(Press-News.org) BOSTON - Researchers have developed a new algorithm for recovering the 3D refractive index distribution of biological samples that exhibit multiple types of light scattering. The algorithm helps optimize a new imaging approach called intensity diffraction tomography (IDT).
Jiabei Zhu from Boston University will present this research at the Optica Imaging Congress. The hybrid meeting will take place 14 – 17 August 2023 in Boston, Massachusetts.
“3D quantitative phase imaging (QPI) has superior features for various applications in the field of biomedical imaging. As a label-free technique, QPI can image transparent living organisms and cells without exogenous contrast agents and dyes which induce phototoxic effects damaging the sample,” explains Zhu. “Compared with traditional phase-contrast and differential interference contrast microscopy, QPI not only provides high-contrast morphological information but gives quantitative phase information as well. Specifically, 3D QPI can provide high-resolution 3D refractive index (RI) distribution inside the samples. This valuable information can facilitate the research on hematology, neurology, and immunology, helping the diagnosis of disease and infection.”
Although 3D imaging techniques can be used to study thick biological samples, achieving both high-speed acquisition and high resolution is challenging. IDT approaches are label-free phase tomography techniques that help overcome this limitation. They can be performed using a programmable LED array that is easily added to a standard microscope.
Zhu’s research team recently developed two IDT methods known as annular IDT (aIDT) and multiplexed IDT (mIDT) that boost the image acquisition speed enough to visualize dynamic biological samples. Annular IDT (aIDT) uses an LED ring that matches the objective’s numerical aperture, and multiplexed IDT (mIDT) uses multiple LEDs to illuminate the sample simultaneously.
When the researchers discovered that existing IDT reconstruction algorithms did not work well with their new approaches due to the use of high-NA objectives, they decided to develop a new algorithm. It uses a multiple scattering model based on the split-step non-paraxial (SSNP) method, which was recently developed to overcome similar limitations in optical diffraction tomography.
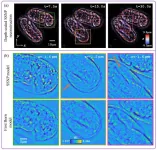
The researchers showed that applying the new IDT reconstruction algorithm to buccal epithelial cells using aIDT allowed easy discrimination of cells at different depths, reconstruction of the cell boundaries and membrane, and visualization of native bacteria around the cells. They also applied it to a thick multi-scattering live C. elegans embryo using mIDT. The resulting reconstructed images showed details of how the worms were folded, and the single-depth cross-section showed the morphological details of the cells’ outline, the buccal cavity and the tail of the worm.
Overall, the experiments showed that by extending the SSNP method to IDT, the researchers were able to achieve high-quality images with a large field of view.
About the Optica Imaging Congress
The 2023 Optica Imaging Congress will provide a comprehensive view of the latest developments in imaging and applied optical sciences, covering the forefront advances in imaging and applied optics as well as the application of these technologies to important industrial, military and medical challenges. Monitor the Imaging Congress for the latest information on conference registration. Media registration is free with credential. Digital assets are available as requested.
About Optica
Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide, is the society dedicated to promoting the generation, application, archiving and dissemination of knowledge in the field. Founded in 1916, it is the leading organization for scientists, engineers, business professionals, students and others interested in the science of light. Optica’s renowned publications, meetings, online resources and in-person activities fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate scientific, technical and educational achievement. Discover more at: Optica.org
Media Contact
mediarelations@optica.org
END
New algorithm captures complex 3D light scattering information from live specimens
Researchers combine algorithm with intensity diffraction tomography to characterize thick biological samples
2023-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advanced magnesium-based hydrogen storage materials and their applications
2023-08-15
As an energy carrier, hydrogen holds the prominent advantages of high gravimetric energy density, high abundance, and zero emission, yet its effective storage and transportation remain a bottleneck problem for the widespread applications of hydrogen energy. To address such an issue, different types of hydrogen storage materials are developed and carefully investigated in the past decades. Among them, magnesium hydride (MgH2) has been considered as one of the most promising hydrogen storage materials because of its high capacity, excellent reversibility, sufficient magnesium reserves, and low cost. However, the poor thermodynamic and kinetic properties ...
Decoding how molecules "talk" to each other to develop new nanotechnologies
2023-08-15
Two molecular languages at the origin of life have been successfully recreated and mathematically validated, thanks to pioneering work by Canadian scientists at Université de Montréal.
Published this week in the Journal of American Chemical Society, the breakthrough opens new doors for the development of nanotechnologies with applications ranging from biosensing, drug delivery and molecular imaging.
Living organisms are made up of billions of nanomachines and nanostructures that communicate to create higher-order entities able to do many essential things, such as moving, thinking, surviving and reproducing.
“The key to life’s emergence ...
Favored asylum seekers are young, female and fleeing war
2023-08-15
Russia’s attack on Ukraine has resulted in one of the largest movements of refugees since the Second World War. More than 7.4 million Ukrainians have sought asylum in Europe, almost three times the number of people who found refuge in Europe during Syria’s civil war in 2015 and 2016.
To investigate whether and how the willingness of host populations to receive refugees has changed since 2016, an international research team involving ETH Zurich, the University of California, Berkeley, and Stanford University surveyed 33,000 people in 15 European countries. The first wave of the survey took place in February 2016 and the second from May to June ...
More than 800 human-harvested shellfish species tend to be more resistant to extinction
2023-08-15
In a new study, scientists Stewart Edie of the Smithsonian, Shan Huang of the University of Birmingham and colleagues drastically expanded the list of bivalve species, such as clams, oysters, mussels, scallops and their relatives, that humans are known to harvest and identified the traits that make these species prime targets for harvesting. They also discovered that some of these same traits have also made this group of shellfish less prone to extinction in the past and may protect these shellfish in the future. The authors flagged certain ocean regions, such as the east Atlantic and northeast and southeast Pacific, as areas of special concern for management and conservation.
The ...
Nearly 50% of environmentalists abandoned Twitter following Musk’s takeover
2023-08-15
In October 2022, Elon Musk purchased Twitter (recently renamed X), which had previously served as the leading social media platform for environmental discourse. Since then, reports a team of researchers in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution on August 15, there has been a mass exodus of environmental users on the platform—a phenomenon that could have serious implications for public communication surrounding topics like biodiversity, climate change, and natural disaster recovery.
“Twitter has been the dominant social ...
Reduced grey matter in frontal lobes linked to teenage smoking and nicotine addiction – study
2023-08-15
Levels of grey matter in two parts of the brain may be linked to a desire to start smoking during adolescence and the strengthening of nicotine addiction, a new study has shown.
A team of scientists, led by the universities of Cambridge and Warwick in the UK and Fudan University in China, analysed brain imaging and behavioural data of over 800 young people at the ages of 14, 19 and 23.
They found that, on average, teenagers who started smoking by 14 years of age had markedly less grey matter in a section of the left frontal lobe linked to ...
Infants admitted to ICUs for RSV infection during the 2022 seasonal peak
2023-08-15
About The Study: In this study, most U.S. infants who required intensive care for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) lower respiratory tract infections were young, healthy, and born at term. These findings highlight the need for RSV preventive interventions targeting all infants to reduce the burden of severe RSV illness.
Authors: Natasha Halasa, M.D., M.P.H., of the Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, and Angela P. Campbell, M.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
Communication of COVID-19 misinformation on social media by physicians in the US
2023-08-15
About The Study: In this study of high-use social media platforms, physicians from across the U.S. and representing a range of medical specialties were found to propagate COVID-19 misinformation about vaccines, treatments, and masks on large social media and other online platforms and that many had a wide reach based on number of followers.
Authors: Sarah L. Goff, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Study explains how part of the nucleolus evolved
2023-08-15
Inside all living cells, loosely formed assemblies known as biomolecular condensates perform many critical functions. However, it is not well understood how proteins and other biomolecules come together to form these assemblies within cells.
MIT biologists have now discovered that a single scaffolding protein is responsible for the formation of one of these condensates, which forms within a cell organelle called the nucleolus. Without this protein, known as TCOF1, this condensate cannot form.
The findings could help to ...
Lundquist Principal Investigator Dr. Michael Yeaman awarded $11.5 million NIAID/HHS grant for innovative research to understand and solve persistent bloodstream infections
2023-08-15
The Lundquist Institute (TLI) at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center announced today that TLI Principal Investigator, Michael Yeaman, PhD, has been awarded a grant totaling $11.5M from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Department of Health & Human Services. Along with his role at TLI, Dr. Yeaman is Professor of Medicine at UCLA, and Chief, Division of Molecular Medicine at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center.
This new NIH U19 Center program will decode patterns of the human immune system and microbial pathogens that result in infections that are not ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] New algorithm captures complex 3D light scattering information from live specimensResearchers combine algorithm with intensity diffraction tomography to characterize thick biological samples