Ye receives National Science Foundation CAREER Award
2023-08-21
(Press-News.org)
Jinwei Ye, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding for the project: "CAREER: Towards Polarimetric Visual Understanding."
In this project, Ye will study how the way surfaces reflect polarized light can be used to help recognize objects more effectively.
Ye will address the following two questions: (1) How does the polarization of light change after interacting with various types of surfaces? (2) What can polarized light tell us about the kinds of objects that it has interacted with?
Addressing these questions can lead to significant improvements in machine vision systems by strengthening their capability to do geometric and semantic scene understanding in which shapes are described and named.
This project will result in new polarization-based vision systems for autonomous navigation and smart manufacturing. It will also produce novel solutions to the challenging problems of imaging and sensing through scattering media, including water, fog, haze, clouds, and bodily tissues.
Ye will receive total funding of $600,000 from NSF for this award. Funding began in July 2023 and will end in late June 2028.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls 38,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the last half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity and commitment to accessibility. Learn more at http://www.gmu.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-21
One of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is disruption to the body’s circadian rhythm, the internal biological clock that regulates many of our physiological processes. Nearly 80% of people with Alzheimer’s experience these issues, including difficulty sleeping and worsening cognitive function at night. However, there are no existing treatments for Alzheimer’s that target this aspect of the disease.
A new study from researchers at University of California San Diego School ...
2023-08-21
How does a gambler maximize winnings from a row of slot machines? This is the inspiration for the "multi-armed bandit problem," a common task in reinforcement learning in which "agents" make choices to earn rewards. Recently, an international research team led by Hiroaki Shinkawa at the University of Tokyo developed an extended photonic reinforcement learning scheme that moves from the static bandit problem towards a more challenging dynamic environment. This study was published July 25 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The success of ...
2023-08-21
August 21, 2022 – Implantable penile prostheses (IPPs) are an established treatment option for erectile dysfunction (ED), and are covered by insurance in about 80% of cases, reports a paper in the September issue of Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
However, some employer-sponsored insurance plans specifically exclude this guideline-recommended treatment option for ED, according to the new research by Dr. Mohit Khera, MD, MBA, MPH, of Baylor College ...
2023-08-21
Neuroscientists at Radboudumc show that adversities permanently change the functioning of the brain. Furthermore, an aberrant reaction of the brain to adversities is related to anxiety symptoms. This may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Your brain is shaped by the things you experience. That sounds logical, but can you really measure that? And what can you do with it? Neuroscientists at Radboud university medical center investigated the influence of adversities in life on patterns in the brain. They found remarkable associations that may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Special ...
2023-08-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Michigan State University today named Judd Herzer as the director of MSU Mobility to help amplify and focus the university’s vast research activities in the smart-vehicle landscape. Satish Udpa, University Distinguished Professor in the College of Engineering at MSU and co-founder of MSU Mobility, has been fulfilling the duties of this newly created role in an interim capacity while the university looked for the ideal candidate.
Mobility is among MSU’s principal areas of research and innovation, and MSU Mobility and its ...
2023-08-21
Harbir Antil, Director, Center for Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, and Professor, Mathematical Sciences, received funding for: "Mathematics for Digital Twins (MATH-DT)."
This award will provide support for a workshop titled "Mathematical Opportunities in Digital Twins" to be held on Dec. 11-13, 2023, at George Mason University's campus in Arlington, VA.
The workshop will bring together key experts working in many aspects of mathematics, key application fields, and industry with the goal of determining ...
2023-08-21
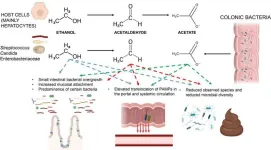
Alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor for gastrointestinal diseases, including cancer. Alcohol can damage the gastrointestinal tract in several ways. It can promote an impairment of several intestinal barrier functions, leading to leaky gut and dysbiosis. Ethanol metabolism can also produce toxic substances such as acetaldehyde and acetate, further damaging the gut and potentially promoting cancer. Ethanol and its metabolites enhance DNA damage response and dysregulate the epithelial proliferation/differentiation program, thereby increasing the risk of cancer development.
In a new paper published in eGastroenterology, ...
2023-08-21
#FRANKFURT. Immediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell’s metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
One viral protein, called the nucleocapsid protein (N), is particularly important for rapid and efficient replication. ...
2023-08-21
Applying ground-up silicate rock to Midwestern farm fields can capture significant amounts of carbon dioxide and prevent it from accumulating in the atmosphere, according to a new study that successfully quantified those climate benefits for the first time.
Working with Eion Corp., researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the Leverhulme Centre for Climate Change Mitigation (LC3M) developed a new method to calculate the CO2-reduction potential of basalt rock amendments applied to cropland soil, a process known as enhanced weathering.
Traditional row-crop agriculture releases sizable amounts of soil-derived carbon to the atmosphere as CO2, a greenhouse gas ...
2023-08-21
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that COVID-19 was not associated with any clinically significant excess mortality among those who survived at least 180 days compared with closely risk-matched comparators, despite having worse 2-year total mortality. This finding has individual level and health system planning implications and should be reassuring to persons who have survived COVID-19 for at least 180 days.
Authors: Theodore J. Iwashyna, M.D., Ph.D., of the Ann Arbor VA in Ann Arbor, Michigan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ye receives National Science Foundation CAREER Award