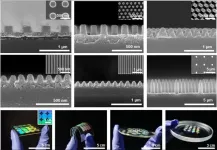
Controlling the source of electromagnetic waves enables control of the period of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS)
2023-08-16
(Press-News.org)
Since the scientists at Bell Labs invented the world’s first transistor in December 1947, a revolution in microelectronics technology has profoundly affected lifestyles worldwide. As electronics get smaller and smaller, it is a challenge to find an easy, fast, and low-cost way to fabricate micro-nano components. Traditional direct writing fabrication methods such as mechanical scribing, focused ion beam etching, electron beam lithography, multiphoton polymerization, and thermal scanning probe etching are inefficient. Although methods such as nanoimprinting, photolithography, plasma etching, and scanning laser interference etching can effectively increase the processing speed, they generally require multiple process steps such as making masks or require very harsh working environments and rely on special Material. Using femtosecond laser to induce surface self-organized periodic structure to manufacture nano-grating structure has attracted people’s attention. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) uses the interference between incident light and surface electromagnetic waves to etch the material, so it has high processing accuracy. Moreover, compared with the traditional laser interference processing method, the self-organized processing method makes its experimental setup simple and scanning with a large light spot makes its fabrication speed rapidly high.
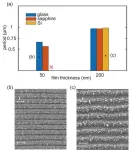
Researchers led by Prof. Min Qiu at Westlake University, China have extensive research experience in LIPSS. They recently discovered that when a periodic grating is induced on the surface of a thin a-Si film, the period of the grating is affected by the interference of incident light with different origins of electromagnetic waves. When the thickness of the amorphous silicon film is small (50 nm) and the substrate is a non-silicon material, LIPSS with a small period is induced under the dominance of the slab waveguide mode. In this case, when the substrate material changes (refractive index changes), the period of the LIPSS also changes. When the thickness of the amorphous silicon film is large (200 nm), the incident light interferes with the quasi-cylindrical wave, and induces the growth of LIPSS under the joint action of near-field and far-field. The period of LIPSS in this mode is slightly smaller than the laser wavelength and is independent of the substrate material. Finite-difference time-domain method-based numerical simulations support the experimental discoveries.
The work entitled “Impact of film thickness in laser-induced periodic structures on amorphous Si films” was published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Jun. 20, 2023).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-16
A prevailing narrative about immigration is that migrants displace U.S.-born residents in the workforce, but new research from University of California, Davis, economists shows that’s not the case.
The study, published in the Journal of Population Economics, details how the COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in immigration to the U.S. and how jobs often filled by migrants were not filled by U.S.-born residents.
“We found that this drop in immigrants corresponded also to a drop in employment in some specific types of occupations, including accommodation ...
2023-08-16
When will the protruding rear camera on smartphones become obsolete? The implementation of a metasurface, which completely disregards the properties of light, promises to reduce the thickness of a camera lens to 1/10,000 of a conventional lens. However, despite this advancement, challenges still persist due to high production costs and intricate processes. Nonetheless, a recent study unveiled a “mold” that dissolves in water, enhancing the efficiency of the fabrication process.
A collaborative team led by Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Department ...
2023-08-16
Recreational drug use may be a factor in a significant proportion of admissions to cardiac intensive care, with various substances detected in 1 in 10 such patients, suggest the findings of a multicentre French study published online in the journal Heart.
Drug use was also associated with significantly poorer outcomes, with users nearly 9 times as likely to die or require emergency intervention as other heart patients while in hospital, and 12 times as likely to do so if they used more than one drug.
Recreational drug use is a known risk factor for cardiovascular incidents, such as a heart attack or abnormal heart rhythm (atrial fibrillation), ...
2023-08-16
Young vapers are at risk of bronchitic symptoms and shortness of breath, even if they, or others around them, smoke cigarettes or cannabis, suggests research published online in the journal Thorax.
The findings prompt the US researchers to call for the respiratory effects of vaping products to be included in regulatory oversight.
Latest US estimates indicate that 14% of high school students vaped in 2022. And it’s known that e-cigarette aerosol contains substances that harm the lungs.
Several published studies have reported respiratory symptoms among teen and young adult vapers. But most of these have focused exclusively on e-cigarette ...
2023-08-16
Good cardiorespiratory fitness when young is associated with up to a 40% lower risk of developing 9 specific cancers later on—at least in men—suggests a large long term study published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
These include cancers of the head and neck, food pipe (oesophagus), stomach, pancreas, liver, bowel, kidney, and lung.
Cardiorespiratory fitness refers to a person’s ability to do aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, and swimming for sustained periods, or even to climb stairs. It's known ...
2023-08-16
A team of researchers have found a shared penchant for sewing reflective shell beds onto clothing and other items across three Indonesian islands that dates back to at least 12,000 years ago.
The team, led by the Australian National University’s Professor Sue O’Connor with Griffith University’s Associate Professor Michelle Langley, used advanced microscopic analysis to investigate Nautilus shell beads from Makpan Cave on the Indonesian island of Alor, and that the trends in style were shared with at least two other islands.
Striking similarities between the beads of Alor, Timor, and Kisar indicate that there ...
2023-08-16
Bats gather to feast as nocturnal insects fly through mountain passes in the Pyrenees each autumn, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists identified seven bat species and 66 insect species (90% of which were moths) in the Pass of Bujaruelo, near Spain’s border with France.
The study shows that migrating insects are a vital food source for both migrating bats and those that live in the mountains.
It also provides the first ever evidence of migratory bats feeding on migratory insects while both are migrating.
“Mountain passes are hotspots for a wide variety of insect species that fly south in the autumn,” said Dr Will ...
2023-08-15
The Division for Planetary Sciences (DPS) of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) has named its prize winners for 2023. AAS awarded the 2023 Alexander Prize to Amy Simon, Senior Scientist for Planetary Atmospheres Research in the Solar System Exploration Division at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Simon won the award for a mid-career scientist who has made and continues to make outstanding contributions that have significantly advanced our knowledge of planetary systems, ...
2023-08-15
The Moral Difference between Faces and FaceTime
Kyle E. Karches
Although telemedicine can be useful in certain situations, physicians should not consider it an adequate substitute for the office visit, writes Karches, an associate professor of health care ethics and internal medicine at St. Louis University. While seeing the potential for telemedicine to improve care for certain patients, he is concerned about what may be lost if telemedicine comes to replace many in-person visits. Telemedicine rules out an embodied encounter between physician and patient, in which the sense of touch has special ...
2023-08-15
The new project creates opportunities for researchers from historically underrepresented groups to develop technology that will help us understand the forces behind an expanding universe.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the Missouri University of Science and Technology (Missouri S&T) have been awarded funding for a program that aims to generate insights about the universe while expanding diversity in the high energy physics field.
Through the $589,000, three-year grant from DOE’s Funding for Accelerated, Inclusive Research (FAIR) initiative, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Controlling the source of electromagnetic waves enables control of the period of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS)