62 percent of young Thai women put off by pap smears | BGI Insight
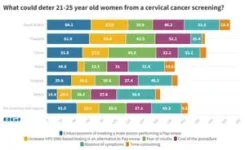
61.6% of Thai women aged 21-25 years deterred by pap smears ranking second globally and is higher than the global average of 43.5%
2023-08-01
(Press-News.org)
Only 28.5% of Thai women are diagnosed at stage I of cervical cancer when survival rates are highest, according to a study published by the Mahidol University. To further motivate action to combat cervical cancer, BGI Genomics released its State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report in Thailand. This report assesses the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination to highlight the associated barriers and opportunities. 1,878 female respondents from six countries and regions were surveyed: Brazil, the Chinese mainland, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Thailand, and Uruguay.
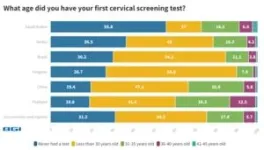
18.8% of Thai women never had a screening test which leads the six countries in this study, far lower than the global average of 32.1%. Yet, 61.6% of young Thai women aged 21 to 25 years old are deterred by meeting a male doctor performing a pap smear, ranking second globally. Therefore, there is an urgent need to offer HPV DNA tests to women, especially young women, in addition to pap smear tests.
Other key takeaways from the report include:
HPV awareness affects cervical cancer screening rates: Among women who are unaware cervical cancer is often caused by HPV, 39.1% of them never undertaken cervical cancer screening which is higher than the global average of 31.2%.
Vaccination and screening form a virtuous cycle: For women who had the HPV vaccine, 82.1% had a cervical cancer screening, significantly higher than 60.6% of unvaccinated women. For women who had undergone screening, 45.8% received the HPV vaccine, which is higher relative to 22.1% of unscreened women. Informing women who missed national vaccination programs about where and when they could get vaccinated and screened is vital.
"Early cervical cancer detection is vital to save lives and eventually eliminate this dreaded disease in line with WHO's global strategy," said Zhang Lin, BGI Genomics Senior Product Manager. "This study shows increased awareness of women could be the missing link to boost vaccination and screening rates further."
To read and view country or region-level comparisons, please see link to access the full BGI Genomics State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report 2023.
About BGI Genomics
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
The CE-certified SENTIS™ HPV test combines self-sampling technology and genotyping assay to detect 14 most important, "high-risk" types of HPV, including HPV -16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68 and 2 "low-risk" types of the virus, HPV -6, 11. The WHO recommends DNA testing as a first-choice screening method for cervical cancer prevention.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-01
Researchers have revealed the unique ‘cheating’ strategy a New Zealand insect has developed to avoid being eaten – mimicking a highly toxic species.
In nature, poisonous species typically advertise their toxicity, often by producing high contrast colours such as black, white and yellow, like wasps and bees.
Along similar lines, New Zealand’s cyanide-producing stonefly, Austroperla cyrene, produces strong ‘warning’ colours of black, white and yellow, to highlight its threat to potential predators.
In a new study published in Molecular Ecology, University of Otago Department of Zoology researchers reveal that an ...
2023-08-01
It’s an elegant solution: Remove the habitat of a parasite-carrying aquatic snail and reduce the level of infection in the local community; all while generating more feed and compost for local farmers.
A collaboration of scientists from the United States and Senegal focused on doing just that by removing overgrown aquatic vegetation from areas upstream of the Diama Dam in northeastern Senegal. In doing so, they generated positive impacts to the local communities’ health and economies.
“It is rare and gratifying when we can find a potential win-win solution to both human health ...
2023-08-01
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time] / 6.30pm [ET] Monday, July 31, 2023**
Peer-reviewed
The Lancet: New study reveals global anemia cases remain ...
2023-08-01
Oat is among the top ten cereal crop species in terms of global production. It can adapt to different climates, and farmers can grow it successfully even in harsh environments where other crops such as rice and corn fail. However, not all oat plants are the same. Based on their grains, two major oak varieties can easily be distinguished: hulled, grains that are covered in a non-edible husk, and naked, grains that have a soft outer casing that easily separates from the edible grain during threshing. To gain information on the origins of these different varieties, researchers in China have sequenced the ...
2023-08-01
With a Fulton County indictment of former President Donald Trump possible at any time, law enforcement in Atlanta is bracing for potential violence, with orange barricades restricting access to the entrance of the county courthouse.
With the anticipation of each new indictment has come threats of violence, decrease in trust in American justice and calls for retribution against the government. Just how concerned should Americans be that we may face another January 6th-type incident?
New data from the Polarization ...
2023-07-31
Sperm play a critical role in the creation of new life, delivering essentially half of the genetic material required.
The success of this process relies on the generation of a developmentally competent sperm cell, which is often determined by shape. Indeed, during in vitro fertilization, the “best-looking” sperm is selected to fertilize an egg.
However, how this optimal shape translates to proper sperm function is difficult to assess because of many confounding factors.
Researchers at the University of Michigan are now delving into the molecular-level details of sperm formation, with a particular focus on how abnormalities in ...
2023-07-31
Technological advancements like autonomous driving and computer vision are driving a surge in demand for computational power. Optical computing, with its high throughput, energy efficiency, and low latency, has garnered considerable attention from academia and industry. However, current optical computing chips face limitations in power consumption and size, which hinders the scalability of optical computing networks.
Thanks to the rise of nonvolatile integrated photonics, optical computing devices can achieve in-memory computing while operating with zero static power consumption. Phase-change materials (PCMs) have emerged as promising candidates for achieving photonic memory and nonvolatile ...
2023-07-31
New research reveals a type of monoclonal antibody already tested in certain forms of cancer may be a promising treatment in stopping the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, a fatal neurodegenerative disease.
The study, led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University, published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, involving a mouse model and confirmed in the tissue of human brains affected by ALS and donated after death, revealed for the first time that modulating immune cells can slow the progression of the disease. Previous research suggested a role for immune cells in ALS, but researchers this time used a high-throughput ...
2023-07-31
A peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of Global Health analyzed data from more than 6,600 families with a child with a neurodevelopmental condition (NDC)—autism, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, developmental language disorder, Down syndrome, Williams syndrome, and intellectual disability—from 70 countries, including the United States.
The study was led by Andrea Samson, associate professor of psychology at UniDistance Suisse and University of Fribourg, Switzerland, and Jo Van Herwegen, professor in developmental psychology and education at University College London’s ...
2023-07-31
“These observations support that accumulation of senescent cells may contribute to fibrotic lung disease [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 14, entitled, “Human senescent fibroblasts trigger progressive lung fibrosis in mice.”
Cell senescence has recently emerged as a potentially relevant pathogenic mechanism in fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (f-ILDs), particularly in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. In a new study, researchers Fernanda Hernandez-Gonzalez, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 62 percent of young Thai women put off by pap smears | BGI Insight
61.6% of Thai women aged 21-25 years deterred by pap smears ranking second globally and is higher than the global average of 43.5%