(Press-News.org) FINDINGS
People from socioeconomically distressed communities who underwent heart transplantation between 2004 and 2018 faced a 10% greater relative risk of experiencing graft failure and dying within five years compared to people from non-distressed communities. In addition, following implementation of the 2018 UNOS Heart Allocation policy, transplant recipients between 2018 and 2022 faced an approximately 20% increase in relative risk of dying or experiencing graft failure within three years compared with the pre-policy period. This is despite the fact that the proportion of distressed patients remained the same over both eras.
BACKGROUND
Significant socioeconomic disparities persist within the U.S. healthcare system. While previous studies have demonstrated the influence of structural deprivation on cardiovascular health, the impact of community distress on survival following heart transplantation has not been explored.
METHOD
The researchers relied on 2004-2022 data from the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) to ascertain the number of adult heart transplant patients, and the Distressed Communities Index (DCI), which uses neighborhood factors such as unemployment, poverty level, median income and housing vacancies to measure community socioeconomic inequity. Of 36,777 heart transplant patients, 7,450 were from distressed communities.
Study limitations include a lack of granular data such as laboratory values and operative times, unavailability of patient medication adherence for analysis, and an inability to identify transplant centers’ location or proximity to socioeconomically distressed communities.
IMPACT
Structural community distress is linked with inferior survival following heart transplantation, with the disparity gap in outcomes widening since the 2018 Policy Change. Novel structural and systemic interventions addressing social determinants of health are needed to improve follow-up care and outcomes for vulnerable populations. Further, the DCI should be integrated into risk-stratification models to prevent risk-averse transplantation strategies that would disproportionately affect under-served patients. Given compounding ramifications from the COVID19 pandemic, particularly on already vulnerable populations, the field of heart transplantation must directly confront expanding inequity in outcomes.
COMMENT
"While social determinants of health have long been recognized to both shape access to and outcomes following heart transplantation, lack of clear metrics to measure such inequity have limited the development of targeted interventions,” said Sara Sakowitz, a medical student at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA who led the study. “Our work demonstrates community-level socioeconomic distress is linked with inferior survival following heart transplantation, and further establishes this socioeconomic disparity gap is widening. Changes in policy are needed to address persistent inequities in access to health.”
AUTHORS
Additional study authors are Dr. Syed Shahyan Bakhtiyar, Dr. Saad Mallick, Joanna Curry, Dr. Nameer Ascandar, and Dr. Peyman Benharash of UCLA. Bakhtiyar also has an appointment at the University of Colorado.
JOURNAL
The study is published in the peer reviewed journal, Annals of Surgery.
END
Heart transplant patients from socioeconomically distressed communities face higher mortality, organ failure risk
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Striking gold with molecular mystery solution for potential clean energy
2023-09-01
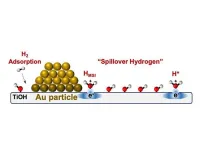
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Hydrogen spillover is exactly what it sounds like. Small metal nanoparticles anchored on a thermally stable oxide, like silica, comprise a major class of catalysts, which are substances used to accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. The catalytic reaction usually occurs on the reactive — and expensive — metal, but on some catalysts, hydrogen atom-like equivalents literally spill from the metal to the oxide. These hydrogen-on-oxide species are called "hydrogen ...
Blood biomarker shows “great promise” predicting progression to Alzheimer’s disease in at-risk population
2023-09-01
DETROIT – Neuroscience researchers at Wayne State University published a review article that confirms the usefulness of neurofilament light (NfL) blood levels to predict the likelihood and rate of progression of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Blood-based NfL is a minimally invasive and easily accessible biomarker, making it a useful clinical biomarker. Youjin Jung and Jessica Damoiseaux, Ph.D., analyzed existing literature to examine the association between serum or plasma NfL and ...
