(Press-News.org) NIH-funded study supports use of ECMO for critically ill patients with obesity
ECMO does not appear to complicate treatment for severe respiratory failure for adults with obesity
A National Institutes of Health-supported study suggests that adults with obesity may benefit from the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), an advanced form of breathing support, when in intensive care for respiratory failure. ECMO’s use was previously questioned for patients with obesity due to the belief that it may complicate treatment. However, the current findings, which published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, show that patients with obesity who received ECMO for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) had lower mortality rates compared to patients with ARDS without obesity who received ECMO.
In this study, researchers retrospectively reviewed data from 790 patients from more than 20 medical centers across 10 countries who received ECMO for ARDS, a critical lung injury. Among these patients, 320 had obesity. They found 24% of patients with obesity died in the intensive care unit compared to 35% of patients without obesity. The authors couldn’t control for all variables among the larger group analysis, including disease severity. However, they conclude the findings support the concept that obesity, a risk factor for ARDS, shouldn’t factor into treatment decisions for ECMO.
“We hope that clinicians will consider the data from this study when making bedside decisions for ARDS patients with obesity instead of preemptively withholding this lifesaving therapy,” said Darya Rudym, M.D., a study author, pulmonologist, and assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York City.
Previous studies have found similar findings looking at data from patient registries and observational reviews. However, this study is the largest to date to assess ECMO survival outcomes among adults with obesity who have ARDS based on data from prospective studies and clinical trials, which better reflect real world clinical outcomes.
ARDS varies in prevalence but accounts for 10% of intensive care unit admissions worldwide. In this study, pneumonia was the most common factor leading to severe respiratory illness. Survival rates for ARDS vary, with about half to three-fourths of patients surviving. Survival rates for ECMO, a last resort for treatment, are also variable, but have ranged from about 60-75%.
Data for this review came from 440 patients who received intensive care for ARDS at hospitals in the United States, France, Australia, and Italy between 2012–2017. An additional 350 patients came from the Ventilation Management of Patients with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (LIFEGARDS) study, which took place at 23 intensive care units in 10 countries.
“The results of this research open up new questions about how obesity affects outcomes in critical illness to inform evidence-based treatment approaches,” said James P. Kiley, Ph.D., director of the Division of Lung Diseases at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which funded the study.
This research was partially supported by NHLBI and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
Study: Rudym D, Pham T, Rakley C, et al. Mortality in patients with obesity and ARDS receiving ECMO: The multicenter ECMObesity study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023; doi: 10.1164/rccm.202212-2293OC.
About the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): NHLBI is the global leader in conducting and supporting research in heart, lung, and blood diseases and sleep disorders that advances scientific knowledge, improves public health, and saves lives. For more information, visit www.nhlbi.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health
END
NIH-funded study supports use of ECMO for critically ill patients with obesity
ECMO does not appear to complicate treatment for severe respiratory failure for adults with obesity
2023-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Muvalaplin, an oral small molecule inhibitor of lipoprotein(a) formation
2023-08-28
About The Study: Muvalaplin was not associated with tolerability concerns and lowered lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) levels up to 65% following daily administration for 14 days in this first-in-human phase 1 study involving healthy participants. Lipoprotein(a) is associated with atherosclerotic disease and aortic stenosis. Longer and larger trials will be required to further evaluate safety, tolerability, and effect of muvalaplin on Lp(a) levels and cardiovascular outcomes.
Authors: Stephen J. Nicholls, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of Monash University in Clayton, ...
Stevens researchers take aim at weather forecasters’ biggest blindspot
2023-08-28
Anyone who’s been caught in an unexpected downpour knows that weather forecasting is an imperfect science. Now, researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology are taking aim at one of meteorologists’ biggest blind spots: extremely short-term forecasts, or nowcasts, that predict what will happen in a given location over the next few minutes.
“This isn’t just about whether you should take your umbrella with you when you go on a walk,” said Temimi. “The forecasts that we’re missing – the ones that look ...
Projected outcomes of optimized statin and ezetimibe therapy in veterans with coronary artery disease
2023-08-28
About The Study: In this study of 111,000 U.S. military veterans with coronary artery disease, suboptimal lipid-lowering therapy was prevalent in the clinical setting. Optimization of statin therapy was projected to produce clinically relevant reductions in the risks of death and cardiovascular events. Despite a lesser lipid-lowering efficacy of ezetimibe, its widespread use on a population level in conjunction with optimized statin therapy may be associated with further meaningful reductions in cardiovascular risk.
