(Press-News.org) Toronto, ON —Older adults who have had cancer had a high risk of experiencing symptoms of depression during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic according to a new study published in Cancer Management and Research.
The study was focused on a sample of 2486 adults aged 50 and older with a history of cancer who participated in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Among the 1765 individuals from the study who had a history of cancer but no lifetime history of depression, researchers found that 1 in 8 experienced depression for the first time during the early stages of the pandemic.
“The findings of our study indicate the substantial impact the pandemic had on the mental health of individuals with cancer,” said first author Meghan Bird, research assistant at the Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social work at the University of Toronto. “Even among those with no history of depression, the pandemic took a significant toll on worsening their mental health.”
“Older adults with cancer also have to navigate the stress of being particularly vulnerable to severe COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality,” said co-author Andie MacNeil, researcher in the Institute for Life Course and Aging at the University of Toronto. “While strict adherence to lockdowns was an important step for many cancer patients to minimize their risk of COVID-19 infection, for many individuals this also meant forgoing social support, which is an important source of strength during cancer treatment and recovery.”
When the researchers focused on the 786 individuals who had previously experienced depression, they found that approximately one-half of these individuals experienced a recurrence or persistence of depression during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Older adults who experienced depression in the past were a particularly vulnerable subset of the population,” said co-author Ying Jiang, Senior Epidemiologist at the Public Health Agency of Canada. She emphasized that “their difficulties were amplified if they had functional limitations, which doubled the odds of depression in this group.”
Experiencing family conflict during the pandemic was associated with an approximate four-fold risk of both new and recurrent depression among older adults with a history of cancer. This finding is in keeping with research that has identified interpersonal conflict as a risk factor for depression among older adults. Other research indicates extended periods of lockdown and quarantine increase familial conflict. “Of particular concern, the pandemic also reduced access to many coping strategies that can help mitigate family conflict, such as time spent outside the home and time spent with friends.” said co-author Grace Li, PhD candidate in the Sociology Department at the University of Victoria.
Incident depression (or depression experienced for the first time) was almost 50% higher among women. Gender roles may have contributed to this increased risk for depression. “Women are more likely to take on time-consuming caretaking roles and household labor. This aligns with existing research which suggests that caretaking roles may be associated with an increased risk of depression,” said co-author, Margaret de Groh, Scientific Manager at the Public Health Agency of Canada.
Esme Fuller-Thomson, senior author and Professor at FIFSW and Director of the Institute for Life Course & Aging says she hopes the study’s findings can help guide healthcare workers and social service providers better understand the pandemic’s impact on the mental health of people with cancer. “Future research should continue to examine depression among older adults with cancer to better understand the pandemic’s long-term impacts,” Fuller-Thomson said.
END
High levels of depression found among Canadian older adults with cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic
The risk of depression was higher among older adults with cancer who were lonely, those with functional limitations, and those who experienced an increase in family conflict during the pandemic
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Timothy Huang awarded $2.6M to solve Alzheimer’s disease puzzle
2023-09-07
With the help of a new grant from the National Institute of Health for more than $2.6 million, Assistant Professor Timothy Huang, Ph.D., will continue his research on the role of the brain’s immune cells on the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease affects more than 47 million people worldwide, with 10 million new cases of dementia diagnosed each year. This number will continue to grow as the world population ages. Newly approved FDA treatments for Alzheimer’s remove beta-amyloid, a protein that accumulates into plaques, from the brain. However, ...
Culture-friendly therapies for treating anxiety and depression in Japanese youth
2023-09-07
Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT) have become increasingly popular over the past few decades. This psychological treatment, used to treat problems ranging from marital issues, eating disorders, anxiety disorders and depression, has been adopted by clinicians around the world. However, the implementation of CBT still lags outside the Western countries where it was first developed.
In a new review article, researchers examined the most popular CBT programs for young people in Japan, a country that ...
Faulkner to be honored by American Heart Association
2023-09-07
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Sept. 7, 2023) – Jessica Faulkner, PhD, a physiologist whose research is focused on sex differences in cardiovascular disease at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, is the recipient of the Harry Goldblatt Award for New Investigators from the American Heart Association’s 2023 Hypertension Council. She will be honored at the Hypertension Scientific Sessions in Boston this week.