Redo transcatheter aortic valve replacement proven effective, safe
2023-09-01
Cedars-Sinai investigators are leaders in the innovation and use of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) with balloon-expandable valves. They now show that redo TAVR procedures are both safe and effective when compared with situations in which patients with similar risk profiles undergo the same procedure for the first time.
The novel findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal The Lancet, are significant because recent randomized clinical trials have shown that TAVR is a meaningful treatment option for both younger and lower-risk surgical ...
Inflammation may influence weight loss surgery outcomes, new study reveals
2023-09-01
Research funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) has shown that higher levels of inflammation in the blood of patients with obesity undergoing bariatric surgery predicts poorer weight loss six months after the procedure.
Published in Psychological Medicine and led by researchers from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN), King’s College London, this is the first study to investigate the links between depression and inflammation in patients with obesity before and after bariatric surgery. The analysis showed a strong relationship ...
Study shows that low-dose aspirin associated with a 15% lower risk of developing diabetes in people aged over 65 years
2023-09-01
*Note- this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) meeting in Hamburg, October 2-6. Please credit the meeting if you use this story*
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October) shows that use of low dose (100mg daily) aspirin among older adults aged 65 years and older is associated with a 15% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The authors, led by Professor Sophia Zoungas, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, ...
New grant to optimize gut microbes, boost health benefits of broccoli
2023-08-31
URBANA, Ill. — Love it or hate it, broccoli is chock-full of health-promoting chemicals linked to heart health, cancer prevention, immune function, weight management, and more. However, some people are less efficient than others at unlocking those chemical benefits. A research team at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign suggests gut microbe communities may be responsible for the variation. With a new grant from the USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture, the team plans to identify which microbes maximize the benefits of broccoli and other brassica ...
Illuminating new horizons: Navigating nonlinear scattering with precision
2023-08-31
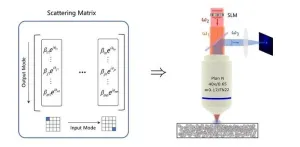
In the intricate world of light, a journey through inhomogeneous media often leads to distortions in space, time, spectrum, and polarization. These distortions, detrimental to applications like optical manipulation, imaging, and communication, have long posed a challenge. Enter the art of wavefront shaping (WS) — a potent tool for correcting these wave maladies in linear optics. But that's not all. Nonlinearity adds a twist, finding purpose in fields from biological sensing to phototherapy. Now, picture combining these forces — ...
Digging deeper into how vaccines work against parasitic disease
2023-08-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have established the effectiveness of vaccines they developed to prevent the disfiguring skin disease leishmaniasis in animal studies, and Phase 1 human trial planning is in motion for the most promising candidate.
But in new work, the research team has determined how these vaccine candidates, created using mutated disease-causing parasites, prompt molecular-level changes in host cells that have specific roles in helping generate the immune response.
Despite using the same CRISPR ...
Housing heroes: New program to support veterans experiencing homelessness
2023-08-31
Since 2009, the number of veterans experiencing homelessness across the United States has shrunk by more than 50%, according to a 2022 Department of Housing report.
With the support of a $150,000 grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the University of Missouri School of Law Veterans Clinic is aiming to continue this trend here at home with a new program designed to further empower veterans in taking steps out of homelessness.
The Veterans Outreach Program will help attorneys connect with veterans experiencing homelessness with the goal of offering them the legal assistance ...
Mapping the coronavirus spike protein could provide insight into vaccine development
2023-08-31
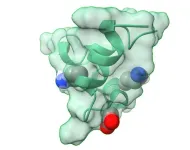
Although the COVID-19 pandemic was the first time most of humanity learned of the now infamous disease, the family of coronaviruses was first identified in the mid-1960s. In a new study, molecular biologist Steven Van Doren, a scientist in the University of Missouri College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources, has uncovered unexpected actions of a key player in how the coronavirus infects its target — a discovery that could guide further vaccine development.
Funded by a National Science Foundation (NSF) grant, Van Doren and his team studied the fusion peptide, an important feature of the spike protein that serves to bind the virus with ...