(Press-News.org) For roughly 80% of breast cancer survivors, treatment doesn’t end with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Instead, for the next five to 10 years, doctors recommend that they take medication to block sex hormones, which can fuel tumor growth and spark recurrence.
The drugs, no doubt, are life-saving: they’ve been shown to cut risk of cancer recurrence by as much as half in patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors (HR+)—the most common form of breast cancer. Yet despite their promised benefits, 40% of patients stop taking them early and a third take them less frequently than directed.
New CU Boulder research, published this month in the "Journal of Clinical Oncology," sheds light on why that is and what doctors and the healthcare system can do about it.
It found that, overall, interventions can increase medication adherence by nearly 1.5 times. But some strategies work better than others.
“Our bottom-line finding is that there are strategies that do work in supporting women to take these life-extending medications, and that we as a cancer care community need to do better,” said senior author Joanna Arch, a professor in the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience and member of the CU Cancer Center on the Anschutz medical campus.
Arch noted that these so-called “adjuvant endocrine therapies (AETs),” like the estrogen-blockers Tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors, can be costly and come with a host of side effects, including weight gain, sexual side effects, joint pain, depression and sleeplessness.
“Imagine going from your normal estrogen activity to little or no estrogen within days. That’s what these medications do,” she said. “But the women who take them as prescribed also have lower recurrence rates and live longer. It’s a dilemma.”
As more next-generation cancer drugs, including chemotherapy agents, shift from infusions provided in a clinic to oral therapies taken at home, the medical community has grown increasingly interested in developing ways to make sure patients take their pills.
In a sweeping meta-analysis, Arch and her colleagues analyzed 25 studies representing about 368,000 women to gain insight into what works and what doesn’t.
The study found that cost-cutting policy changes, such as providing generic alternatives or requiring insurance companies to cover pills at the same level as infusions, consistently worked. Such “oral parity laws” have been passed in 43 states in recent years.
Mobile apps and texts to remind patients to take their medication, and psychological/coping strategies also yielded modest improvements.
The study’s findings around managing side effects were complicated: Simply educating women on side effects, via pamphlets or verbal explanations, generally failed to increase the likelihood that women took their medication as directed.
But things like physical therapy, exercise and behavioral counseling aimed at alleviating or managing side effects often worked.
“Education in and of itself is not enough. That is a clear finding,” said Arch, suggesting that doctors write referrals to practitioners who specialize in side effects and follow up with appointment reminders. “Most oncologists, I believe, don’t realize how low adherence is for these women. They assume that if the write the prescription, it’s being taken.”
One study included in the meta-analysis was Arch’s own.
In it, women were asked to identify their primary motivation for taking their medication—whether it was living to see their child or grandchild grow up, pursuing their art or running a marathon someday. Via an online program, they created a sticker with a photo representing that goal, and the words “I take this for…” below it. Then, they stuck it on their pill box.
Participants were more likely to take their pills, at least for the first month, than those who didn’t.
“Even just a tiny thing like this can help,” said Arch.
Notably, very few studies looked at whether treating depression can help. Arch, aiming to fill this gap, recently launched her own pilot trial.
“One of the most consistent predictors of not adhering to any medication is depression,” she said. “Depression taps motivation.”
The study is the first meta-analysis to show that such interventions can be helpful, and that’s important, said Arch, because insurance companies need data to make decisions about what to cover.
But the study also found that the effects were relatively modest.
She said she hopes the study will spark more research into novel ways to support survivors:
“We have a lot of work to do.”
END
Study sheds light on why breast cancer survivors don’t take their medications, and what can be done about it
2023-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neural network helps design brand new proteins
2023-08-29
WASHINGTON, August 29, 2023 – With their intricate arrangements and dynamic functionalities, proteins perform a plethora of biological tasks by employing unique arrangements of simple building blocks where geometry is key. Translating this nearly limitless library of arrangements into their respective functions could let researchers design custom proteins for specific uses.
In Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, Markus Buehler of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology combined attention neural networks, often referred to as transformers, with graph neural ...
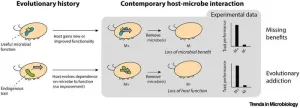
Some hosts have an “evolutionary addiction” to their microbiome
2023-08-29
We’ve long known that hosts malfunction without their microbiome—whether they are missing key microbial species or are completely microbe free. This malfunctioning is usually explained by the need for microbes to perform unique and beneficial functions, but evolutionary ecologist Tobin Hammer of the University of California, Irvine, is questioning that narrative.
