Unveiling dynamics of human macrophage specification during prenatal development
2023-09-12
(Press-News.org)
Researchers led by Prof. LI Hanjie from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have unveiled the dynamics of human macrophage specification across 19 different tissues from early embryonic stages.
The study was published in Cell on Sept. 12.
Macrophages, i.e., pivotal immune cells, have long been enigmatic in terms of their diversity and roles during human development. Based on findings in rodents, the scientific community has gained some insights into the diversity, developmental origins, and tissue-specific formation of macrophage subtypes. However, it was not clear whether these findings are conserved in humans.
In this study, Prof. LI's team combined single-cell transcriptome sequencing, bioinformatic techniques, immunofluorescence, and in vitro functional assays to construct a high-resolution spatiotemporal dynamic map of human prenatal immune system development across 18 gestational stages (postconceptional weeks 4–26) and 19 tissues.
Based on this map, the team focused on the most tissue-specific lineage, macrophages. They revealed the origin of differentiation, spatial localization, functional characteristics, and transcriptional regulation mechanisms of multiple macrophage subtypes during development.
"Key finding of our study is the identification of 15 distinct macrophage subtypes, with particular attention to two novel populations: microglia-like cells and proangiogenic macrophages (PraM)," said Prof. LI.
Surprisingly, microglia-like cells, reminiscent of those in the central nervous system, were found in unexpected locations such as the fetal epidermis, testicles, and heart. These cells were found to influence neural crest cell differentiation, contributing to early tissue development.
The research also highlighted the strategic placement of proangiogenic macrophages in perivascular areas across various fetal organs. These macrophages, likely originating from the yolk sac, play a critical role in vascular development during prenatal stages.
"Our study offers a comprehensive map of human macrophage diversity and developmental processes, revealing their multifaceted roles in development," said Dr. WANG Zeshuai, first author of the study. "These findings are poised to revolutionize our understanding of these immune cells and offer promising avenues for potential therapeutic interventions."
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-12
Researchers discover genes behind antibiotic resistance in deadly superbug infections
Australian researchers have uncovered new genetic insights into Staphylococcus aureus, revealing what makes the bacterium so dangerous when it enters the blood.
While common, Staphylococcus aureus infections – known as Golden staph – can be life-threatening if the bacteria enter the bloodstream, causing sepsis. Golden staph is notorious for its ability to become resistant to antibiotics, making it hard to treat, which can lead to adverse health outcomes for patients infected with a drug-resistant ...
2023-09-12
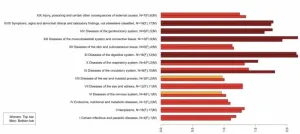
About The Study: In this study of Medicare beneficiaries with comorbid chronic low back pain and opioid use disorder (OUD), receipt of physical therapy and chiropractic care was low overall and lower across most racial and ethnic minority groups compared with non-Hispanic white persons. The findings underscore the need to address inequities in guideline-concordant pain management, particularly among Black or African American and Hispanic persons with OUD.
Authors: Patience Moyo, Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in ...
2023-09-12
Milan, Italy: Particular combinations of bacteria found in dust at day care facilities have been linked to wheezing in young children in a study presented at the European Respiratory Society International Congress in Milan, Italy [1]. Wheezing in young children is often an early sign of asthma.
Children may spend many hours in day care each week and research suggests that conditions in day care settings can have an impact on respiratory health in early childhood. The new research offers some clues ...
2023-09-12
During the Dutch Hunger Winter Famine, infants experienced the highest absolute and relative mortality of all children under 14 years of age. These are findings from a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Wageningen University & Research and the Netherlands Interdisciplinary Demographic Institute in the Hague. the Netherlands. In the famine cities, infant mortality increased to one percent or 922 deaths per 10,000 compared to 109 deaths per 10,000 children between the ages of one and four, and 27 deaths per 10,000 deaths at ages 5 to 14. ...
2023-09-12
New research published today in Blood Advances reveals that since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, PCV7 and PCV13, invasive pneumococcal infection (IPD) rates among children living with sickle cell disease (SCD) have declined significantly. The study explores the efficacy of existing and emerging vaccines to protect children living with SCD from life-threatening infections.
SCD is the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States, affecting an estimated 100,000 people. ...
2023-09-12
A groundbreaking discovery has been made by Professor Hyug Moo Kwon and his research team in the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Jaeseok Yang from Yonsei University. Their study sheds new light on the protein called ‘TonEBP,’ revealing its significant role in the development of lupus and lupus nephritis. This breakthrough not only enhances our understanding of these conditions, but also opens up potential avenues for future treatment options.
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder characterized by autoreactive B cells and dysregulation of various immune cells, including myeloid cells. Lupus nephritis (LN), which ...
2023-09-12
COVID-19 mRNA vaccination protects babies and young children against COVID-19-associated emergency department/urgent care visits, according to a multistate study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s VISION Network. The study found that children, age five and younger, who received the original COVID-19 vaccine and the updated vaccine were protected against the need for medical care for COVID in an emergency department or urgent care facility.
Emergency department/urgent care visits are considered indicators of moderate disease. The small number of hospitalizations for children ages six months to five years old limited the assessment of vaccine ...
2023-09-12
Multimorbidity describes the state of having more than one disease. Anthony Webster sought to untangle a puzzle at the heart of multimorbidity: does having had disease make a patient more likely to have another disease, independent of broad risk factors, such as age, smoking status, or weight? Webster applied a Poisson-Binomial distribution with a Weibull model to predict the incidence of 222 common diseases for approximately 500,000 individuals within the UK Biobank cohort, taking into account their age and established risk factors, but ignoring their history of previous disease or pre-existing conditions. Webster then compared the expected number ...
2023-09-12
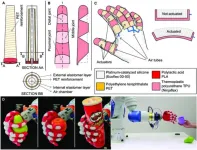
A research paper by scientists at the University of Coimbra proposed a soft robotic hand that composed of soft actuator cores and an exoskeleton, featuring a multimaterial design aided by finite element analysis to define the hand geometry and promote finger’s bendability. The new research paper, published on Aug. 8 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, presented the development, fabrication, and control of a bioinspired soft robotic hand and demonstrated finite element analysis can serve as a valuable tool to support the design and control of the hand’s fingers.
“Recent research led to impactful achievements in functional designs, modeling, ...
2023-09-12
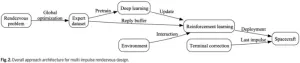
Multi-impulse orbital rendezvous is a classical spacecraft trajectory optimization problem, which has been widely studied for a long time. Numerical optimization methods, deeplearning (DL) methods, reinforcement learning (RL) methods have been proposed. However, for the numerical optimization methods, they need long computation time, and they are usually not valid for the many-impulse rendezvous case with the magnitude constraints. For the machine learning (ML) methods, the DL method needs large amounts of data, and the RL method has the weakness of low efficiency. Nevertheless, ML demonstrates more accurate predictions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Unveiling dynamics of human macrophage specification during prenatal development