(Press-News.org) Research Highlights:
An analysis of data from a long-running study of more than 11,000 adults from four diverse communities in the United States has found that adults who had high blood pressure while both seated upright and lying supine (flat on their backs) had a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure or premature death compared to adults without high blood pressure while upright and supine.
Adults who had high blood pressure while lying supine but not while seated upright had similar elevated risks of heart attack, stroke, heart failure or premature death as adults who had high blood pressure in both supine and upright positions.
The increased risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure or premature death did not differ by the type of blood pressure medication used among participants.
Embargoed until 6:30a.m. CT/7:30 a.m. ET Thursday, Sept. 7, 2023
BOSTON, Sept. 7, 2023 — People who had high blood pressure while lying flat on their backs had a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, heart failure or premature death, according to new research to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Hypertension Scientific Sessions 2023, to be held Sept. 7-10, 2023, in Boston. The meeting is the premier scientific exchange focused on recent advances in basic and clinical research on high blood pressure and its relationship to cardiac and kidney disease, stroke, obesity and genetics.
The autonomic nervous system regulates blood pressure in different body positions; however, gravity may cause blood to pool when seated or upright, and the body is sometimes unable to properly regulate blood pressure during lying, seated and standing positions, the authors noted.
“If blood pressure is only measured while people are seated upright, cardiovascular disease risk may be missed if not measured also while they are lying supine on their backs,” said lead study author Duc M. Giao, a researcher and a 4th-year M.D. student at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
To examine body position, blood pressure and heart health risk, the researchers examined health data for 11,369 adults from the longitudinal Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. The data on supine and seated blood pressure was gathered during the enrollment period, ARIC visit 1, which took place between 1987–1989. Participants had their blood pressure taken while briefly lying down at a clinic. The average age of participants at that time was 54 years old; 56% of the group self-identified as female; and 25% of participants self-identified as Black race. Participants in this analysis were followed for an average of 25 to 28 years, up through ARIC visit 5, which includes health data collected from 2011-2013.
The researcher’s findings included:
16% percent of participants who did not have high blood pressure — defined in this study as having top and bottom blood pressure measures greater than or equal to 130/80 mm Hg — while seated had high blood pressure while lying supine (flat on their backs), compared to 74% of those with seated high blood pressure who also had supine high blood pressure.
In comparison to participants who did not have high blood pressure while seated and supine, participants who had high blood pressure while seated and supine had a 1.6 times higher risk of developing coronary heart disease; a 1.83 times higher risk of developing heart failure; a 1.86 times higher risk of stroke; a 1.43 times higher risk of overall premature death; and a 2.18 times higher risk of dying from coronary heart disease
Participants who had high blood pressure while supine but not while seated had similar elevated risks as participants who had high blood pressure while both seated and supine.
Differences in blood pressure medication use did not affect these elevated risks in either group.
“Our findings suggest people with known risk factors for heart disease and stroke may benefit from having their blood pressure checked while lying flat on their backs,” Giao said.
“Efforts to manage blood pressure during daily life may help lower blood pressure while sleeping. Future research should compare supine blood pressure measurements in the clinic with overnight measurements.”
The study’s limitations included that it focused on adults who were middle-aged at the time of enrollment, meaning the results might not be as generalizable to older populations, Giao said.
Note: Giao presents Seated And Supine Blood Pressure And Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease And Mortality From The Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities Study at 2:15 p.m. ET on Saturday, Sept. 9, 2023, Presentation #071; Abstract #452
Background:
The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study is an ongoing, community-based cohort of 15,792 adults in the United States enrolled from 1987-1989 to investigate the causes for atherosclerotic disease (plaque or fatty buildup in the arteries). ARIC study participants were ages 45–65 years at the start of the study and from rural areas in the U.S. (Forsyth County, North Carolina, and Washington County, Maryland) and urban areas: Minneapolis and Jackson, Mississippi. The research and data from the ARIC clinical visits — including hospital record abstraction, ECG tracings, and physician and coroner questionnaires, as well as death certificate data — have led to discoveries and guidelines surrounding atherosclerosis, heart disease, kidney disease, diabetes, stroke and cognitive decline.
The 2017 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults classifies hypertension as having top and bottom numbers greater than or equal to 130/80 mm Hg, which was the definition of hypertension used in this study.
Co-authors and their disclosures are listed in the abstract. The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Statements and conclusions of studies that are presented at the American Heart Association’s scientific meetings are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers and the Association’s overall financial information are available here.
Additional Resources:
Available multimedia is on right column of release link https://newsroom.heart.org/news/high-blood-pressure-while-lying-down-linked-to-higher-risk-of-heart-health-complications?preview=3a007402d06b4cd7cbc3c53acb93b5f5
Program abstracts online at embargo
AHA news release: If blood pressure rises upon standing, so may risk for heart attack (March 2022)
AHA news release: Blood pressure rising at night linked to doubling risk of death in adults with diabetes (Sept. 2021)
AHA news release: Abnormal blood pressure levels while sleeping increase risk of heart disease (November 2020)
Follow AHA/ASA news on X (formerly known as Twitter) @HeartNews #Hypertension23
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
END
High blood pressure while lying down linked to higher risk of heart health complications
American Heart Association Hypertension Scientific Sessions – Abstract 452
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cold weather may pose challenges to treating high blood pressure
2023-09-07
Research Highlights:
An analysis of electronic health records for more than 60,000 adults in the United States found that systolic, or top-number, blood pressure rose slightly during the winter compared to summer months. The health records were of adults being treated for high blood pressure from 2018 to 2023 at six health care centers of varying sizes located in the southeast and midwestern United States.
