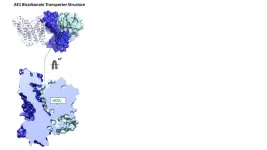
The research team, led by Daniel Wacker, PhD, Bin Zhang, PhD, and Avner Schlessinger, PhD, found that this transporter facilitates the movement of a substance called bicarbonate, which certain drugs can inhibit. They discovered how these drugs block the transporter and devised novel compounds capable of achieving the same effect.
"Our findings provide a detailed understanding of how bicarbonate transporters work, and the newly identified tool compounds open doors to studying conditions involving red blood cells, including hemolytic anemias," says Dr. Wacker, corresponding author and an Assistant Professor of Pharmacological Sciences, Neuroscience, and Genetic and Genomic Sciences at Icahn Mount Sinai.
Previously, human bicarbonate transporters were poorly understood, despite being involved in many aspects of human physiology, including regulating pH that involves keeping the level of acidity within a specific range.
Using cryo-electron microscopy, the team identified high-resolution structures revealing bicarbonate and inhibitor binding, and their impact on the transport mechanism. With these insights, the researchers used computer simulations to analyze millions of compounds that could interact with the substrate binding site.
Their experiments pinpointed a group of innovative chemical inhibitors specifically designed for anion exchanger 1, a protein that is crucial for maintaining the proper function of the blood and red blood cells.
"Our study also demonstrates the potential for developing new inhibitors with medical potential for other solute carrier (SLC) proteins, a protein family gaining importance in drug development," says co-author Dr. Zhang, the Willard T.C Johnson Research Professor of Neurogenetics and Director of the Mount Sinai Center for Transformative Disease Modeling at Icahn Mount Sinai.
Next, the researchers plan to expand their studies to other SLC proteins involved in a variety of disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, psychiatric maladies, and cancer.
“This study effectively paves the way to using atomic-level insights toward the rapid development of promising drug-like molecules for SLC proteins,” says co-author Dr. Schlessinger, Associate Professor of Pharmacological Sciences and Associate Director of the Mount Sinai Center for Therapeutics Discovery at Icahn Mount Sinai.
The paper is titled “Substrate binding and inhibition of the anion exchanger 1 transporter.”
Additional co-authors, all with Icahn Mount Sinai except where indicated, are Michael J. Capper, PhD; Shifan Yang, PhD; Alexander C. Stone; Sezen Vatansever, MD, PhD (Amgen); Gregory Zilberg, PhD Candidate; Yamuna Kalyani Mathiharan, PhD; Raul Habib, (University of California, Berkeley);
Keino Hutchinson, PhD; Yihan Zhao, PhD Candidate; Mihaly Mezei, PhD; and Roman Osman, PhD.
The project was supported by National Institutes of Health grants R35GM133504, R01GM108911, U01AG046170, RF1AG057440, R01AG068030, R01DK073681, R01DK067555, R01DK061659, T32GM062754, T32DA053558, as well as a Sloan Research Fellowship in Neuroscience, an Edward Mallinckrodt, Jr. Foundation Grant, and a McKnight Foundation Scholars Award.
-####-
About the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is internationally renowned for its outstanding research, educational, and clinical care programs. It is the sole academic partner for the eight- member hospitals* of the Mount Sinai Health System, one of the largest academic health systems in the United States, providing care to a large and diverse patient population.
Ranked 14th nationwide in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and among the 99th percentile in research dollars per investigator according to the Association of American Medical Colleges, Icahn Mount Sinai has a talented, productive, and successful faculty. More than 3,000 full-time scientists, educators, and clinicians work within and across 44 academic departments and 36 multidisciplinary institutes, a structure that facilitates tremendous collaboration and synergy. Our emphasis on translational research and therapeutics is evident in such diverse areas as genomics/big data, virology, neuroscience, cardiology, geriatrics, as well as gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
Icahn Mount Sinai offers highly competitive MD, PhD, and Master’s degree programs, with current enrollment of approximately 1,300 students. It has the largest graduate medical education program in the country, with more than 2,000 clinical residents and fellows training throughout the Health System. In addition, more than 550 postdoctoral research fellows are in training within the Health System.
A culture of innovation and discovery permeates every Icahn Mount Sinai program. Mount Sinai’s technology transfer office, one of the largest in the country, partners with faculty and trainees to pursue optimal commercialization of intellectual property to ensure that Mount Sinai discoveries and innovations translate into healthcare products and services that benefit the public.
Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to breakthrough science and clinical care is enhanced by academic affiliations that supplement and complement the School’s programs.
Through the Mount Sinai Innovation Partners (MSIP), the Health System facilitates the real-world application and commercialization of medical breakthroughs made at Mount Sinai. Additionally, MSIP develops research partnerships with industry leaders such as Merck & Co., AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, and others.
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is located in New York City on the border between the Upper East Side and East Harlem, and classroom teaching takes place on a campus facing Central Park. Icahn Mount Sinai’s location offers many opportunities to interact with and care for diverse communities. Learning extends well beyond the borders of our physical campus, to the eight hospitals of the Mount Sinai Health System, our academic affiliates, and globally.
-------------------------------------------------------
* Mount Sinai Health System member hospitals: The Mount Sinai Hospital; Mount Sinai Beth Israel; Mount Sinai Brooklyn; Mount Sinai Morningside; Mount Sinai Queens; Mount Sinai South Nassau; Mount Sinai West; and New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
END