(Press-News.org) [Bethesda, Maryland, USA -- September 6] The new Climate Intervention Environmental Impact Fund (CIEIF, www.cieif.org) begins operations today, with the goal of helping kickstart new approaches to restoring Earth’s climate in the face of rapid deterioration. CIEF makes direct grants to investigators worldwide working to stop and reverse global warming. The grants are focused on predictive environmental impact assessments, impact modeling studies, and stakeholder engagement for proposed small-scale field tests of innovative climate intervention technologies. CIEIF also offers investigators expert advice on doing impact assessment and stakeholder outreach.
CIEIF is now taking applications for 2023 for three awards of $50,000 each. The due date for applying is November 1. Grants will be made by December 15.
To be eligible, an applicant’s technology must be ready for field testing and potentially scalable to globally relevant levels. Within those criteria, the Fund is open to a range of ideas such as marine cloud brightening, coatings and structures that remove greenhouse gases, enhanced weathering, ice and land albedo enhancements, methane removal, ocean fertilization, and other ocean interventions.
Certain other technologies are not eligible for CIEIF financial support. For example, field tests of stratospheric solar radiation management (SRM) are ineligible, given how difficult it would be to control its effects and to govern its use. CIEIF also excludes grants for carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) and direct air capture (DAC), since they are already backed by large funding programs.
A key criterion for CIEIF-funded projects is commitment to transparency, including publishing results of the analysis of the project. CIEIF funding will neither replace nor undermine any applicable governmental permit processes; instead, it will complement them.
“We believe independent, objective, environmental impact analysis and well-conceived stakeholder outreach are key for progress toward scalable climate solutions,” said CIEIF’s Manager Peter T. Jenkins, a longtime Washington, DC environmental attorney and program manager with extensive experience in environmental impact assessment. “CIEIF fills a vital need for non-bureaucratic funding in an area that too many investigators have ignored or taken lightly to date. And we will aim to increase our grants in future annual funding cycles.”
In addition to Peter Jenkins CIEF is advised by Renaud de Richter, PhD., one of the world’s most knowledgeable scientists on innovative climate interventions with numerous peer-reviewed publications in the field, and attorney John Fitzgerald, who has decades of U.S. and international experience in environmental law and policy including impact assessments.
For more details, see www.cieif.org.
END
New global climate restoration fund announces first grant cycle
Applications open to fund environmental impact studies and stakeholder outreach
2023-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
IU researchers identify new gene mutation that alters Alzheimer’s disease risk
2023-09-06
INDIANAPOLIS—A groundbreaking study led by experts from Indiana University School of Medicine has shed new light on the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer's disease. The team's research, rooted in human genetics studies, has unearthed a critical mutation within a key gene operating in the brain's immune cells, potentially elevating the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
The research team included several IU investigators within Stark Neurosciences Research Institute—Gary Landreth, PhD, the Martin Professor of Alzheimer’s Research; Bruce Lamb, PhD, executive director of Stark Neuroscience Research Institute; Stephanie Bissel, PhD, assistant ...
NIH investigates multidrug-resistant bacterium emerging in community settings
2023-09-06
New “hypervirulent” strains of the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae have emerged in healthy people in community settings, prompting a National Institutes of Health research group to investigate how the human immune system defends against infection. After exposing the strains to components of the human immune system in a laboratory “test tube” setting, scientists found that some strains were more likely to survive in blood and serum than others, and that neutrophils (white blood cells) are more likely to ingest and kill some strains than others. The study, published in mBio, was led by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
“This ...
Study reports discovery of new cell type in thymus
2023-09-06
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- It came as a surprise to Professor David Lo and his graduate student Diana Del Castillo when they were recently consulted by researchers in Israel for their expertise on specialized cells called Microfold cells, or M cells, which are mostly known for their presence in the intestinal epithelium. The Israeli group had identified similar cells in the thymus, an organ located just above the heart that makes lymphocytes — white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system and protect the body against infection.
