(Press-News.org) RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- The mosquito-borne infectious disease malaria resulted in about 241 million clinical episodes and 627,000 deaths in 2020. In young children and pregnant women living in areas where the disease is endemic, a major cause of death is Plasmodium falciparum, the most virulent, prevalent, and deadly human malaria parasite.
Scientists are keen to understand the mechanisms that regulate gene expression through the different stages of P. falciparum’s lifecycle because such knowledge can help in the discovery of novel antimalarial therapies. One focus of their research is “lncRNAs,” which are long noncoding ribonucleic acid molecules found in cells of eukaryotes — organisms whose cells have a nucleus. Many noncoding RNAs have been linked to cancer and neurological disorders. LncRNAs are found also to regulate genome structure and gene expression.
A team led by Karine Le Roch, a professor of molecular, cell and systems biology at the University of California, Riverside, studied the role lncRNAs play in P. falciparum and found that one lncRNA — lncRNA-ch14 — partially regulates sexual differentiation and sex determination in P. falciparum.
“We can now target specific lncRNAs to stop P. falciparum’s life cycle progression, including sexual differentiation,” Le Roch said. “We found evidence that lncRNAs are distributed in distinct cellular compartments in P. falciparum. Depending on their localization, they are found to play important roles in regulating gene expression and the malaria parasite’s life cycle progression.”
Study results appear in Nature Communications.
The research team identified 1,768 lncRNAs in P. falciparum, of which 718 lncRNAs had never before been identified. The team validated that some of these novel lncRNAS are critical for the parasite’s life cycle progression.
“Our findings bring new insight into the role of lncRNAs in P. falciparum’s capacity to cause malaria, gene regulation, and sexual differentiation,” said Le Roch, who directs UCR’s Center for Infectious Disease and Vector Research. “This can open up new avenues for targeted approaches towards therapeutic strategies against P. falciparum that are aimed at stopping the parasite’s life cycle progression and its sexual differentiation and blocking the transmission of the parasite into mosquitoes.”
The research was a collaboration with scientists at the University of Washington, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, and The Wellcome Sanger Institute.
The research was supported by grants to Le Roch from the National Institutes of Health and UCR.
The title of the research paper is “Novel insights into the role of long non-coding RNA in the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.”
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment is more than 26,000 students. The campus opened a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual impact of more than $2.7 billion on the U.S. economy. To learn more, visit www.ucr.edu.
END
New approach to fighting malaria
UC Riverside-led study zeroes in on special RNA molecules in the human malaria parasite
2023-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UMass Amherst computer scientists use AI to accelerate computing speed by thousands of times
2023-08-28
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, led by Emery Berger, recently unveiled a prize-winning Python profiler called Scalene. Programs written with Python are notoriously slow—up to 60,000 times slower than code written in other programming languages—and Scalene works to efficiently identify exactly where Python is lagging, allowing programmers to troubleshoot and streamline their code for higher performance.
There are many different programming ...
Rare disease shares mechanism with cystic fibrosis
2023-08-28
Aug. 28, 2023
Images
ANN ARBOR—University of Michigan researchers have discovered that the same cellular mechanism involved in a form of cystic fibrosis is also implicated in a form of a rare disease called cystinosis.
The mechanism cleans up mutated proteins. In cystinosis, a genetic disease, this allows cystine crystals to build up in the cell. This disrupts the cell, and eventually, tissues and ultimately organs, particularly the kidneys and the eyes.
The problem begins when the lysosome, an organelle within the cell, is unable to ...
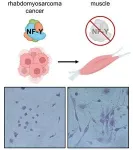
Once rhabdomyosarcoma, now muscle
2023-08-28
“Every successful medicine has its origin story. And research like this is the soil from which new drugs are born,” says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Christopher Vakoc.
For six years, Vakoc’s lab has been on a mission to transform sarcoma cells into regularly functioning tissue cells. Sarcomas are cancers that form in connective tissues like muscle. Treatment often involves chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation—procedures that are especially tough on kids. If doctors could transform cancer cells into healthy cells, it would offer patients a whole new treatment option—one that could spare them and their families a great deal of ...