In a peer-reviewed opinion article publishing August 29 in the journal Trends in Microbiology, Hammer argues that, in some cases, microbes might not actually be helping their hosts; instead, microbe-free hosts might malfunction because they have evolved an addiction to their microbes. ...
A lightweight wearable device helps users navigate with a tap on the wrist
2023-08-29
Scientists at Rice University in Houston, Texas have developed a fabric-based wearable device that “taps” a user’s wrist with pressurized air, silently helping them navigate to their destination. The study, published August 29 in the journal Device, demonstrated that users correctly interpreted which direction the device was telling them to go an average of 87% of the time. Since the wearable embeds most of its control system within the fabric itself, using air instead of electronics, it can be built lighter and more compact than existing designs.
“We envision this device will be used by individuals who need or desire information to be transmitted ...
Long-term maternal and child outcomes following postnatal SSRI treatment
2023-08-29
About The Study: The results of this study of 61,000 mother-child dyads suggest that postnatal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment was associated with a reduced risk of postnatal depression–associated maternal mental health problems and child externalizing behaviors across early childhood years. These findings suggest that postnatal SSRI treatment may bring benefits in the long term to women with postnatal depression and their offspring.
Authors: Chaoyu Liu, M.D., Ph.D., of King’s College in London, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Cannabis use disorder and reasons for use in a state where recreational cannabis use is legal
2023-08-29
About The Study: In this study of primary care patients in a state with legal recreational cannabis use, cannabis use disorder (CUD) was common among patients who used cannabis. Moderate to severe CUD was more prevalent among patients who reported any nonmedical use. These results underscore the importance of assessing patient cannabis use and CUD symptoms in medical settings.
Authors: Gwen T. Lapham, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.S.W., of the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
#MedEd: How doctors use social media to advance medicine
2023-08-29
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 11:00 A.M. EDT ON TUESDAY, AUGUST 29, 2023
Social media’s effects on propagating misinformation among the lay public are widely debated, but a new paper from JAMA suggests physicians using social media are revolutionizing medical education.
La Jolla, Calif. (August 29, 2023) — Ever wonder what your doctor is doing on social media? A new study published in JAMA led by John W. Ayers, Ph.D., from the Qualcomm Institute within the University of California San Diego, finds some physicians are harnessing the reach ...
Underutilized antidepressant treatment for postnatal depression associated with improved child outcomes at age five
2023-08-29
New research led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment for postnatal depression is associated with improvements in child behaviour up to five years after childbirth.
Up to 15% of women experience postnatal depression which has been shown to be associated with poor outcomes for mothers’ and their children. Researchers at King’s IoPPN, in collaboration with the University of Oslo, analysed data from ...
Broken by bison, aspen saplings having a tough time in northern Yellowstone
2023-08-29
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In northern Yellowstone National Park, saplings of quaking aspen, an ecologically important tree in the American West, are being broken by a historically large bison herd, affecting the comeback of aspen from decades of over-browsing by elk.
Findings of the research led by Luke Painter of Oregon State University were published today in Ecology and Evolution.
The study comes five years after Painter, who teaches ecology and conservation in the OSU College of Agricultural Sciences, published a paper in Ecosphere showing that wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone had been a catalyst for aspen recovery both outside and ...
Partners from more than 100 countries collaborate as LOINC® issues 1,945 new concepts in semiannual release
2023-08-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semiannual content update with 1,945 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations exchange medical data. The release contains newly created content based on requests submitted by stakeholders from more than 100 countries.
LOINC version 2.75 is available for download from the LOINC website and via the LOINC Terminology Service using HL7® FHIR®. The updated version includes new, edited and newly mapped concepts ...
New study will examine impact of lifestyle physical activity on cognition for older adults
2023-08-29
Jason Yang has been awarded nearly $400,000 from the National Institute on Aging to explore the role of lifestyle physical activity (light movements, walking) in cognition among insufficiently active older adults with higher risks for Alzheimer’s or related dementias. The exercise science assistant professor will use the two-year R21 grant to help determine if frequent and regular engagement in lifestyle physical activity over time may benefit cognitive function for this population.
A ...