60s, it still is beneficial.”
Nguyen will present the findings at NUTRITION 2023, the flagship annual meeting of the American Society for Nutrition held July 22–25 in Boston.
For the study, scientists used data from medical records and questionnaires collected between 2011-2019 from 719,147 people enrolled in the Veterans Affairs Million Veteran Program, a large, nationally representative study of U.S. veterans. The analysis included data from adults age 40-99 and included 33,375 deaths during follow-up.
Overall, the results showed that low physical activity, opioid use, and smoking had the biggest impact on lifespan; these factors were associated with around a 30-45% higher risk of death during the study period. Stress, binge drinking, poor diet, and poor sleep hygiene were each associated with around a 20% increase in the risk of death, and a lack of positive social relationships was associated with a 5% increased risk of death.
According to researchers, the findings underscore the role of lifestyle factors in contributing to chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease that lead to premature disability and death. The results also help to quantify the degree to which making healthy lifestyle choices can help people reduce their risk of such diseases and live longer.
“Lifestyle medicine is aimed at treating the underlying causes of chronic diseases rather than their symptoms,” said Nguyen. “It provides a potential avenue for altering the course of ever-increasing health care costs resulting from prescription medicine and surgical procedures.”
The estimated gain in life expectancy from adopting the eight healthy lifestyle factors grew slightly smaller with age but remained significant, meaning that adopting healthier habits at an older age can still help you live longer. “It is never too late to adopt a healthy lifestyle,” said Nguyen.
As an observational study, the research does not definitively prove causality, Nguyen noted. However, the findings align with a growing body of research supporting the role of lifestyle factors in preventing chronic diseases and promoting healthy aging.
Nguyen will present this research at 8:29 a.m. EDT on Monday, July 24, during the Nutrition-related Factors in Aging and Chronic Disease Poster Theater Flash Session in the Sheraton Boston, Fairfax (abstract; presentation details).
Please note that abstracts presented at NUTRITION 2023 were evaluated and selected by a committee of experts but have not generally undergone the same peer review process required for publication in a scientific journal. As such, the findings presented should be considered preliminary until a peer-reviewed publication is available.
About NUTRITION 2023
NUTRITION 2023 is the flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition and the premier educational event for nutritional professionals around the globe. NUTRITION brings together lab scientists, practicing clinicians, population health researchers, and community intervention investigators to identify solutions to today’s greatest nutrition challenges. Our audience also includes rising leaders in the field – undergraduate, graduate, and medical students. NUTRITION 2023 will be held July 22-25, 2023 in Boston. https://nutrition.org/N23 #Nutrition2023
About the American Society for Nutrition (ASN)
ASN is the preeminent professional organization for nutrition research scientists and clinicians around the world. Founded in 1928, the society brings together the top nutrition researchers, medical practitioners, policy makers and industry leaders to advance our knowledge and application of nutrition. ASN publishes four peer-reviewed journals and provides education and professional development opportunities to advance nutrition research, practice, and education. Since 2018, the American Society of Nutrition has presented NUTRITION, the leading global annual meeting for nutrition professionals. http://www.nutrition.org
Find more news briefs from NUTRITION 2023 at: https://www.eurekalert.org/newsroom/nutrition2023.
###
END
More people are drinking milk alternatives made from plant sources such as oats, soy, or almonds, but do plant-based products deliver the same nutrition as cow’s milk? Results from a new study suggest that most don’t.
Cow’s milk is an important source of calcium and vitamin D, both of which are identified in the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans as nutrients of public health concern for underconsumption. Cow’s milk is also a major source of protein in the American diet.
To assess how the nutritional content of plant-based milk alternatives compares to that of cow’s milk, researchers examined more than ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – When people who publicly reject COVID-19 vaccines later die from the disease, observers have complex reactions to their fates, a new study suggests.
While very few rejoice in the deaths of anti-vaxxers, some people believe those who are dogmatic against vaccines are deserving of worse outcomes – and that reaction is related to the political party affiliation and vaccination status of the person evaluating the anti-vaxxer.
