(Press-News.org) Good cardiorespiratory fitness when young is associated with up to a 40% lower risk of developing 9 specific cancers later on—at least in men—suggests a large long term study published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
These include cancers of the head and neck, food pipe (oesophagus), stomach, pancreas, liver, bowel, kidney, and lung.
Cardiorespiratory fitness refers to a person’s ability to do aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, and swimming for sustained periods, or even to climb stairs. It's known to be associated with lower risks of certain cancers, but few large, long term studies of multiple cancer sites have been reported.
The researchers therefore drew on linked Swedish registry data up to the end of 2019, covering background information, medical diagnoses, and deaths for conscripts who started their military service between 1968 and 2005.
At the start of their stint, when they were aged between 16 and 25, conscripts underwent a standard battery of assessments. These included height, weight (BMI), blood pressure, muscular strength and cardiorespiratory fitness..
Conscripts with a low level of cardiorespiratory fitness were slightly more likely to be obese, more likely to have a history of alcohol and substance misuse, and to have parents with lower educational attainment than conscripts with a higher fitness level.
In all, 365,874 conscripts had a low level of cardiorespiratory fitness; 519,652 had a moderate level; and 340,952 had a high level.
The final analysis included more than 1 million men (1,078,000), 84,117 (7%) of whom subsequently developed cancer in at least one site during an average monitoring period of 33 years.
Compared with men with a low level of fitness at conscription, higher cardiorespiratory fitness was linearly associated with a lower risk of developing specific types of cancer.
It was associated with a 5% lower risk of rectal cancer (2337); a 12% lower risk of pancreatic cancer (1280); an 18% lower risk of bowel cancer (3222); a 19% lower risk of head and neck cancer (2738 men); a 20% lower risk of kidney cancer (1753); a 21% lower risk of stomach cancer (902); a 39% lower risk of food pipe cancer (689); a 40% lower risk of liver cancer (1111); and a 42% lower risk of lung cancer (1635).
But higher cardiorespiratory fitness was also associated with a 7% heightened risk of prostate cancer (14, 232 men) and a 31% heightened risk of skin cancer (23, 064). Prostate cancer screening and exposure to sunlight might account for these findings, suggest the researchers.
This is an observational study, so no firm conclusions can be drawn about cause and effect, and the researchers acknowledge that they didn’t have full data on other potentially influential lifestyle risk factors, such as diet, alcohol intake, and smoking, in particular. Nor were they able to track any changes in cardiorespiratory fitness over time or gather any genetic information on participants.
Nevertheless, their findings are reflected in the American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines on exercise during cancer treatment, they point out.
And they conclude: “This study shows that higher fitness in healthy young men is associated with a lower hazard of developing 9 out of 18 investigated site-specific cancers, with the most clinically relevant hazard rates in the gastrointestinal tract.
“These results could be used in public health policymaking, further strengthening the incentive for promoting interventions aimed at increasing [cardiorespiratory fitness] in youth.”
END
Good cardiorespiratory fitness associated with up to 40% lower risk of 9 cancers
These include head and neck, food pipe, stomach, pancreas, liver, bowel, kidney, lung
2023-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sea sequin ‘bling’ links Indonesian islands’ ancient communities
2023-08-16
A team of researchers have found a shared penchant for sewing reflective shell beds onto clothing and other items across three Indonesian islands that dates back to at least 12,000 years ago.
The team, led by the Australian National University’s Professor Sue O’Connor with Griffith University’s Associate Professor Michelle Langley, used advanced microscopic analysis to investigate Nautilus shell beads from Makpan Cave on the Indonesian island of Alor, and that the trends in style were shared with at least two other islands.
Striking similarities between the beads of Alor, Timor, and Kisar indicate that there ...
Bats feast as insects migrate through Pyrenees
2023-08-16
Bats gather to feast as nocturnal insects fly through mountain passes in the Pyrenees each autumn, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists identified seven bat species and 66 insect species (90% of which were moths) in the Pass of Bujaruelo, near Spain’s border with France.
The study shows that migrating insects are a vital food source for both migrating bats and those that live in the mountains.
It also provides the first ever evidence of migratory bats feeding on migratory insects while both are migrating.
“Mountain passes are hotspots for a wide variety of insect species that fly south in the autumn,” said Dr Will ...
