(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. – States that enacted laws permitting children to carry and apply sunscreen at school experienced an increased interest in sun protection and a higher rate of sunscreen use among adolescents, according to new research by a University of Massachusetts Amherst resource economist.
Brandyn Churchill, assistant professor of resource economics at UMass Amherst, is co-author of the study that is the first to examine state-level “SUNucate” laws, which permit students to apply sunscreen at school and wear sun-protective clothing even if it does not conform to school dress codes. In some cases, the laws also include health class curricula on skin cancer prevention.
“These policies are effective at increasing awareness about sun protection and use of sunscreen, with no discernable downside,” Churchill says.
Because the federal Food and Drug Administration considers sunscreen an over-the-counter drug, many states have prohibited students from carrying and applying sunscreen in school as part of broader medication bans. In these states, students wishing to use sunscreen at school might have to obtain a note from a physician and apply it in front of a school nurse.
To overcome this barrier, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association assembled a coalition of more than 50 stakeholders, crafting model SUNucate legislation to create a specific exception for sunscreen use in schools. The number of states that have adopted policies based on the model language has grown from one in 2013 to 27 this year.
Churchill and his co-authors find SUNucate laws are associated with increased Google searches related to sun protection. For example, search popularity for “sunscreen” increased by an average of 27.2% in states that enacted SUNucate laws compared to states without them.
In addition, the legislation is linked to an 8.3% increase in sunscreen use by high school students, based on self-reported results in the national Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
“The increase appears to be led by populations that typically are not large sunscreen users,” Churchill says. “What we see in the data is that it’s the white boys and non-white girls who seem to be driving this effect — groups that historically had lower rates of sunscreen use.”
SUNucate laws eliminate the ambiguity of whether students are allowed to apply sunscreen at school, policies that may vary by school district or even from school to school.
“These laws provide clarity to students, parents and educators,” Churchill says. “For legislators, they carry a low cost to enact and are relatively uncontroversial. This seems to be one of the bipartisan issues for the time: Kids should use sunscreen.”
Churchill collaborated on the research with Christopher S. Carpenter and Michelle Marcus of Vanderbilt University and Dr. Mary-Margaret Chren of Vanderbilt University Medical Center. The study was funded in part by the American Cancer Society.
The full paper, “State SUNucate Laws, the popularity of Google Searches for Terms Related to Sun Protection, and Youth Sunscreen Use,” is published in the latest edition of the journal Health Behavior and Policy Review.
Contacts: Brandyn Churchill, bfchurchill@umass.edu
Aaron Kupec, akupec@umass.edu
END
UMass Amherst researcher shines light on effectiveness of school sunscreen legislation
‘SUNucate’ laws linked to increased interest in sun protection, youth sunscreen use
2023-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fossil spines reveal deep sea’s past
2023-09-05
Right at the bottom of the deep sea, the first very simple forms of life on earth probably emerged a long time ago. Today, the deep sea is known for its bizarre fauna. Intensive research is being conducted into how the number of species living on the sea floor have changed in the meantime. Some theories say that the ecosystems of the deep sea have emerged again and again after multiple mass extinctions and oceanic upheavals. Today's life in the deep sea would thus be comparatively young in the history of the Earth. But there is increasing evidence that parts of this world are much older than previously thought. A research team led by the University ...
MSU researchers discover link between cholesterol and diabetic retinopathy
2023-09-05
Images
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Advancements that could lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment for diabetic retinopathy, a common complication that affects the eyes, have been identified by a multi-department research team from Michigan State and other universities.
Their findings were recently published in Diabetologia, the official journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Additional contributors are from the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Case Western Reserve University and Western University ...
New model helps FAMU-FSU researchers locate best spots for field hospitals after disasters
2023-09-05
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers want Floridians to be prepared when the next pandemic or hurricane hits the state. A new study published in the International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction examines the best locations for field hospitals that can supplement health care facilities when resources are stretched thin.
