(Press-News.org) August 25, 2023 – Potentially modifiable comorbid conditions and complications have a major impact on the risks of total hip arthroplasty (THA) for people in their nineties, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Patients ³90 years old have higher complication and mortality rates following THA, as compared with younger patients. But while age is a significant factor, the risks associated with THA in nonagenarians are largely related to the patient's overall health and fitness for surgery, according to the new research by Dr Vincent J. Leopold, MD, and colleagues of the Charité-University Hospital Berlin.
New data on safety of THA at age 90 or older
With the aging of the population, there is ongoing debate regarding the safety of THA in the oldest age groups. While some studies have found no increase in complications following THA for nonagenarians, others have reported that the risk of complications increases with age.
Dr. Leopold and colleagues analyzed the characteristics and outcomes of 263,967 patients ³60 years old who underwent THA between 2012 and 2021. Of these, 1,859 patients – 0.7% of the total – were in their nineties. The analysis focused on how patient age and health status affected the risks of complications and death associated with THA.
Overall, nonagenarians had higher complication and mortality rates compared with younger age groups. Major complications occurred in 19.9% of patients in their nineties, compared with 10.7% for patients in their eighties, 6.2% in their seventies, and 3.7% in their sixties. Common major complications included acute kidney failure, delirium, and blood clotting abnormalities.
Rate of minor complications also increased with age – up to 62.7% for nonagenarians. Patients in their nineties also had the highest mortality rate: 26.5%, compared to 11.8% for patients in their eighties, 6.0% in their seventies, and 2.8% in their sixties.
Comorbidity has major impact on THA risks
While age itself was an independent risk factor, the increased risks in nonagenarians were strongly associated with the presence of comorbid diseases. For example, the risk of major complications following THA was about 17 times greater for patients with clotting abnormalities, nine times greater for those with paralysis, and nearly eight times greater for those with pulmonary circulation disorders.
For mortality, the strongest risk factors were metastatic cancer, pulmonary circulation disorders, alcohol abuse, paralysis, or congestive heart failure. For major and minor complications as well as mortality, risk increased with each additional year of age, with the greatest increase among nonagenarians.
Complications had a major impact on mortality rate. One year after THA, survival rate was 94.4% for nonagenarians without any major complications versus 79.8% for those with major complications.
Even for patients with complications, mortality rates for nonagenarians undergoing THA were lower than in the general population of people in their nineties. "We believe that this was most likely because elderly patients who become candidates for elective THA are healthier and biologically younger than the reference group of the general population; the resulting selection bias would be expected to lower the mortality of the nonagenarians in the study cohort," the researchers write.
The findings lend new insights into the safety of elective THA for nonagenarians. While complication and mortality rates are higher than in younger age groups, those risks may be minimized by "careful patient selection and adequate preparation." Dr. Leopold and colleagues conclude: "[E]lective THA can be appropriately considered by surgeons and patients when symptoms of hip osteoarthritis are present."
Read [Is Elective Total Hip Arthroplasty Safe in Nonagenarians: An Arthroplasty Registry Analysis]
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
###
About The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery
The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS) has been the most valued source of information for orthopaedic surgeons and researchers for over 125 years and is the gold standard in peer-reviewed scientific information in the field. A core journal and essential reading for general as well as specialist orthopaedic surgeons worldwide, The Journal publishes evidence-based research to enhance the quality of care for orthopaedic patients. Standards of excellence and high quality are maintained in everything we do, from the science of the content published to the customer service we provide. JBJS is an independent, non-profit journal.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the healthcare, tax and accounting, financial and corporate compliance, legal and regulatory, and corporate performance and ESG sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with specialized technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2022 annual revenues of €5.5 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 20,900 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube.
END
ST. LOUIS — Erectile dysfunction (ED) is more common in older individuals with long-term Type 2 diabetes. However, emerging research at Saint Louis University School of Medicine has found that ED indicates undiagnosed prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in young men under 40.
Although the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes declined in the United States from 1988 to 2020, 2.5% of the population has persistent undiagnosed diabetes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate 8.5 million adults have undiagnosed diabetes, and a quarter of these cases are among young persons 18 to 44.