Lo, a distinguished professor of biomedical sciences in the UC Riverside School of Medicine, and Del Castillo, ...
Devices offers long-distance, low-power underwater communication
2023-09-06
MIT researchers have demonstrated the first system for ultra-low-power underwater networking and communication, which can transmit signals across kilometer-scale distances.
This technique, which the researchers began developing several years ago, uses about one-millionth the power that existing underwater communication methods use. By expanding their battery-free system’s communication range, the researchers have made the technology more feasible for applications such as aquaculture, coastal hurricane prediction, and climate change modeling.
“What started as a very exciting ...
Beauty salon–based intervention increases trust of PrEP among Black cisgender women
2023-09-06
September 6, 2023 — Among African American and other Black cisgender women, a beauty salon–based intervention improved knowledge and awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against HIV and increased trust in it, according to a pilot study published in the September issue of The Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (JANAC), the official journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care. JANAC is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
However, most study participants did not self-identify as requiring PrEP or having risk factors for HIV. "Like ...
Pumping like the heart
2023-09-06
Pumping liquids may seem like a solved problem but optimizing the process is still an area of active research. Any pumping application—from industrial scales to heating systems at home—would benefit from a reduction in energy demands. Researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now showed how pulsed pumping can reduce both friction from and energy consumption of pumping. For this, they took inspiration from a pumping system intimately familiar to everyone: the human heart.
According to an international study, nearly twenty percent of global electric power are used for pumping liquids around—ranging from industrial applications ...
Chinese paleontologists find new fossil link in bird evolution
2023-09-06
Birds descended from theropod dinosaurs by the Late Jurassic, but our understanding of the earliest evolution of the Avialae, the clade comprising all modern birds but not Deinonychus or Troodon, has been hampered by a limited diversity of fossils from the Jurassic.
As of now, no definitive avialans have been reported except from the Middle–Late Jurassic Yanliao Biota in northeast China (166–159 million years ago; Ma) and the slightly younger German Solnhofen Limestones, which preserve Archaeopteryx. Consequently, there is a gap of about 30 million years before the oldest ...
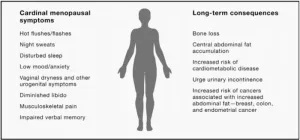
Review of over 70 years of menopause science highlights research gaps and calls for individualized treatment
2023-09-06
Although about half of people go through menopause, less than 15% of them receive effective treatment for their symptoms. Treatment options for people experiencing irritating or severe menopause symptoms are often under researched, and some have questionable efficacy, or cause harmful side effects. In a comprehensive review publishing in the journal Cell on September 6, a team of world-renowned menopause experts summarizes what we know about menopause, calls for more research into the timeline and treatment of menopause, ...
Commercialization of cannabis linked to increased traffic injuries
2023-09-06
Ottawa, ON, September 5, 2023 – Annual rates of emergency department visits for cannabis-involved traffic injury increased by 475 percent over 13 years, according to a new study from The Ottawa Hospital, Bruyère Research Institute, and ICES.
The study examined cannabis-involvement in emergency department (ED) visits for traffic injuries between 2010 and 2021 and looked for changes after the legalization of cannabis in October 2018 and following the commercialization of the legal market (expanded cannabis products and retail stores), which overlapped with the ...
The discovery of a new kind of cell shakes up neuroscience
2023-09-06
Neuroscience is in great upheaval. The two major families of cells that make up the brain, neurons and glial cells, secretly hid a hybrid cell, halfway between these two categories. For as long as Neuroscience has existed, it has been recognized that the brain works primarily thanks to the neurons and their ability to rapidly elaborate and transmit information through their networks. To support them in this task, glial cells perform a series of structural, energetic and immune functions, as well as stabilize physiological constants. Some of these glial cells, known as astrocytes, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
[Press-News.org] New global climate restoration fund announces first grant cycleApplications open to fund environmental impact studies and stakeholder outreach