The researchers found that, on average, participants’ systolic blood pressure increased by up to 1.7 mm Hg in the winter months compared to the summer months.
They also found that population ...
Community-based, self-measured blood pressure control programs helped at-risk patients
2023-09-07
Research Highlights:
Community health centers participating in the National Hypertension Control Initiative (NHCI) that introduced self-measured blood pressure interventions to their patients — including individuals from Black, Hispanic and American Indian/Alaskan Native populations, who are disproportionately impacted by hypertension and by the COVID-19 pandemic — experienced improvements in blood pressure control rates since 2021, when NHCI began.
Community Health Centers in the NHCI that received funding from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Service’s Health Resources and Services Administration and Office of Minority Health and ...
Amsterdam UMC study finds elite athletes safely return to top-level sports after COVID-19: no issues found in more than 2 years of follow-up
2023-09-07
Heart problems after a COVID infection are a serious concern for both elite athletes and recreational athletes alike. A study from Amsterdam UMC, published today in Heart, offers some reassuring news. "We examined over 250 elite athletes and found that those who had contracted COVID-19 did not experience severe heart issues that impacted their careers," says Juliette van Hattum, a PhD candidate in sports cardiology at Amsterdam UMC.
The study specifically focused on elite athletes, a group that could be particularly susceptible to heart issues, particularly heart ...
Stability inspection for West Antarctica shows: marine ice sheet is not destabilized yet, but possibly on a path to tipping
2023-09-07
Antarctica’s vast ice masses seem far away, yet they store enough water to raise global sea levels by several meters. A team of experts from European research institutes has now provided the first systematic stability inspection of the ice sheet’s current state. Their diagnosis: While they found no indication of irreversible, self-reinforcing retreat of the ice sheet in West Antarctica yet, global warming to date could already be enough to trigger the slow but certain loss of ice over the next hundreds to thousands ...
Early findings suggest clinical and lab-based approach critical to tracking head and neck cancer recurrence
2023-09-07
Early findings of two studies from the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center shed light on new ways to anticipate recurrence in HPV-positive head and neck cancer sooner. The papers, published in Cancer and Oral Oncology, offer clinical and technological perspectives on how to measure if recurrence is happening earlier than current blood tests allow, and provide a framework for a new, more sensitive blood test that could help in this monitoring.
“When metastatic head and neck cancer returns, it impacts their quality of life and can be disfiguring, interfering with the ability to talk, ...
Many people have biased perceptions of EDI leaders
2023-09-07
For the past decade, companies across North America have paid more attention to supporting equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI). This has prompted many organizations to create a leadership role fully dedicated to advancing EDI — so much so that between 2015 and 2020, the job title “head of diversity” increased 107 percent on LinkedIn. By 2021, more than half of S&P 500 firms had named a chief diversity officer.
But a new study from the UBC Sauder School of Business shows many people have deeply held beliefs about who should ...
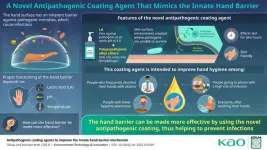
Novel formulation boosts antimicrobial properties of the natural hand barrier
2023-09-07
Contact infection is among the most common ways pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, spread from one person to another. Hand washing and disinfection are important hygiene practices to minimize the probability of catching infectious diseases. Interestingly, our hands also have a natural barrier that fights off pathogens. While this had been known to science for quite some time, the exact mechanisms by which this barrier acts on pathogens remained a mystery until recently.
In a 2021 study published in Scientific Reports, researchers from Kao Corporation, Japan, revealed that lactic acid (LA), which has a molecular ...
US Department of Defense backs Cosimo Commisso’s pancreatic cancer research
2023-09-07
Cosimo Commisso, Ph.D., has received a grant from the Department of Defense for $1 million to advance the research of a small molecule that kills pancreatic cancer cells by disrupting their pH equilibrium. The project is funded as part of the Pancreatic Cancer Research Program (PCARP), which aims to improve our understanding of pancreatic cancer for the benefit of service members, veterans, their families and the general public.
“We’ve seen that this small molecule—called IMD-0354—works on cancer cells in the lab,” says Commisso, associate professor and director of the Cancer Metabolism and Microenvironment Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys. “This ...
High levels of depression found among Canadian older adults with cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-09-07
Toronto, ON —Older adults who have had cancer had a high risk of experiencing symptoms of depression during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic according to a new study published in Cancer Management and Research.
The study was focused on a sample of 2486 adults aged 50 and older with a history of cancer who participated in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Among the 1765 individuals from the study who had a history of cancer but no lifetime history of depression, researchers found that 1 in 8 experienced depression for the first time during the early stages of the pandemic.
“The ...
Timothy Huang awarded $2.6M to solve Alzheimer’s disease puzzle
2023-09-07
With the help of a new grant from the National Institute of Health for more than $2.6 million, Assistant Professor Timothy Huang, Ph.D., will continue his research on the role of the brain’s immune cells on the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease affects more than 47 million people worldwide, with 10 million new cases of dementia diagnosed each year. This number will continue to grow as the world population ages. Newly approved FDA treatments for Alzheimer’s remove beta-amyloid, a protein that accumulates into plaques, from the brain. However, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] High blood pressure while lying down linked to higher risk of heart health complicationsAmerican Heart Association Hypertension Scientific Sessions – Abstract 452