(Press-News.org) LOGAN, UTAH, USA - When we think of soil, most of us think of dirt on the ground. But a surprising amount of the planet’s soil thrives in the treetops of old-growth forests, high above terra firma.
This organic matter, composed of decaying leaves and branches, airborne particulates and moisture, is called canopy soil or arboreal soil. Its study is relatively new, says Utah State University ecologist Jessica Murray. She’s among researchers unraveling mysteries of the dense, mossy humus that provides rich habitat for insects, birds, fungi, worms and plants, as well as a generous reservoir for carbon storage.
Murray and colleagues from Texas A&M University, the University of Toronto Scarborough and Imperial College London published new information about the enigmatic resource in the July 27, 2023, online edition of Geoderma. The team’s research was supported by USU, the U.S. Department of Agriculture National Institute of Food and Agriculture, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
“In this study, we sought to understand where canopy soils are found, where they are most abundant, and if their properties – and thus, soil development processes – differ as a function of climate or other small-scale factors,” says Murray, a doctoral student in USU’s Department of Biology and Ecology Center. “This is the first study to look at the distribution patterns of canopy soils across forests and one of very few studies that have sought to examine canopy soil properties.”
Murray collected much of the data for the study some 80 feet above the ground at six primary forest sites across Costa Rica’s Cordillera de Tilarán and Cordillera Volcánica Central, encompassing both Caribbean and Pacific slope mountain ranges. Her field gear includes climbing gear, ropes, a safety harness and helmet.
“I climbed about 30 trees to collect data,” she says. “And getting to one of those sites was the hardest hike of my life.”
Murray is referring to a site designated “Puesto 1070,” located along a contiguous tract of primary forest, which required a steep trek from about 1,970 feet in elevation to 3,608 – in thick mud.
“It took eight hours to complete the hike just to the study site,” she says. “We were carrying all of our climbing gear, food for eight days, sleeping bags and sampling equipment. Thank heavens we finished that site early, because, with our hard-earned appetites, we also nearly finished our food supply ahead of schedule.”
Murray says tree canopies in the tropical montane forest systems are especially dense, with thick moss, soil and an abundance of epiphytes – plants that grow on other plants – often referred to as “air plants” – that are not parasitic and have little or no attachment to other obvious nutrient sources.
“It’s like another world in the air – canopies teeming with plant, insect and animal life,” she says. “I initially conducted surveys to assess canopy soil abundance from the ground with binoculars. But it was really necessary to climb up into the trees to get an accurate picture of what was going on.”
Murray asserts forest canopies store much more carbon that generally assumed.
“It’s kind of a back-of-the-envelope calculation on my part, but one I’m ready to defend and eager to investigate further,” she says. “I think canopy soil stores 0.4 to 4 percent of total soil carbon in the forests where it is found, which is not being counted in ecosystem carbon budgets.”
Mentored by USU Biology Professor John Stark and former USU faculty member Bonnie Waring, the latter now with Imperial College London and an author on the paper, Murray says the team’s results indicate both climate and tree size play an important role in canopy soil abundance, carbon stocks and chemistry.
“Climate, particularly fog and temperature changes, appear to drive canopy soil abundance across forests, while tree size determines canopy soil abundance within a forest,” she says. “Our findings reveal canopy soil’s vulnerability to climate change, and its decline, could cause a significant decrease in carbon storage resources.”
Further, she says, those resources could take longer than expected to restore.
“When we talk about reforestation, we don’t stop to consider the time needed for forest regrowth plus canopy mat regrowth,” Murray says. “It may take decades longer for recovered forests destroyed by wildfire or development to regenerate robust canopy soil mats.”
A 2022 recipient of the Ecological Society of America’s Katherine S. McCarter Graduate Student Policy Award, Murray is among a number of Aggies presenting at the ESA’s 2023 Annual Meeting Aug. 6-11, in Portland, Oregon. She presents the talk, “The Persistence of Metabolically Protected vs. Mineral-Associated Soil Organic Carbon in the Presence of Organic Inputs,” Thursday, Aug. 10, at 4:45 p.m., in Room B115 of the Oregon Convention Center.
“For that meeting, I’ll be presenting on research different from, but related to, the study published in Geoderma, including work about the basic mechanisms of soil carbon sequestration that uses canopy soils from my sites in Costa Rica,” she says.
END
In the treetops: USU ecologist studies canopy soil abundance, chemistry
Jessica Murray studies tree canopies in tropical montane forest systems of Costa Rica
2023-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
HSE researchers question the correctness of experiments denying free will
2023-08-04
Neuroscientists from HSE University have criticized the famous studies that question the free will of our decisions. You can’t shift responsibility for your actions to the brain. The results of the new work were published in the Neuropsychologia journal.
The dispute about how much free will people have in making their decisions has been going for decades. Neuroscientists have joined this discussion thanks to the electroencephalographic (EEG) experiments of Benjamin Libet. In the 1970-1980s, he showed that 0.5–1.5 seconds before conscious awareness of the intention to perform a movement, subjects ...
