(Press-News.org)
Research conducted at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health detected significant levels of metals in the blood and urine among marijuana users, concluding that marijuana may be an important and under-recognized source of lead and cadmium exposure. This is among the first studies to report biomarker metal levels among marijuana users and most likely the largest study to date, that links self-reported marijuana use to internal measures of metal exposure, rather than just looking at metal levels in the cannabis plant. The results are published online in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives,
Measurements reported by participants for exclusive marijuana use compared to nonmarijuana-tobacco had significantly higher lead levels in blood (1.27 ug/dL) and urine (1.21 ug/g creatinine).
“Because the cannabis plant is a known scavenger of metals, we had hypothesized that individuals who use marijuana will have higher metal biomarker levels compared to those who do not use,” said Katelyn McGraw, postdoctoral researcher in Columbia Public Health’s Department of Environmental Health Sciences, and the first author. “Our results therefore indicate marijuana is a source of cadmium and lead exposure.”
The researchers combined data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for the years 2005-2018). Led by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) at the CDC, NCHS NHANES is a biannual program of studies designed to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the U. S.
McGraw and colleagues classified the 7,254 survey participants by use: non-marijuana/non-tobacco, exclusive marijuana, exclusive tobacco, and dual marijuana and tobacco use. Five metals were measured in the blood and 16 in urine.
The researchers used four NHANES variables to define exclusive marijuana and tobacco use: current cigarette smoking, serum cotinine levels, self-reported ever marijuana use, and recent marijuana use. Exclusive tobacco use was defined as individuals who either answered yes to ‘do you now smoke cigarettes, or if individuals had a serum cotinine level >10ng/mL.
Marijuana is the third most commonly used drug in the world behind tobacco and alcohol. As of 2022, 21 states and Washington D.C., covering more than 50 percent of the U.S. population, have legalized recreational use of marijuana; and medical marijuana is legal in 38 states and Washington D.C. However, because marijuana is still illegal at the federal level, regulation of contaminants in all cannabis-containing products remains piecemeal and there has been no guidance from federal regulatory agencies like the FDA or EPA. As of 2019, 48.2 million people, or 18 percent of Americans, report using marijuana at least once in the last year.
While 28 states regulate inorganic arsenic, cadmium, lead, and total mercury concentrations in marijuana products, regulation limits vary by metal and by state.
“Going forward, research on cannabis use and cannabis contaminants, particularly metals, should be conducted to address public health concerns related to the growing number of cannabis users,” said Tiffany R. Sanchez, PhD, assistant professor of environmental health sciences at Columbia Public Health, and senior author.
Co-authors are Anne E. Nigra, Joshua Klett, Marisa Sobel, and Ana Navas-Acien, Columbia Public Health; Elizabeth C. Oelsner, Columbia University Irving Medical Center; and Xin Hu, Emory University School of Medicine.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Environmental Health grants P30ES009089 and T32ES007322.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the fourth largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master’s and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit www.mailman.columbia.edu.
END
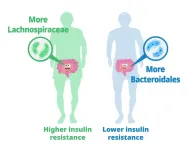
Researchers led by Hiroshi Ohno at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS) in Japan have discovered a type of gut bacteria that might help improve insulin resistance, and thus protect against the development of obesity and type-2 diabetes. The study, published August 30 in the scientific journal Nature, involved genetic and metabolic analysis of human fecal microbiomes and then corroborating experiments in obese mice.
Insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas in response to blood sugar. Normally, it helps get the sugar ...
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 30 August 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Cells
Researchers identify stem cells in the thymus for the first time
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified stem cells in the human thymus for the first time. These cells represent a potential new target to understand immune diseases and cancer and how to boost the immune system.
The thymus is a gland located in the front part of the chest, the place where thymocytes (the cells in the thymus) mature into T ...
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 16:00 BST / 11:00 ET WEDNESDAY 30 AUGUST 2023
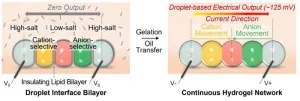
Researchers have developed a miniature battery that could be used to power tiny devices integrated into human tissues.
The design uses an ionic gradient across a chain of droplets – inspired by how electric eels generate electricity.
The device was able to regulate the biological activity of human neurons.
This could open the way to the development of tiny bio-integrated devices, with a range of applications in biology and medicine.
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature ...
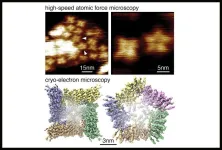
A member of an important class of ion channel proteins can transiently rearrange itself into a larger structure with dramatically altered properties, according to a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The discovery is a significant advance in cell biology, likely solves a long-standing mystery about an unusual feature of some ion channels and has implications for the development of drugs targeting these proteins and for drug delivery.
Ion channels are ubiquitous in the cell membranes of higher organisms. ...
AURORA, Colo. (Aug. 30, 2023) – Scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have made a `paradigm shifting’ discovery on the mechanisms required for learning and memory that could lead to new therapies for Alzheimer’s disease and potentially Down syndrome.
The study was published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
For over 30 years, researchers believed that LTP or long-term potentiation, which is crucial for learning and memory, required enzymatic actions by an enzyme known as CaMKII.
But a team of researchers led by Ulli ...
Modern medicine depends on antibiotics to treat infections by disabling targets inside bacterial cells. Once inside these cells, antibiotics bind to certain sites on specific enzyme targets to stop bacterial growth. Randomly occurring changes (mutations) in the genes for these targets occur naturally, in some cases making the target harder for the antibiotic to attach to, and that bacterial version resistant to treatment.
For this reason, the more antibiotics have been used over time, the greater the chances that bacterial populations will evolve to have mutants resistant to existing antibiotics, and the more urgent the call for new approaches ...
Coastal wetlands and coral reef islands will struggle to grow fast enough to keep pace with rising sea levels driven by climate change, according to a new study published in Nature. The study was conducted by an international team that includes a Tulane University researcher. The findings show that the future of marshes and other low-lying coastal areas depend heavily on whether global warming can be limited to less than 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) as formulated by the Paris Agreement.
A key finding of the paper is that coastal marshes, mangroves, ...
Researchers have a new way to connect quantum devices over long distances, a necessary step toward allowing the technology to play a role in future communications systems.
While today’s classical data signals can get amplified across a city or an ocean, quantum signals cannot. They must be repeated in intervals — that is, stopped, copied and passed on by specialized machines called quantum repeaters. Many experts believe these quantum repeaters will play a key role in future communication networks, allowing enhanced security and enabling connections between remote quantum computers.
The Princeton study, published Aug. ...
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of racial disparities in mortality between Black and white people in the United States. New research from the University of Chicago Medicine suggests that parental incarceration may be contributing to these health gaps.
According to the new study, people who experienced a parent or parental figure’s incarceration anytime before the age of 18 had higher levels of hypertension and coronary disease biomarkers than people whose parents were not incarcerated. These results indicate that mass incarceration may have transgenerational health consequences.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are difficult ...
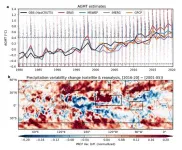
A collaborative international research team led by Professor Yoo-Geun Ham from Chonnam National University and Professor Seung-Ki Min from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has made a discovery on the impact of global warming on global daily precipitation. Using a deep learning approach, they have unveiled a significant change in the characteristics of global daily precipitation for the first time. Their research findings were published on August 30 in the online version of Nature, the ...