Democrats and those who were vaccinated were more likely than Republicans and the unvaccinated to think anti-vaxxers who died got what they deserved ...
As artificial intelligence expands across more professions, robot preachers and AI programs offer new means of sharing religious beliefs, but they may undermine credibility and reduce donations for religious groups that rely on them, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“It seems like robots take over more occupations every year, but I wouldn’t be so sure that religious leaders will ever be fully automated because religious leaders need credibility, and robots aren’t credible,” said lead researcher Joshua Conrad Jackson, PhD, an assistant professor at the University of ...
July 24, 2023 – Characters with facial disfigurement have long been a recurring theme in films. Their characteristics and outcomes lend insights into perceptions of facial deformities and the effects of plastic surgery, reports a study in The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery under the guidance of Editor-in-Chief Mutaz B. Habal, MD, FRCS, FACS of Tampa, Florida. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Movie characters who undergo successful plastic surgery to improve their facial appearance are more likely to have happy endings, according to the new research by Young Suk Kim, BA, and Kun Hwang, MD, PhD, of Armed Forces ...
A new study suggests that incorporating olive oil into your diet could help reduce the risk of dying from dementia. As many countries face rising rates of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia, the study offers hope that healthy lifestyle factors such as diet can help to prevent or slow the progression of these devastating conditions.
“Our study reinforces dietary guidelines recommending vegetable oils such as olive oil and suggests that these recommendations not only support heart health but potentially brain health, as well,” said Anne-Julie Tessier, RD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Harvard T.H. ...
Researchers report that blood levels of the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) were inversely correlated with hearing difficulty in a new population-based cross-sectional study. Middle-aged and older adults with higher DHA levels were 8-20% less likely to report age-related hearing issues than those with lower DHA levels.
“Higher DHA levels have previously been found to be associated with a lower risk of heart disease, cognitive impairment, and death. Our study extends these findings to suggest a role for DHA in maintaining ...
Losing weight is often a goal for people with type 2 diabetes, which is strongly associated with being overweight or obese. However, it hasn’t been clear what dieting strategy works best for people with this metabolic disorder.
A new randomized controlled study of people with type 2 diabetes showed that study participants who restricted eating to between noon and 8 p.m. daily lost more weight than those who reduced their overall calorie intake by counting calories. Both dieting strategies produced similar improvements in blood sugar levels.
“Many people find counting calories very hard to stick to in the long term, ...
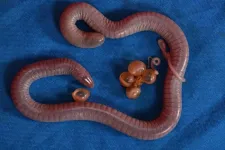
Caecilians are an elusive type of amphibian that primarily live underground and look like a cross between a worm and a snake. One of the few things that is known about caecilians is their unique method for feeding their young. Mothers produce a special layer of fatty skin tissue, which juvenile caecilians tear off with baby teeth that evolved specifically for that purpose.
A new study shows that skin-feeding does more than provide nutrients for young caecilians. It also helps the mother pass microbes from her skin and gut down to her young, inoculating them to jump-start a healthy ...
A technique that uses imaging technology as a guide can make radiation therapy safer for patients with prostate cancer by helping clinicians accurately aim radiation beams at the prostate while avoiding nearby tissue in the bladder, urethra, and rectum. That is the finding of a thorough analysis of all published clinical trials of the technique, called magnetic resonance–guided daily adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy (MRg-A-SBRT). The analysis is published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
By providing detailed images, MRg-A-SBRT can be used to adjust a patient’s radiation plan every ...
Children and adolescents living in food-insecure households had a 55% higher frequency of physician visits for mental health reasons than those with adequate food supplies, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230332.
In 2021, almost 6 million people Canada, including 1.4 million children and adolescents younger than 18 years faced food insecurity; that is, inadequate food intake because of financial problems.
The study looked at population health survey data from the Canadian Community Health Survey on ...