Shehu conducting collaborative research on deep learning & experimentation for property-controlled molecule generation
2023-08-07
(Press-News.org)
Amarda Shehu, Associate Vice President of Research, Institute for Digital Innovation (IDIA); Associate Dean for AI Innovation (CEC); Professor, Computer Science, received funding for the project: "Collaborative Research: IIBR: Innovation: Bioinformatics: Linking Chemical and Biological Space: Deep Learning and Experimentation for Property-Controlled Molecule Generation."
This project advances property-controlled molecule generation. A key insight propelling property-controlled molecule generation is that machine learning models need to be situated in biological data and knowledge.
The research activities for this project are organized in three thrusts: (1) developing generalizable and interpretable models capable of incorporating biological constraints, (2) accommodating small, incomplete, and noisy wet-laboratory data, and (3) integrating computation and wet-lab inquiry under an active learning formulation.
The project catalyzes synergistic and innovative work at the interface of machine learning, artificial intelligence, generative artificial intelligence, and the biological sciences to address long-standing challenges in molecular biology—both broadly and specifically on particular classes of molecules. The project additionally addresses small disinfectant antimicrobial compounds, where structural innovation has been sorely lacking and resistant bacteria represent an uncountered threat (quaternary ammonium compounds).
The total award amount is $299,320 and Shehu has received $97,078 from the National Science Foundation for this research for FY24. The intended project duration is Aug. 2023 to July 2026.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls 38,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the last half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity and commitment to accessibility. Learn more at http://www.gmu.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-07
Mary L. Cummings, Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Electrical & Computer, Computer Science, received funding for the project: "Synthesizing temporal logic and human performance models for deception mitigation."
Deception is a key element in attacks on military and civilian cyber-physical systems. With increasing use of automation and autonomy in such systems, such vulnerabilities to deception are growing, with catastrophic outcomes, as evidenced by recent major breaches in cybersecurity across the U.S. Department of Defense.
There is a pressing need to understand long-term adversarial strategies where one hostile action is largely harmless ...
2023-08-07
Antonios Anastasopoulos, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding from the National Science Foundation for: "CCRI: Planning-C: Facilitating Language Technologies for Crisis Response."
This CISE Computing Research Infrastructure (CCRI) planning grant will lay out a concrete path for using language technologies for crisis/disaster response that will be useful for everyone. This requires developing crucial infrastructure to support research toward technological solutions that enable and support communications ...
2023-08-07
· Cardiovascular health and social determinants of health explain racial differences
· Premature babies have more cardiovascular disease as adults
· Being born early is linked to neurodevelopment deficits
CHICAGO --- Non-Hispanic Black individuals have a significantly higher rate of pre-term births than non-Hispanic white individuals, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
In 2019, nearly 12% of non-Hispanic Black individuals experienced preterm births compared with 7% of non-Hispanic white individuals.
“This is important because this ...
2023-08-07
About The Study: Despite guidelines recommending medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD), approximately 1 in 5 adults with past-year opioid use disorder received any MOUD, according to data from a 2021 nationally representative survey. Furthermore, some groups were substantially less likely to receive MOUD, in particular Black adults, women, those unemployed, and those in nonmetropolitan areas. Addressing disparities in MOUD uptake should be prioritized in program, policy, and clinical initiatives.
Authors: Christopher ...
2023-08-07
About The Study: The results of this study of 18.4 million patients in the U.S. with overweight and obesity indicate that the annual probability of 5% or greater weight loss was low (1 in 10) despite the known benefits of clinically meaningful weight loss, but 5% or greater weight loss was more likely than body mass index (BMI) reduction to the healthy weight category, especially for patients with the highest initial BMIs.
Authors: Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To ...
2023-08-07
About The Study: Using a regular blood pressure (BP) cuff size for all individuals regardless of arm size resulted in strikingly inaccurate BP readings with an automated device in this randomized crossover trial including 195 adults. This is particularly concerning for settings where one regular BP cuff size is routinely used in all individuals, regardless of arm size. A renewed emphasis on individualized BP cuff selection is warranted.
Authors: Tammy M. Brady, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3264)
Editor’s ...
2023-08-07
About The Study: This study of 500,000 participants demonstrated that balanced levels of moderate aerobic physical activity, vigorous aerobic physical activity, and muscle strengthening activity combined may be associated with optimal reductions of mortality risk. Higher-than-recommended levels of moderate aerobic physical activity and vigorous aerobic physical activity may further lower the risk of cancer and all-cause mortality, respectively.
Authors: Rubén López-Bueno, Ph.D., of the University of Zaragoza in Zaragoza, Spain, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
2023-08-07
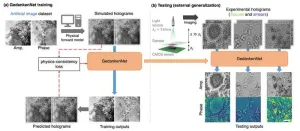
Researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have unveiled an artificial intelligence-based model for computational imaging and microscopy without training with experimental objects or real data.
In a recent paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, UCLA’s Volgenau Professor for Engineering Innovation Aydogan Ozcan and his research team introduced a self-supervised AI model nicknamed GedankenNet that learns from physics laws and thought experiments.
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the imaging process across ...
2023-08-07
Heliconius butterflies are capable of spatial learning, scientists have discovered.
The results provide the first experimental evidence of spatial learning in any butterfly or moth species.
The findings, published today in Current Biology, also suggest Heliconius butterflies may be able to learn spatial information at large scales, consistent with the apparent importance of long-range spatial learning for traplining, which involves foraging within a home range of a few hundred square metres.
Spatial learning is known in insects, but much of the research has focused on ant and bee species which live socially ...
2023-08-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- For a small percentage of cancer patients, doctors are unable to determine where their cancer originated. This makes it much more difficult to choose a treatment for those patients, because many cancer drugs are typically developed for specific cancer types.
A new approach developed by researchers at MIT and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute may make it easier to identify the sites of origin for those enigmatic cancers. Using machine learning, the researchers created a computational model that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Shehu conducting collaborative research on deep learning & experimentation for property-controlled molecule generation