(Press-News.org)
· Cardiovascular health and social determinants of health explain racial differences
· Premature babies have more cardiovascular disease as adults
· Being born early is linked to neurodevelopment deficits
CHICAGO --- Non-Hispanic Black individuals have a significantly higher rate of pre-term births than non-Hispanic white individuals, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
In 2019, nearly 12% of non-Hispanic Black individuals experienced preterm births compared with 7% of non-Hispanic white individuals.
“This is important because this represents a large number of individuals who are being born early every year that have much higher risk for bad health outcomes and is significantly different between non-Hispanic Black and white individuals,” said corresponding author Dr. Sadiya Khan, assistant professor of medicine in cardiology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine cardiologist.
The study found that pre-pregnancy cardiovascular health explained 8% of the racial difference while social determinants of health explained 20% of the racial difference between Black and white pregnant individuals.
This is the first study that helps explain which of the individual-level maternal health factors (obesity, diabetes, hypertension) and socioeconomic factors (insurance, prenatal care, education) can be targeted to improve birth outcomes and how much each contributes to differences in preterm birth.
“Differences that occur when someone is born early can have important implications not just for the first year of life, but also throughout their life,” Khan said. “Being born early is linked to a higher risk of having heart disease and affects neurodevelopment.”
The study will be published Aug. 7 in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
The study included more than 2 million individuals who identified as non-Hispanic white and non-Hispanic Black who had a live birth in 2019. It also utilized data from birth registration records from the National Center for Health Statistics, which collects data on all live births.
“Pre-term birth is the starting point for racial differences across the life course, not just in childhood,” Khan said.
One big problem, she said, is the loss of Medicaid for millions of people in the last three months.
“If you don’t have health insurance when you become pregnant, you are much less likely to get prenatal or cardiovascular care,” Khan said. “Prenatal care in the first trimester is critical to improving birth outcomes.”
Khan said two-thirds of the differences causing pre-term birth weren’t explained by the factors they identified in the study.
“We need to understand the problem so we can fix it,” Khan said. “Understanding racial differences in preterm birth is critical to identifying opportunities for prevention and awareness.”
Other Northwestern authors are Dr. Priya Mehta, Dr. Natalie Cameron, Dr. Priya Freaney, Dr. Amanda Perak, Dr. Nilay Shah, Dr. William Grobman, Dr. Philip Greenland and Kiarri Kershaw.
The paper is titled: “Association of Pre-pregnancy Risk Factors with Racial Differences in Preterm Birth Rates.”
The research was funded by grant HL161514 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health.
[KS1]Maybe “entering”? “Coming into” feels awkward.
END
About The Study: Despite guidelines recommending medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD), approximately 1 in 5 adults with past-year opioid use disorder received any MOUD, according to data from a 2021 nationally representative survey. Furthermore, some groups were substantially less likely to receive MOUD, in particular Black adults, women, those unemployed, and those in nonmetropolitan areas. Addressing disparities in MOUD uptake should be prioritized in program, policy, and clinical initiatives.
Authors: Christopher ...
About The Study: The results of this study of 18.4 million patients in the U.S. with overweight and obesity indicate that the annual probability of 5% or greater weight loss was low (1 in 10) despite the known benefits of clinically meaningful weight loss, but 5% or greater weight loss was more likely than body mass index (BMI) reduction to the healthy weight category, especially for patients with the highest initial BMIs.
Authors: Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To ...
About The Study: Using a regular blood pressure (BP) cuff size for all individuals regardless of arm size resulted in strikingly inaccurate BP readings with an automated device in this randomized crossover trial including 195 adults. This is particularly concerning for settings where one regular BP cuff size is routinely used in all individuals, regardless of arm size. A renewed emphasis on individualized BP cuff selection is warranted.
Authors: Tammy M. Brady, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3264)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: This study of 500,000 participants demonstrated that balanced levels of moderate aerobic physical activity, vigorous aerobic physical activity, and muscle strengthening activity combined may be associated with optimal reductions of mortality risk. Higher-than-recommended levels of moderate aerobic physical activity and vigorous aerobic physical activity may further lower the risk of cancer and all-cause mortality, respectively.
Authors: Rubén López-Bueno, Ph.D., of the University of Zaragoza in Zaragoza, Spain, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
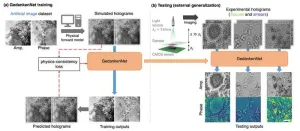
Researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have unveiled an artificial intelligence-based model for computational imaging and microscopy without training with experimental objects or real data.
In a recent paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, UCLA’s Volgenau Professor for Engineering Innovation Aydogan Ozcan and his research team introduced a self-supervised AI model nicknamed GedankenNet that learns from physics laws and thought experiments.
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the imaging process across ...
Heliconius butterflies are capable of spatial learning, scientists have discovered.
The results provide the first experimental evidence of spatial learning in any butterfly or moth species.
The findings, published today in Current Biology, also suggest Heliconius butterflies may be able to learn spatial information at large scales, consistent with the apparent importance of long-range spatial learning for traplining, which involves foraging within a home range of a few hundred square metres.
Spatial learning is known in insects, but much of the research has focused on ant and bee species which live socially ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- For a small percentage of cancer patients, doctors are unable to determine where their cancer originated. This makes it much more difficult to choose a treatment for those patients, because many cancer drugs are typically developed for specific cancer types.
A new approach developed by researchers at MIT and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute may make it easier to identify the sites of origin for those enigmatic cancers. Using machine learning, the researchers created a computational model that ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA The Covid-19 pandemic created a global increase in domestic violence against women. Now, an MIT-led experiment designed with that fact in mind shows that some forms of social media can increase awareness among women about where to find resources and support for addressing domestic violence.
In the randomized experiment, set in Egypt, women recruited via Facebook were sent videos via social media as well as reminders to watch television programming from a well-known Egyptian human rights lawyer focused on gender norms and violence. The study found that receiving the videos or reminders increased consumption of media content about the issue, increased knowledge ...
BOSTON – Researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have created an AI-based tool that uses tumor gene sequencing data to predict the primary source of a patient’s cancer. The study, published in in Nature Medicine, suggests that this predictive tool, called OncoNPC, could help guide treatment of cancer and improve outcomes in difficult to diagnose cases.
The primary source of cancer is traditionally diagnosed by a standardized diagnostic work-up, including radiology and pathology assessments based on slides of cells taken from a tumor biopsy. In 3-5% of cancer ...
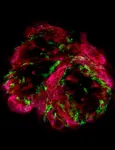
A remarkable breakthrough, a collaborative team of researchers, led by Professor Yaakov Nahmias from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, and Tissue Dynamics Ltd., has unveiled a miniature human heart model that could potentially transform drug testing and cardiovascular research. This study, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, introduces a self-paced multi-chambered human heart model, no larger than a grain of rice, which promises to revolutionize the way we study the heart and its functions.
Cardiovascular ...