This prestigious award is named for the pathologist who established the first animal model of hypertension in 1934 and recognizes an early career independent investigator working in hypertension or cardiovascular research who has significantly contributed ...
New test shows promise for detecting hard-to-find cervical cancers
2023-09-07
September 7, 2023—(BRONX, NY)—In findings with potentially important implications for cervical cancer screening, scientists at the National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated Montefiore Einstein Cancer Center (MECC) have developed a test for detecting a type of cervical cancer that Pap tests often miss. The findings published online today in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI).
“Our novel test appears sensitive for detecting cervical adenocarcinoma [ADC]—which now accounts for up to 25% of cervical cancer cases—as well as its precursor ...
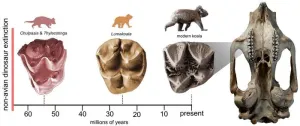
New koala relative fills a branch of Australia’s unique marsupial story
2023-09-07
Koalas are endangered in much of Australia now but in in the past there were multiple species living across the continent. The discovery of an ancient relative of the koala helps fill a 30 million year gap in the amazing evolution of Australia’s marsupials, according to a new study by Australian and British scientists published in Scientific Reports.
The study was led by Flinders University PhD student Arthur Crichton, who found fossil teeth of the new species at the Pwerte Marnte Marnte fossil site south of Alice ...
Eye-tracking technology helps give a voice to older people living with dementia
2023-09-07
More than 50% of Australians living in residential aged care facilities have a dementia diagnosis, with aged care services around the world preparing for the number of older people aged 65 years and above to double in the next 30 years.
For the first time, experts at the Caring Futures Institute at South Australia’s Flinders University are using innovative eye-tracking technology to ensure that the voices of all older people are heard to drive positive and effective change in keeping with the Royal Commission into Aged Care Quality and Safety’s call to re-assess the quality of aged care in Australia.
The Flinders University ...
Capturing carbon in savannas: New research examines role of grasses for controlling climate change
2023-09-07
In recent years, the escalating impact of global warming has prompted efforts to reverse troubling trends, often by planting trees to capture and remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it. New research from a team led by Young Zhou, from the Quinney College of Natural Resources and the Ecology Center, shows that, in addition to trees, humble grasses also play an essential role in capturing carbon — more important than previously thought.
A recent initiative set its sights on capturing carbon in tropical savannas, an ecosystem characterized by shared space of trees and grasses. The project initiated ...
Street medicine filling a major gap by providing behavioral health care for people who are homeless
2023-09-07
Mental health and substance use disorders are prevalent among people experiencing homelessness, yet access to care for these health issues is challenging for people living on the streets. Now, a new survey conducted by a team of researchers from USC Street Medicine found that, in California, street medicine programs are helping to fill this gap, delivering critical, high-level mental health and substance use treatments to the state’s unsheltered population.
The survey, published in Community Mental Health Journal, shows that street medicine has the potential to serve as the basis for a strategy to expand access to behavioral health care for people who ...
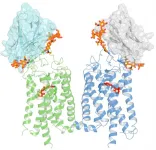
UC Irvine researchers discover a nanobody which may lead to treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa
2023-09-07
A team of scientists from the University of California, Irvine, believe they have discovered a special antibody which may lead to a treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa, a condition that causes loss of central vision, as well as night and color vision.
The study, Structural basis for the allosteric modulation of rhodopsin by nanobody binding to its extracellular domain, was published in Nature Communications. Authors of the study were Arum Wu, PhD, David Salom, PhD, John D. Hong, Aleksander Tworak, PhD, Philip D. Kiser, PharmD, PhD, and Krzysztof Palczewski, PhD, in the Department ...
Use of common painkillers alongside hormonal contraception linked to heightened risk of blood clots
2023-09-07
Women who use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers alongside hormonal contraception appear to be at a small increased risk of blood clots known as venous thromboembolism (VTE), finds a large Danish study published by The BMJ today.
The risk was greater in women using combined oral contraceptives containing third or fourth generation progestins, but smaller in women using progestin-only tablets, implants and coils, alongside the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen.
The researchers stress ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] High levels of depression found among Canadian older adults with cancer during the COVID-19 pandemicThe risk of depression was higher among older adults with cancer who were lonely, those with functional limitations, and those who experienced an increase in family conflict during the pandemic