Authors: Gregory G. Schwartz, M.D., Ph.D., of the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center in Aurora, Colorado, is the corresponding author.
To ...
COVID-19 virus is evolving rapidly in white-tailed deer
2023-08-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – White-tailed deer across Ohio have been infected with the virus that causes COVID-19, new research has found – and the results also show that viral variants evolve about three times faster in deer than in humans.
Scientists collected 1,522 nasal swabs from free-ranging deer in 83 of the state’s 88 counties between November 2021 and March 2022. More than 10% of the samples were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and at least one positive case was found in 59% of the counties in which testing took place.
Genomic analysis showed that at least 30 infections in deer had been introduced by humans – ...
Are cannabis products safe and effective for reducing symptoms in children with cancer?
2023-08-28
A recent analysis of all relevant published studies reveals a lack of evidence to determine the dosing, safety, and efficacy of medical marijuana or cannabis-containing products for managing symptoms experienced by children with cancer. The analysis is published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Although treatments for childhood cancer have improved significantly, even leading to cures for many patients, many children still suffer from symptoms such as pain, anxiety, and weight loss related to cancer and its treatment. Over the last decade, cannabis ...
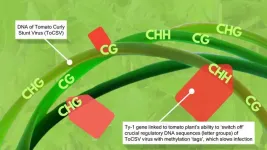
First defence against devastating ToCSV tomato virus explored
2023-08-28
How tomato plants defend themselves against a devastating ‘young’ Southern African virus has now been investigated at a molecular genetics level for the first time by researchers at the University of Johannesburg (UJ).
The Ty-1 gene is known to confer resistance to the well-known tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV). UJ researchers investigated what happens when tomato plants that harbour the Ty-1 gene are infected with the relatively unknown tomato curly stunt virus (ToCSV). They found a link between tolerance to ToCSV, a plant defence called viral DNA methylation, and Ty-1 gene activity.
The research is published ...
Sleep can be most restful for older adults when nighttime temperature range is between 68 to 77 °F, study finds
2023-08-28
New research finds that sleep can be most efficient and restful for older adults when nighttime bedroom ambient temperature ranges between 68 to 77 °F.
The authors observed an overall trend: a 5-10 % drop in sleep efficiency as the nighttime ambient temperature increases from 77°F to 86°F. Importantly, this research also reveals substantial between-individual differences in optimal bedroom temperature.
“These results highlight the potential to enhance sleep quality in older adults by optimizing home thermal environments and emphasizing the importance ...
New study reveals anti-cancer properties in Kencur ginger
2023-08-28
You may know it as an aromatic spice to add flavor to your dishes or as a soothing herbal remedy to use for upset stomachs, but researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have uncovered promising findings that Kencur, a tropical plant in the ginger family native to Southeast Asia, possesses anti-cancer effects.
Led by Associate Professor Akiko Kojima of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology, the researchers demonstrated that Kencur extract and its main active component, ethyl p-methoxycinnamate (EMC), significantly suppressed cancer cell growth at the cellular and animal levels.
While previous studies on EMC indicated its anti-cancer potential by decreasing the expression ...
New type of visible-light responsive photocatalyst is efficient, stable and very economical
2023-08-28
A new type of versatile economical photocatalyst that harnesses the visible portion of the sunlight spectrum has been developed by researchers from the University of Johannesburg. It is simple to manufacture.
Currently, economical photocatalysts only ‘use’ the UV spectrum of sunlight.
The new photocatalyst harnesses about a third of the visible light spectrum.
The extremely stable, powder-form three-component photocatalyst is built from graphitic carbon (89% of mass), a modified calixarene (10%) and a niobium-containing MXene (1%).
Researchers at the University of Johannesburg have developed a new type of photocatalyst that harnesses the visible ...
Low cost, high efficiency, multiple colors at the same time!
2023-08-28
A research team led by Dr. Jung-dae Kwon from the Department of Energy & Electronic Materials at the Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS) has succeeded in realizing the world's first transparent thin-film solar cell on a flexible substrate that exhibits different reflective colours and does not significantly reduce solar cell's efficiency. KIMS is a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
This is a technology that achieves reflective colour only a single material by periodically incorporating hydrogen into zinc oxide material doped with aluminium, which is a transparent electrode, to induce a refractive index difference. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
[Press-News.org] NIH-funded study supports use of ECMO for critically ill patients with obesityECMO does not appear to complicate treatment for severe respiratory failure for adults with obesity