New MRI technology: a non-invasive look at iron balance
2023-09-12
(Press-News.org)
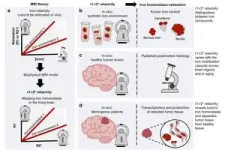
Research team led by Shir Filo and Prof. Aviv Mezer of the Safra Center for Brain Science at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (ELSC) and Dr. Tal Shahar currently, Director of the Neurosurgical Oncology Unit at the Neurosurgery Department, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, have unveiled a groundbreaking magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology that promises to revolutionize our understanding of iron homeostasis in the human brain. Their research, demonstrates the ability to non-invasively assess different molecular iron environments within the brain, shedding light on its vital role in normal brain function, aging, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
Traditional MRI scans provide qualitative images that necessitate subjective interpretation by medical professionals. In contrast, quantitative MRI seeks to replicate the precision of assessing body temperature accurately when ill, moving beyond qualitative observations like “too hot” or “too cold.” Achieving this involves intricate physical models that amalgamate multiple MRI scans to extract a diverse array of measurements. These MRI measurements are then leveraged to uncover valuable biological insights, akin to a blood test's ability to reveal our blood's composition, encompassing proteins, fats, and potential irregularities. One critical aspect of brain function is maintaining the balance, or homeostasis, of iron, crucial for overall health. Imbalances in brain iron levels have implications for various conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Until recently, the non-invasive assessment of the molecular iron environment within the living human brain posed a significant challenge.
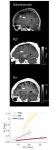
The research team from Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center and Shaare Zedek Medical Center introduces a novel MRI approach based on the quantitative MRI, which can sensitively detect changes in brain iron homeostasis. In their in vitro experiments, this MRI technology revealed distinct paramagnetic properties of key iron compounds, including ferritin, transferrin, and ferrous iron. The real breakthrough came with in vivo MRI scans of patients with brain tumors, operated at the Neurosurgery Department at Shaare Zedek Medical Center where the technology was also validated against ex vivo iron compound quantification of the resected tumors. These ex vivo transcriptomics and proteomics analyses were done in the lab of Dr. Naomi Habib in the Hebrew University and the lab of Molecular Neuro-oncology at Shaare Zedek Medical Center, directed at the time of the study by Dr. Tal Shahar.
This innovative MRI approach demonstrates sensitivity to changes in iron mobilization capacity across different brain regions and during brain aging. It offers insights into changes in iron homeostasis and iron-related gene expression in pathological tissues. Most notably, it can differentiate between tumor tissue and non-pathological tissue without the need for toxic contrast agents injection.
Shir Filo, explained, "Our technology opens up new possibilities for understanding the role of iron in cancer, normal aging, and neurodegenerative diseases. It enables non-invasive research and diagnosis of iron homeostasis in the living human brain, offering a potential game-changer for healthcare and neuroscience."
Prof. Aviv Mezer emphasized, "The strength of our team lies in its diverse composition, comprising experts from various disciplines and specialties. Dr. Tal Shahar was leading the medical aspect of the study involving meningioma patients and the proteomic studies. Dr. Rona Shahrabani was instrumental in conducting experiments with iron proteins, while Dr. Nevo Margalit, Chair of the Neurosurgery Department at Shaarei Zedek Medical Center made a substantial contributions through his involvement in a significant portion of the surgeries and recruitment of patients. Additionally, Dr. Eli Ben David, a radiologist at Shaarei Zedek Medical Center, played an indispensable role in enabling the MRI scans and Dr. Naomi Habib brought the valuable knowledge in gene expression. Their collective and truly interdisciplinary expertise and unwavering dedication significantly enhanced the success of this pioneering study."
In summary, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem's MRI quantification, represents a groundbreaking advance in our ability to assess iron homeostasis in the human brain. It shows promising ability to distinguish between pathological and healthy brain tissue without the use of toxic contrast agents and offers insights into molecular iron states inaccessible to conventional MRI techniques. The technology’s sensitivity to in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo iron environments validates its potential to enhance our understanding of iron-related disorders and opens new avenues for research and diagnosis in the living human brain.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-12
The University of Manchester will partner with the Martingale Foundation to improve postgraduate access to STEM subject through a fully funded scholarship.
The University is one of three new universities chosen to partner with the Martingale Postgraduate Foundation to support passionate and talented students facing financial barriers to pursue postgraduate degrees at leading research institutions in the UK.
