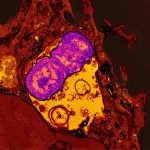
(Press-News.org) New “hypervirulent” strains of the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae have emerged in healthy people in community settings, prompting a National Institutes of Health research group to investigate how the human immune system defends against infection. After exposing the strains to components of the human immune system in a laboratory “test tube” setting, scientists found that some strains were more likely to survive in blood and serum than others, and that neutrophils (white blood cells) are more likely to ingest and kill some strains than others. The study, published in mBio, was led by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
“This important study is among the first to investigate interaction of these emergent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains with components of human host defense,” Acting NIAID Director Hugh Auchincloss, M.D., said. “The work reflects the strength of NIAID’s Intramural Research Program. Having stable research teams with established collaborations allows investigators to draw on prior work and quickly inform peers about new, highly relevant public health topics.”
More than a century ago scientists identified K. pneumoniae as a cause of serious, often fatal, human infections, mostly in people already ill or with weakened immune systems and especially people in hospitals. Over a span of many decades, some strains developed resistance to multiple antibiotics, and became difficult to treat. This bacterium, often called classical Klebsiella pneumoniae (cKp), ranks as the third most common pathogen isolated from hospital bloodstream infections. Certain other Klebsiella pneumoniae strains cause severe infections in healthy people in community settings (outside of hospitals) even though they are not multidrug-resistant. They are known as hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, or hvKp. More recently, strains with both multidrug resistance and hypervirulence characteristics, so-called MDR hvKp, have emerged in both settings.
NIAID scientists have studied this general phenomenon before. In the early 2000s they observed—and actively investigated—virulent strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria that had emerged in U.S. community settings and caused widespread infections in otherwise healthy people.
Now, the same NIAID research group at Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, is investigating similar questions about the new Klebsiella strains, such as whether the microbes can evade human immune system defenses. Their findings were unexpected: the hvKp strains were more likely to survive in blood and serum than MDR hvKp strains. And neutrophils had ingested less than 5% of the hvKp strains, but more than 67% of the MDR hvKp strains—most of which were killed.
The researchers also developed an antibody serum specifically designed to help neutrophils ingest and kill two selected hvKp and two selected MDR hvKp strains. The antiserum worked, though not uniformly in the hvKp strains. These findings suggest that a vaccine approach for prevention/treatment of infections is feasible.
Based on the findings, the researchers suggest that the potential severity of infection caused by MDR hvKp likely falls in between the classical and hypervirulent forms. The work also suggests that the widely used classification of K. pneumoniae into cKp or hvKp should be reconsidered.
The researchers also are exploring why MDR hvKp are more susceptible to human immune defenses than hvKp: Is this due to a change in surface structure caused by genetic mutation? Or perhaps because combining components of hypervirulence and antibiotic resistance reduces the bacterium's ability to replicate and survive in a competitive environment.
As a next step, the research team will determine the factors involved in MDR hvKp susceptibility to the body’s immune defenses using mouse infection models. Ultimately, this knowledge could inform treatment strategies to prevent or decrease disease severity.
Reference: F DeLeo et al. Interaction of multidrug-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae with components of human innate host defense. mBio DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01949-23 (2023).
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- It came as a surprise to Professor David Lo and his graduate student Diana Del Castillo when they were recently consulted by researchers in Israel for their expertise on specialized cells called Microfold cells, or M cells, which are mostly known for their presence in the intestinal epithelium. The Israeli group had identified similar cells in the thymus, an organ located just above the heart that makes lymphocytes — white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system and protect the body against infection.
Lo, a distinguished professor of biomedical sciences in the UC Riverside School of Medicine, and Del Castillo, ...
MIT researchers have demonstrated the first system for ultra-low-power underwater networking and communication, which can transmit signals across kilometer-scale distances.
This technique, which the researchers began developing several years ago, uses about one-millionth the power that existing underwater communication methods use. By expanding their battery-free system’s communication range, the researchers have made the technology more feasible for applications such as aquaculture, coastal hurricane prediction, and climate change modeling.
“What started as a very exciting ...
September 6, 2023 — Among African American and other Black cisgender women, a beauty salon–based intervention improved knowledge and awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against HIV and increased trust in it, according to a pilot study published in the September issue of The Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (JANAC), the official journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care. JANAC is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
However, most study participants did not self-identify as requiring PrEP or having risk factors for HIV. "Like ...
Pumping liquids may seem like a solved problem but optimizing the process is still an area of active research. Any pumping application—from industrial scales to heating systems at home—would benefit from a reduction in energy demands. Researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now showed how pulsed pumping can reduce both friction from and energy consumption of pumping. For this, they took inspiration from a pumping system intimately familiar to everyone: the human heart.
According to an international study, nearly twenty percent of global electric power are used for pumping liquids around—ranging from industrial applications ...
Birds descended from theropod dinosaurs by the Late Jurassic, but our understanding of the earliest evolution of the Avialae, the clade comprising all modern birds but not Deinonychus or Troodon, has been hampered by a limited diversity of fossils from the Jurassic.
As of now, no definitive avialans have been reported except from the Middle–Late Jurassic Yanliao Biota in northeast China (166–159 million years ago; Ma) and the slightly younger German Solnhofen Limestones, which preserve Archaeopteryx. Consequently, there is a gap of about 30 million years before the oldest ...
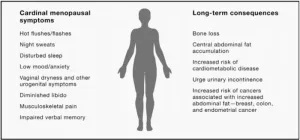
Although about half of people go through menopause, less than 15% of them receive effective treatment for their symptoms. Treatment options for people experiencing irritating or severe menopause symptoms are often under researched, and some have questionable efficacy, or cause harmful side effects. In a comprehensive review publishing in the journal Cell on September 6, a team of world-renowned menopause experts summarizes what we know about menopause, calls for more research into the timeline and treatment of menopause, ...
Ottawa, ON, September 5, 2023 – Annual rates of emergency department visits for cannabis-involved traffic injury increased by 475 percent over 13 years, according to a new study from The Ottawa Hospital, Bruyère Research Institute, and ICES.
The study examined cannabis-involvement in emergency department (ED) visits for traffic injuries between 2010 and 2021 and looked for changes after the legalization of cannabis in October 2018 and following the commercialization of the legal market (expanded cannabis products and retail stores), which overlapped with the ...
Neuroscience is in great upheaval. The two major families of cells that make up the brain, neurons and glial cells, secretly hid a hybrid cell, halfway between these two categories. For as long as Neuroscience has existed, it has been recognized that the brain works primarily thanks to the neurons and their ability to rapidly elaborate and transmit information through their networks. To support them in this task, glial cells perform a series of structural, energetic and immune functions, as well as stabilize physiological constants. Some of these glial cells, known as astrocytes, ...
By improving hospital care pathways, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center successfully reduced inpatient opioid use by 50% after pancreatic cancer surgery and cut the median opioid prescription volumes at discharge to zero. This approach, described in a study published today in JAMA Surgery, could help reduce the risk of long-term opioid dependence in patients.
In this cohort study, which involved 832 patients undergoing pancreatic resection surgery, the researchers investigated how making incremental modifications to post-surgery procedures affected the amounts of opioids used by inpatients and at the point of discharge. In less ...
Analysis led by Brigham researchers showed an increase in out-of-state abortion travelers to Massachusetts from other states including Texas, Louisiana, Florida, and Georgia after Dobbs.
Use of non-profit funding by charitable organizations for abortion care more than doubled among out-of-state travelers
A rigorous analysis by researchers confirms a rise in out-of-state travelers coming to Massachusetts to seek abortion care. In a new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member ...