In a recent study published ...
Pupils with special educational needs and disabilities should be given equal opportunities to learn languages, a new report argues.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that children with SEND are often removed from language lessons, because the subject is perceived as “difficult”, an assumption that is further exacerbated by trends with GCSE subject choices. Instead of withdrawing children with additional needs from the foreign languages classroom, opportunities should be provided for them to thrive within it.
Evidence shows learning new languages can be possible and hugely beneficial for many children with ...
CHICAGO, Aug. 25, 2023 – Acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are recommended as first-line treatments for managing short-term dental pain in children under age 12, according to a new clinical practice guideline developed by the American Dental Association Science & Research Institute (ADASRI), the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine and the Center for Integrative Global Oral Health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine. The guideline has been endorsed by the American Dental Association.
A guideline panel determined that, when used as directed, acetaminophen alone, ...
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In 2012, University of Alabama at Birmingham researcher Anath Shalev, M.D., reported that a decades-old blood pressure medication called verapamil completely reversed diabetes in animal models. In 2018, the team had translated these findings into a randomized, controlled, clinical trial, demonstrating significantly improved beta cell function for one year in human subjects with recent onset Type 1 diabetes. By last year, in a small follow-up study, Shalev and colleagues had found that adult Type 1 diabetes patients taking oral verapamil required less daily insulin ...
A new study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has examined how T cells of the immune system are affected by weightlessness. The results, which are published in the journal Science Advances, could explain why astronauts’ T cells become less active and less effective at fighting infection.
The next steps in the exploration of space are human missions to the moon and to Mars. Space is an extremely hostile environment that poses threats to human health. One such threat is changes to the immune system that occur in astronauts while in space and ...
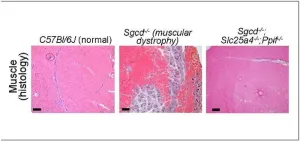
Ever since the Jerry Lewis telethons began in the 1960s, millions of people have become familiar with an otherwise rare disease called muscular dystrophy (MD).
The medical world has learned much over the ensuing years, including that more than 30 closely related disorders exist that can produce the gradual muscle degeneration that steals a child’s ability to walk and eventually disrupts other organ functions. An estimated 250,000 people in the U.S. are living with a muscular dystrophy. While many are living longer lives thanks to improved treatments, no cure has been found.
Now an eye-opening study ...
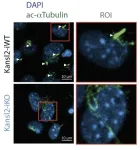
Cilia are thin, eyelash-like extensions on the surface of cells. They perform a wide variety of functions, acting as mechanosensors or chemosensors, and play a crucial role in many signaling pathways. In the last few decades, the organelle has undergone a remarkable, but at the same time sinister, career transformation. It evolved from an organelle whose relevance was unclear to becoming a central player in the pathogenesis of a large group of diseases. These so-called ciliopathies are associated with a wide range of symptoms, including hearing loss, visual impairment, obesity, kidney disease, and mental disability. Different gene mutations impair cilia formation, ...
Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering looked to origami to create new sensors that could someday be employed to detect deformations in organs and also for use in wearables and soft robotics.
Their paper, “High-Stretchability and Low-Hysteresis Strain Sensors Using Origami-Inspired 3D Mesostructures,” featured in Science Advances explains how USC researchers Hangbo Zhao, Xinghao Huang, Liangshu Liu, Yung Hsin Lin, Rui Feng, Yiyang Shen, and Yuanning Chang developed “stretchable strain sensors,” ...
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Semaglutide improves heart failure-related symptoms and physical function and results in greater weight loss compared with placebo in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Approximately half of patients with heart failure in the community have HFpEF.2 Most patients with HFpEF are overweight or obese, and growing evidence suggests that obesity and excess adiposity are not simply comorbidities, ...
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Blood thinners (anticoagulants) cause bleeding without preventing stroke in patients with atrial high rate episodes (AHRE), but without electrocardiogram (ECG)-diagnosed atrial fibrillation, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.1
Anticoagulants prevent strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation but are not effective in those without atrial fibrillation, for example in patients with ...