Past abrupt changes in North Atlantic Overturning have impacted the climate system across the globe
2023-08-28
The Dansgaard-Oeschger events are rapid Northern-Hemisphere temperature jumps of up to 15°C in Greenland that repeatedly occurred within a few decades during the last ice age. “These events are the archetype of abrupt climate changes and further increasing our understanding of them is crucial for more reliable assessments of the risk and possible impacts of future large-scale climate tipping events”, says Niklas Boers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and the Technical University of Munich, one of the authors of the study to be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences PNAS.
In the ...
Historic red tide event of 2020 fueled by plankton super swimmers
2023-08-28
A major red tide event occurred in waters off Southern California in the spring of 2020, resulting in dazzling displays of bioluminescence along the coast. The spectacle was caused by exceedingly high densities of Lingulodinium polyedra (L. polyedra), a plankton species renowned for its ability to emit a neon blue glow. While the red tide captured the public’s attention and made global headlines, the event was also a harmful algal bloom. Toxins were detected at the height of the bloom that had the potential to harm marine life, and dissolved oxygen levels dropped to near-zero as the extreme biomass of the red tide decomposed. This lack of oxygen led to fish die-offs ...
Intravascular imaging associated with improved outcomes compared with angiography
2023-08-28
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 27 Aug 2023: Intravascular imaging-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is associated with a lower rate of target lesion failure compared with angiography-guided PCI, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Numerous randomised trials have compared intravascular imaging-guided PCI with angiography-guided PCI. However, most of these prior trials have used intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). Optical coherence ...
Pulsed field ablation is noninferior to thermal ablation in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
2023-08-28
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 27 Aug 2023: Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is as effective and safe as conventional thermal ablation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF), according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
ESC guidelines recommend catheter ablation after failure of drug therapy in patients with paroxysmal AF.2 Conventional ablation technology uses thermal energy (either heat/radiofrequency energy or cold/cryothermal energy) to ablate the tissue. Unlike thermal ablation, PFA uses high energy electrical pulses to destroy tissue by a process called electroporation. Preclinical ...
Mazin to study ab initio engineering of doped-covalent-bond superconductors
2023-08-28
Mazin To Study Ab Initio Engineering Of Doped-Covalent-Bond Superconductors
Igor Mazin, Professor of Practice for Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Quantum Materials Center, Physics and Astronomy, is set to receive funding for the project: "Collaborative research: Ab Initio Engineering of Doped-Covalent-Bond Superconductors."
This EAGER award will support a joint computational and theoretical effort to guide the search for practical superconducting materials.
Superconductors carry electrical current without any resistance when cooled down below a certain material-dependent ...
Marasco bridging chemistry & AI-empowered imaging for secure & trustworthy human identity verification
2023-08-28
Marasco Bridging Chemistry & AI-Empowered Imaging For Secure & Trustworthy Human Identity Verification
Emanuela Marasco, Assistant Professor, Center for Secure Information Systems, received funding for the project: "EAGER: SaTC: Sweaty Digits: Bridging Chemistry and AI-Empowered Imaging for Secure and Trustworthy Human Identity Verification."
Marasco seeks to characterize a person's extrinsic and intrinsic features for a more accurate representation of their identity by exploiting selected compounds ...
COS researchers transitioning training dataset labeling tool to support discoveries in earth science & heliophysics
2023-08-28
COS Researchers Transitioning Training Dataset Labeling Tool To Support Discoveries In Earth Science & Heliophysics
Chaowei Yang, Professor, Director, NSF Spatiotemporal Innovation Center, Geography and Geoinformation Science, and Jie Zhang, Professor, Physics and Astronomy, received funding for the project: "Transitioning a Training Dataset Labeling Tool (TDLT) to Support Discoveries in Earth Science and Heliophysics."
The researchers are creating a generalizable training dataset labeling tool for both Earth and heliophysics by ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] New approach to fighting malariaUC Riverside-led study zeroes in on special RNA molecules in the human malaria parasite