(Press-News.org) About The Study: This case series found that young brain donors exposed to repetitive head impacts were highly symptomatic regardless of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) status, and the causes of symptoms in this sample are likely multifactorial. Future studies that include young brain donors unexposed to repetitive head impacts are needed to clarify the association among exposure, white matter and microvascular pathologic findings, CTE, and clinical symptoms.
Authors: Ann C. McKee, M.D., of the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2907)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2907?guestAccessKey=a1d4b21c-b751-494f-a738-615e39b1bc25&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=082823
END
Neuropathologic and clinical findings in young contact sport athletes exposed to repetitive head impacts
JAMA Neurology
2023-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Due to sea-ice retreat, zooplankton could remain in the deep longer
2023-08-28
Due to intensifying sea-ice melting in the Arctic, sunlight is now penetrating deeper and deeper into the ocean. Since marine zooplankton respond to the available light, this is also changing their behaviour – especially how the tiny organisms rise and fall within the water column. As an international team of researchers led by the Alfred Wegener Institute has now shown, in the future this could lead to more frequent food shortages for the zooplankton, and to negative effects for larger species including seals and whales. The study ...
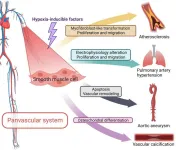
Hypoxia and panvascular diseases: exploring the role of hypoxia-inducible factors in vascular smooth muscle cells under panvascular pathologies
2023-08-28
This study is led by Prof. Junbo Ge (Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases), Prof. Hua Li (Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases), and Prof. Hao Lu (Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases).
As an emerging concept, panvascular diseases encompass a group of cardiovascular disorders characterized mainly by atherosclerosis, involving crucial organs such as the ...
Spintronics: X-ray microscopy unravels the nature of domain walls
2023-08-28
Magnetic skyrmions are tiny vortices-like of magnetic spin textures that - in principle - can be used for spintronic devices, for example very fast and energy-efficient data storage devices. But at the moment it is still difficult to control and manipulate skyrmions at room temperature. A new study at BESSY II analyses the formation of skyrmions in ferrimagnetic thin films of dysprosium and cobalt in real time and with high spatial resolution. This is an important step towards characterising suitable materials with skyrmions more precisely in the future.
Isolated magnetic skyrmions are topologically protected spin textures that are in the focus of research ...
World first drug to target form of previously untreatable life-threatening ‘bad cholesterol’
2023-08-28
A new drug offers a breakthrough world first treatment for Lipoprotein(a), a largely genetic form of cholesterol that increases the risk of heart attack and stroke, announced today by study lead Professor Stephen Nicholls, Director of the Monash University’s Victorian Heart Institute and Victorian Heart Hospital.
High levels of Lipoprotein(a), known as Lp(a) or spoken as ‘LP little a’, impact one in five people globally with no approved treatment currently on the market.
The trial demonstrated the success of Muvalaplin - the first oral drug ever ...
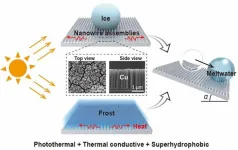
An all-in-one surface design of copper nanowire assemblies to achieve ~100% defrosting efficiency
2023-08-28
Scientists at Dalian University of Technology propose a design of copper nanowire assemblies that can sufficiently enhance the de-icing and defrosting efficiency without conventional energy input. Specifically, the defrosting efficacy approaches 100%, a record-high value compared to reported studies.
The research, published in International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, shows a simple electrochemical method for fabricating nanowire assemblies with controlled pattern, hierarchy, and size. This enables the simultaneous presentation of photothermal, thermal conductive, and superhydrophobic ...
Social justice for traditional knowledge holders will help conserve Europe’s nature
2023-08-28
It is well known that biodiversity of cultural landscapes is threatened by land abandonment and agricultural intensification. Traditional, low chemical and machinery input management systems have long been acknowledged for their diverse benefits to maintain and enhance biodiversity, however, the recognition of traditional knowledge, on which these traditional management practices are based, started only relatively recently. The recognition of traditional knowledge holders themselves is an even more recent phenomenon. A recently published paper aims to ...
Trial re-evaluates routine defibrillator implantation after myocardial infarction
2023-08-28
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 26 Aug 2023: Is the routine implantation of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) in myocardial infarction survivors with heart failure still an adequate therapy for prevention of sudden cardiac death? The PROFID EHRA trial is set to answer this question in a large, multicentre, EU-funded study set to enrol the first patient this summer. The consortium of partners and colleagues involved in the trial, including the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), will meet during ESC Congress 2023 to discuss the start of the study.
Myocardial ...
Price tag on cardiovascular disease in Europe higher than entire EU budget
2023-08-28
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 26 Aug 2023: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) cost the EU an estimated €282 billion in 2021, according to late breaking research presented at ESC Congress 2023.1 Health and long-term care accounted for €155 billion (55%) of these costs, equalling 11% of EU health expenditure. The analysis was a collaborative effort by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the University of Oxford, UK.
Study author Dr. Ramon Luengo-Fernandez of the University of Oxford said: “CVD had a significant impact ...
NIH-funded study supports use of ECMO for critically ill patients with obesity
2023-08-28
NIH-funded study supports use of ECMO for critically ill patients with obesity
ECMO does not appear to complicate treatment for severe respiratory failure for adults with obesity
A National Institutes of Health-supported study suggests that adults with obesity may benefit from the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), an advanced form of breathing support, when in intensive care for respiratory failure. ECMO’s use was previously questioned for patients with obesity due to the belief that it may complicate ...
Muvalaplin, an oral small molecule inhibitor of lipoprotein(a) formation
2023-08-28
About The Study: Muvalaplin was not associated with tolerability concerns and lowered lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) levels up to 65% following daily administration for 14 days in this first-in-human phase 1 study involving healthy participants. Lipoprotein(a) is associated with atherosclerotic disease and aortic stenosis. Longer and larger trials will be required to further evaluate safety, tolerability, and effect of muvalaplin on Lp(a) levels and cardiovascular outcomes.
Authors: Stephen J. Nicholls, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of Monash University in Clayton, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
[Press-News.org] Neuropathologic and clinical findings in young contact sport athletes exposed to repetitive head impactsJAMA Neurology