Kordofan giraffes face local extinction if poaching continues
2023-08-04
For immediate release
Friday 4 August 2023
Kordofan giraffes face local extinction if poaching continues
Poaching of two Critically Endangered Kordofan giraffes per year could result in extinction in just 15 years within Cameroon’s Bénoué National Park without intervention. These are the alarming new findings of a University of Bristol and Bristol Zoological Society-led study published in the African Journal of Ecology.
One of the last populations of Kordofan giraffes roam Cameroon's Bénoué ...
Team creates power generator that runs on natural atmospheric humidity
2023-08-04
Scientists are looking for ways to use the low-value energy widely distributed in natural environments to generate electricity. A research team has created a power generator that collects the natural atmospheric humidity and produces continuous electrical signals. This is the first humidity generator designed using a nano-sized material called polyoxometalates. It holds the potential of being a new research direction for polyoxometalates in the sustainable utilization of low-value energy.
The team’s work is published in the journal Nano Research on August 01.
The team set out to solve ...
New deep-learning approach gets to the bottom of colonoscopy
2023-08-04
Researchers have developed a pair of modules that gives a boost to the use of artificial neural networks to identify potentially cancerous growths in colonoscopy imagery, traditionally plagued by image noise resulting from the colonoscopy insertion and rotation process itself.
A paper describing the approach was published in the journal CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research on June 30.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard for detecting colorectal growths or ‘polyps’ in the inner lining of your colon, also known as the large intestine. ...
Influenza shows no seasonality in tropics, posing challenges for health care
2023-08-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In temperate climates, like North America and Europe, flu season starts in the fall, peaks in the winter and ends in the spring. While public health officials have generally assumed that influenza is also seasonal in tropical climates, new research led by Penn State has found little evidence of a repeatable pattern in influenza cases in Vietnam. The findings suggest that influenza is likely unpredictable throughout the tropics, posing substantial challenges for prevention and management of cases for the one-third of the global population living in tropical areas.
“The World ...
Prevalence, risk factors for school-associated transmission of SARS-CoV-2
2023-08-04
About The Study: In this study of Massachusetts schools, the secondary attack rate for SARS-CoV-2 among school-based contacts was low during two periods, and factors associated with transmission risk varied over time. These findings suggest that ongoing surveillance efforts may be essential to ensure that both targeted resources and mitigation practices remain optimal and relevant for disease prevention.
Authors: Sandra B. Nelson, M.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.2310)
Editor’s ...
Racial, ethnic disparities in survival among people with second primary cancer
2023-08-04
About The Study: In this study of 230,000 persons with second primary cancers in the U.S., the Black population had a higher risk of death from both cancer and cardiovascular disease compared with the white population, whereas the Hispanic population had a higher risk of death from cancer. These results suggest that research priorities to address survival disparities in the growing population of survivors of multiple primary cancers are warranted.
Authors: Hyuna Sung, Ph.D., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is ...
New study shows substantial racial and ethnic disparities among survivors of second primary cancers in the US
2023-08-04
ATLANTA, August 4, 2023 — In new findings from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS), non-Hispanic Black individuals diagnosed with a second primary cancer (SPC) experienced 21% higher cancer-related death rates and 41% higher cardiovascular-related death rates compared with their non-Hispanic White counterparts. The study also showed that Hispanic individuals diagnosed with a second primary cancer also experienced 10% higher cancer-related death rates compared with their non-Hispanic White counterparts, but 10% lower cardiovascular-related death rates. The paper was published ...
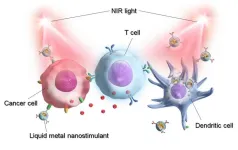
Novel liquid metal nanoparticles for cancer photoimmunotherapy
2023-08-04
Ishikawa, Japan -- Liquid metals (LM) such as pure gallium (Ga) and Ga-based alloys are a new class of materials with unique physicochemical properties. One of the most prominent applications of LMs is photothermal therapy against cancer, in which functional LM nanoparticles convert light energy to heat energy, thus killing cancerous cells. LM-based phototherapy is superior to traditional cancer therapy owing to its high specificity, repeatability, and low side effects.
In a new cutting-edge study, Associate Professor Eijiro Miyako and his colleagues from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) synthesized multifunctional Ga-based nanoparticles that combine cancer ...
Study finds breastfeeding helps mother’s cardio health for 3 years or more
2023-08-04
Breastfeeding for six months or more appears to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems developing in mothers for at least three years after delivery, a new South Australian study has found.
The surprising cardio-metabolic benefit for maternal health is particularly important for women who experienced a complicated pregnancy, which can increase their chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life.
The new results – published this month in the International Breastfeeding Journal by experts from the University of Adelaide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] In the treetops: USU ecologist studies canopy soil abundance, chemistryJessica Murray studies tree canopies in tropical montane forest systems of Costa Rica