A Martingale Scholar will receive a fully funded scholarship to pursue a master's degree in Mathematics at ...
2023-09-12
early one in three people exposed to SARS-CoV2 is infected, and as many as two in five with the Omicron variant. In the case of immunity — conferred by vaccination, infection or a combination of the two — this rate drops to one in ten. However, immunity disappears within a few months, confirms a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and Geneva University Hospitals (HUG), after revisiting epidemiological data collected in Geneva. While protection following infection appears to be slightly greater than after vaccination — albeit at the risk of potentially severe ...
2023-09-12
How many relatives do Swedes have? And at what age is the family the largest? Researchers in demography at Stockholm University have found out in a new study.
Relatives often play an important role in people’s lives. Family members such as cousins, grandparents and grandchildren form part of an individual’s social network and can provide significant support, ranging from child-rearing to elderly care to financial assistance.
In a new study in the journal Demography, Martin Kolk and a group of researchers at Stockholm University have documented for the first time how many relatives Swedes have.
“There has been a lack of knowledge about how many kin people have in modern ...
2023-09-12
A ground-breaking study by researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS) has revealed crucial insights into the role of the histone methyltransferase NSD2 and its epigenetic target PKCα in causing t(4;14) translocated multiple myeloma (MM), a high-risk subtype of blood cancer, to be more aggressive and resistant to treatment.
The study was led by Professor Wee Joo Chng, Senior Principal Investigator at CSI Singapore, and Dr Phyllis Chong Shu Yun, Senior Research Fellow at CSI Singapore. The research team discovered that NSD2 triggers elevated glycolysis through the ...
2023-09-12
It is said that there is waste in haste, but researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have proven that doing things rapidly does not necessarily mean working ineffectively. A research group led by Professor Hiroshi Shiigi at the Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka Metropolitan University has developed a technology that can rapidly and accurately determine the number of viable bacteria in food products electrochemically, using tetrazolium salt (MTT), a water-soluble molecule.
One of the most important assessment indicators for ensuring that food is free from contamination is the number of viable bacteria. However, conventional measurement methods take up to 2 days to yield results, ...
2023-09-12
Sixty-six percent of U.S. teachers who responded to a new, nationally representative RAND Corporation survey said their base salary was inadequate, compared with 39% of U.S. working adults. These teachers want a $17,000 increase in base pay, on average, to feel that their pay is adequate.
This equates roughly to a 27% pay increase, which is comparable to the estimated gap in pay between teachers and other similarly college-educated workers, also known as the “teacher pay penalty.”
In early 2023, RAND researchers surveyed public-school teachers about how salary and work hours affect ...
2023-09-12
The targeted use of ultrasound technology can bring about significant changes in brain function that could pave the way towards treatment of conditions such as depression, addiction, or anxiety, a new study suggests.
Research by neuroscientists at the University of Plymouth explored the impacts of an emerging technique called transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS).
Typically, ultrasound examinations involve diffuse broad beams of ultrasound being used to create images while leaving the target tissue unaffected.
However, focusing the beams through TUS can increase the pressure in the target region and change the way ...
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - A unified and concentrated lung cancer advocacy program in the United States resulted in a 25 percent increase in funding to a U.S.-based lung cancer research program, according to a presentation given today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
Lung cancer remains a major health concern, with mortality rates posing a significant challenge both globally and in the United States. The U.S. Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program/Lung Cancer Research Program (LCRP) was established in 2009 with a funding level of $20 million, but ...
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] – A model developed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer in 2009 to help better stage mesothelioma cases performed well, according to an independent analysis presented today at The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2023 Conference in Singapore.
Pleural mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive cancer primarily caused by asbestos exposure and presents complex challenges for effective staging and prognostication. The IASLC took a significant step in 2009 by establishing an international pleural mesothelioma database aimed at enhancing staging ...
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, or IMRT, should be utilized for locally advanced NSCLC to reduce the risk of severe pulmonary toxicity and radiation exposure to the heart, according to research presented today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
Dr. Stephen Chun, MD Anderson in Houston, Texas, presented a comprehensive analysis of the phase III trial NRG Oncology-RTOG 0617, comparing intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) with 3D-conformal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New MRI technology: a non-invasive look at iron balance