(Press-News.org) Neuroscientists at Radboudumc show that adversities permanently change the functioning of the brain. Furthermore, an aberrant reaction of the brain to adversities is related to anxiety symptoms. This may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Your brain is shaped by the things you experience. That sounds logical, but can you really measure that? And what can you do with it? Neuroscientists at Radboud university medical center investigated the influence of adversities in life on patterns in the brain. They found remarkable associations that may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Special group
The researchers conducted their study on approximately 170 people. A special group, because all kinds of data have been collected from them during their lifetime. For this study, the scientists specifically focused on adversities: factors or events that are known to have a negative effect on development. Consider, for example, the mother's smoking during pregnancy, complications during childbirth, abuse, or a major accident.
In addition to this data, the researchers determined the brain structure of these people with scans. They did so at both 25 and 33 years of age. Artificial intelligence was then used to find connections between adversities and patterns in the brain. ‘They came out very clearly’, says researcher Nathalie Holz. ‘And these relationships are very stable. We found them at both ages. With our results, we can now predict how the brain reacts to adversities.’
Anxiety complaints
‘I find it very special that we can still trace the influence of events that sometimes took place 25 years ago in the brain’, says research leader André Marquand. ‘And perhaps more importantly, it may help us predict who is more likely to develop psychiatric disorders.’
Marquand explains how this works: 'We have uncovered how the brain normally reacts to adversities. Therefore, we can also determine when that reaction is abnormal. And we found that such a deviating pattern was related to anxiety symptoms.’ These kinds of complaints play a central role in many psychiatric disorders.
The scientists expect that their findings can ultimately contribute to the earlier detection of psychiatric disorders. This allows healthcare providers to treat patients earlier and more effectively. But more research is needed before that becomes a reality. For example, the researchers are now applying their method to a group of patients with these disorders. This will show how great the predictive value is.
END
Adversities permanently change our brains
An aberrant reaction to adversities may increase the risk of psychiatric disorders
2023-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MSU hires Judd Herzer for new mobility director role
2023-08-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Michigan State University today named Judd Herzer as the director of MSU Mobility to help amplify and focus the university’s vast research activities in the smart-vehicle landscape. Satish Udpa, University Distinguished Professor in the College of Engineering at MSU and co-founder of MSU Mobility, has been fulfilling the duties of this newly created role in an interim capacity while the university looked for the ideal candidate.
Mobility is among MSU’s principal areas of research and innovation, and MSU Mobility and its ...
Antil receives funding for workshop on digital twins
2023-08-21
Harbir Antil, Director, Center for Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, and Professor, Mathematical Sciences, received funding for: "Mathematics for Digital Twins (MATH-DT)."
This award will provide support for a workshop titled "Mathematical Opportunities in Digital Twins" to be held on Dec. 11-13, 2023, at George Mason University's campus in Arlington, VA.
The workshop will bring together key experts working in many aspects of mathematics, key application fields, and industry with the goal of determining ...
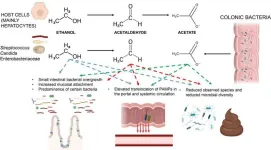
Understanding mechanisms of alcohol-associated bowel disease
2023-08-21
Alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor for gastrointestinal diseases, including cancer. Alcohol can damage the gastrointestinal tract in several ways. It can promote an impairment of several intestinal barrier functions, leading to leaky gut and dysbiosis. Ethanol metabolism can also produce toxic substances such as acetaldehyde and acetate, further damaging the gut and potentially promoting cancer. Ethanol and its metabolites enhance DNA damage response and dysregulate the epithelial proliferation/differentiation program, thereby increasing the risk of cancer development.
In a new paper published in eGastroenterology, ...
SARS-CoV-2: The grasping fingers of the viral N protein
2023-08-21
#FRANKFURT. Immediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell’s metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
One viral protein, called the nucleocapsid protein (N), is particularly important for rapid and efficient replication. ...
Climate win-win: study quantifies benefits of enhanced weathering
2023-08-21
Applying ground-up silicate rock to Midwestern farm fields can capture significant amounts of carbon dioxide and prevent it from accumulating in the atmosphere, according to a new study that successfully quantified those climate benefits for the first time.
Working with Eion Corp., researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the Leverhulme Centre for Climate Change Mitigation (LC3M) developed a new method to calculate the CO2-reduction potential of basalt rock amendments applied to cropland soil, a process known as enhanced weathering.
Traditional row-crop agriculture releases sizable amounts of soil-derived carbon to the atmosphere as CO2, a greenhouse gas ...
Late mortality after COVID-19 infection in veterans vs risk-matched comparators
2023-08-21
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that COVID-19 was not associated with any clinically significant excess mortality among those who survived at least 180 days compared with closely risk-matched comparators, despite having worse 2-year total mortality. This finding has individual level and health system planning implications and should be reassuring to persons who have survived COVID-19 for at least 180 days.
Authors: Theodore J. Iwashyna, M.D., Ph.D., of the Ann Arbor VA in Ann Arbor, Michigan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Screen time at age 1 and communication, problem-solving developmental delay at ages 2 and 4
2023-08-21
About The Study: In this study including 7,097 mother-child pairs, greater screen time for children at age 1 was associated with developmental delays in communication and problem-solving at ages 2 and 4. These findings suggest that domains of developmental delay should be considered separately in future discussions on screen time and child development.
Authors: Taku Obara, Ph.D., of Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
International pediatric COVID-19 severity over the course of the pandemic
2023-08-21
About The Study: This study including 31,000 hospitalized children with SARS-CoV-2 infection suggested that while intensive care unit admission decreased over the course of the pandemic in all age groups, ventilatory and oxygen support did not decrease over time in children younger than age 5. These findings highlight the importance of considering different pediatric age groups when assessing disease severity in COVID-19.
Authors: Kirsty Short, Ph.D., of the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3117)
Editor’s ...
Websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone Tests
2023-08-21
About The Study: In this study including content analysis of 27 websites across multiple countries, most websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) tests included false and misleading claims which might lead consumers to purchase an AMH test in the belief that it can reliably predict fertility potential and age of menopause. Depending on the test result, this may in turn lead to misplaced anxiety or reassurance about one’s fertility and modifications to subsequent conception or contraceptive plans and behavior.
Authors: Tessa Copp, Ph.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the ...
Artificial intelligence beyond the clinic
2023-08-21
With the advent of ChatGPT4, the use of artificial intelligence in medicine has absorbed the public’s attention, dominated news headlines, and sparked vigorous debates about the promise and peril of medical AI.
But the potential of AI reaches far beyond the frontlines of medicine.
AI is already changing the way scientists discover and design drugs. It is predicting how molecules interact and proteins fold with never-before-seen speed and accuracy. One day, AI may even be used routinely to safeguard the function of nuclear reactors.
These are but a few of the exciting applications of AI in the natural sciences, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
[Press-News.org] Adversities permanently change our brainsAn aberrant reaction to adversities may increase the risk of psychiatric disorders