NASA’s Amy Simon Awarded AAS 2023 Alexander Prize
2023-08-15
The Division for Planetary Sciences (DPS) of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) has named its prize winners for 2023. AAS awarded the 2023 Alexander Prize to Amy Simon, Senior Scientist for Planetary Atmospheres Research in the Solar System Exploration Division at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Simon won the award for a mid-career scientist who has made and continues to make outstanding contributions that have significantly advanced our knowledge of planetary systems, ...
Hastings Center Report, July-August 2023 Issue
2023-08-15
The Moral Difference between Faces and FaceTime
Kyle E. Karches
Although telemedicine can be useful in certain situations, physicians should not consider it an adequate substitute for the office visit, writes Karches, an associate professor of health care ethics and internal medicine at St. Louis University. While seeing the potential for telemedicine to improve care for certain patients, he is concerned about what may be lost if telemedicine comes to replace many in-person visits. Telemedicine rules out an embodied encounter between physician and patient, in which the sense of touch has special ...
Department of Energy grant supports inclusive high energy physics research
2023-08-15
The new project creates opportunities for researchers from historically underrepresented groups to develop technology that will help us understand the forces behind an expanding universe.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the Missouri University of Science and Technology (Missouri S&T) have been awarded funding for a program that aims to generate insights about the universe while expanding diversity in the high energy physics field.
Through the $589,000, three-year grant from DOE’s Funding for Accelerated, Inclusive Research (FAIR) initiative, ...
Could exposure to chemicals in plastics predispose you and your children to cardiovascular disease?
2023-08-15
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Exposure to environmental chemicals, including those in common plastic products, has been linked with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, or CVD, the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2019.
Changcheng Zhou, a professor of biomedical sciences in the School of Medicine at the University of California, Riverside, has received an eight-year award of nearly $6.8 million from the Revolutionizing Innovative, Visionary Environmental Health Research (RIVER) program of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, or NIEHS, to investigate how ...
Cancer organizations recommend mindfulness-based interventions to treat anxiety and depression in patients
2023-08-15
WASHINGTON, D.C. (August 15, 2023) — The Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) and the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) formally recommend mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) and other integrative therapies to manage anxiety and depression symptoms in adults living with cancer. The guideline, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, reviews the effectiveness of integrative therapies such as yoga, relaxation, hypnosis, acupuncture, and music therapy in treating anxiety and depression symptoms during ...
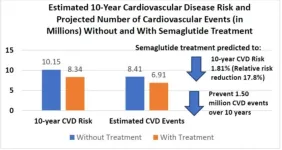
Recent study at UC Irvine found that semaglutide medication may benefit 93 million U.S. adults
2023-08-15
Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have just published a study that projects 93 million U.S. adults that are overweight and obese may be suitable for the 2.4 mg dosage of semaglutide, a weight loss medication known under the brand name Wegovy.
They projected based on the known weight loss effects (15% average weight loss) of this therapy that its use could result in 43 million fewer people with obesity, and prevent up to 1.5 million heart attacks, strokes, and other adverse cardiovascular events over 10 years.
The study, US Population Eligibility and Estimated Impact of ...
Carnegie Mellon University developed AI method uses transformer models to study human cells
2023-08-15
Researchers in Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science have developed a method that uses artificial intelligence to augment how cells are studied and could help scientists better understand and eventually treat disease.
Images of organ or tissue samples contain millions of cells. And while analyzing these cells in situ is an important part of biological research, such images make it nearly impossible to identify individual cells, determine their function and understand their organization. A technique called spatial transcriptomics ...
Kessler Foundation receives 4 grants totaling nearly $1.7 million from New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research
2023-08-15
East Hanover, NJ – August 15, 2023 – Kessler Foundation scientists received four grants from the New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research, totaling nearly $1.7 million for studies based on a variety of novel approaches aimed at improving the lives of individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI). Researchers will use funds to address identity reconstruction, physical and mental fatigue, and upper limb (UL) function.
Helen Genova, PhD, associate director, Center for Autism Research, received $528,824 for her study, “Using my Strengths: Evaluation of a Strength-Based Intervention in Adults with TBl.” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
[Press-News.org] Good cardiorespiratory fitness associated with up to 40% lower risk of 9 cancersThese include head and neck, food pipe, stomach, pancreas, liver, bowel, kidney, lung