“One of the goals of RIDER is to look after our most vulnerable when disasters hit,” said Eren Ozguven, director of the Resilient Infrastructure ...
OHSU scientists discover new cause of Alzheimer’s, vascular dementia
2023-09-05
Researchers have discovered a new avenue of cell death in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
A new study, led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University and published online in the journal Annals of Neurology on Aug. 21, reveals for the first time that a form of cell death known as ferroptosis — caused by a buildup of iron in cells — destroys microglia cells, a type of cell involved in the brain’s immune response, in cases of Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia.
The ...
JNM publishes consensus statement on patient selection and appropriate use of Lu-177 PSMA-617 radionuclide therapy
2023-09-05
Reston, VA—The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) has issued a new consensus statement to provide standardized guidance for the selection and management of metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients being treated with 177Lu-PSMA radionuclide therapy. The statement, published in the July issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, also reviews current clinical struggles physicians face during treatment with 177Lu-PSMA-617 radionuclide therapy.
Recently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved 177Lu-PSMA-617 for the treatment of men with mCRPC after progressing on taxane-based chemotherapy ...
Making plant-based meat more ‘meaty’ — with fermented onions
2023-09-05
Plant-based alternatives such as tempeh and bean burgers provide protein-rich options for those who want to reduce their meat consumption. However, replicating meat's flavors and aromas has proven challenging, with companies often relying on synthetic additives. A recent study in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry unveils a potential solution: onions, chives and leeks that produce natural chemicals akin to the savory scents of meat when fermented with common fungi.
When food producers want to make plant-based meat alternatives taste ...
Water-quality risks linked more to social factors than money
2023-09-05
When we determine which communities are more likely to get their water from contaminated supplies, median household income is not the best measure.
That’s according to a recent study led by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin that found social factors — such as low population density, high housing vacancy, disability and race — can have a stronger influence than median household income on whether a community’s municipal water supply is more likely to have health-based water-quality violations. In general, rural communities and communities that grew up around large industries that have since left are most likely to face water-quality issues.
About 10% ...
Researchers use AI to find new magnetic materials without critical elements
2023-09-05
A team of scientists from Ames National Laboratory developed a new machine learning model for discovering critical-element-free permanent magnet materials. The model predicts the Curie temperature of new material combinations. It is an important first step in using artificial intelligence to predict new permanent magnet materials. This model adds to the team’s recently developed capability for discovering thermodynamically stable rare earth materials.
High performance magnets are essential for technologies such as wind energy, data storage, electric vehicles, ...
Aging alters pancreatic circadian rhythm
2023-09-05
“Overall, our study identified previously unknown circadian transcriptome reorganization of pancreas by aging [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- September 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, “Reorganization of pancreas circadian transcriptome with aging.”
The evolutionarily conserved circadian system allows organisms to synchronize internal processes with 24-h cycling environmental timing cues, ensuring optimal adaptation. Like other organs, the pancreas function is under circadian control. Recent evidence ...
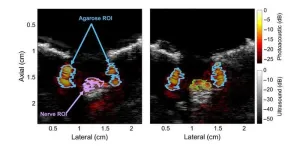
Visualizing nerves with photoacoustic imaging
2023-09-05
Invasive medical procedures, such as surgery requiring local anesthesia, often involve the risk of nerve injury. During operation, surgeons may accidentally cut, stretch, or compress nerves, especially when mistaking them for some other tissue. This can lead to long-lasting symptoms in the patient, including sensory and motor problems. Similarly, patients receiving nerve blockades or other types of anesthesia can suffer from nerve damage if the needle is not placed at the correct distance from the targeted peripheral nerve.
Consequently, researchers have been trying to develop medical imaging techniques to mitigate the risk of nerve damage. For instance, ultrasound and magnetic resonance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
[Press-News.org] UMass Amherst researcher shines light on effectiveness of school sunscreen legislation‘SUNucate’ laws linked to increased interest in sun protection, youth sunscreen use