(Press-News.org) About The Study: Receiving at least two doses of wild-type BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer) was associated with a reduced risk of COVID-19 emergency department or urgent care and outpatient visits in children younger than five years. The risk of SARS-CoV-2 encounters appeared lower for those with two versus three doses of BNT162b2, albeit with wide CIs, which is likely due to more immune-evasive Omicron sublineages (e.g., BQ.1-related and XBB-related strains) becoming dominant by the time young children received their third dose and longer median time since dose three compared with dose two.
Authors: Sara Y. Tartof, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Kaiser Permanente Southern California Department of Research & Evaluation in Pasadena, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.17473)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.17473?guestAccessKey=3c77918c-2e4c-42f9-b7e9-84eed4b3aa00&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=091523
END
Receipt of BNT162b2 vaccine and COVID-19 ambulatory visits in young US children
JAMA
2023-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New parent? Night shift? New analysis suggests ideal nap strategy to survive all-nighters
2023-09-15
New analysis of pilot studies on night shift naps conducted from 2012 to 2018 revealed the ideal snoozing strategy that might help counteract drowsiness and fatigue during a 16-hour overnight duty. The findings can also benefit new parents.
Reanalysis of data showed that when staying up all night, scheduling two nap sessions — a 90-minute one followed by a quick 30-minute shut-eye later — is the optimal choice over a single 120-minute snooze in putting off drowsiness and fatigue. The study was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
“A 90-minute nap to maintain long-term performance and a ...
Anesthesiology researcher pipeline lags behind other specialties
2023-09-15
CHICAGO — Anesthesiology researchers are responsible for some of medicine’s most significant advances, from the Apgar score that tests a newborn’s health to cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). But the number of medical residents in the anesthesiology physician-scientist (researcher) pipeline trails other specialties, particularly among women, according to findings of the Anesthesia Research Council (ARC), published in the journal Anesthesia & Analgesia.
Out of eleven medical specialties, anesthesiology ranked eighth both for the percentage of entering residents ...
Third Elaine Redding Brinster Prize awarded for development of sickle cell disease therapy
2023-09-15
PHILADELPHIA—For his work discovering the basis for hemoglobin gene switching and applying those insights to develop a therapy for sickle cell disease and other blood diseases, the Institute for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania awarded Stuart Orkin, MD the third Elaine Redding Brinster Prize in Science or Medicine.
Orkin’s research advanced the understanding of how the fetal hemoglobin gene— the main oxygen carrier protein in the human fetus—is silenced in adults. He also developed a therapy that re-activates the fetal gene for adult hemoglobin gene defects, which cause ...
Corning® launches Videodrop, revolutionizing real-time nanoparticle detection and analysis
2023-09-15
CORNING, N.Y. | Corning Incorporated | September 15, 2023 - Corning Incorporated (NYSE: GLW) today announced the launch of Corning® Videodrop, an optical technology that applies the principles of interferometric microscopy to quantify the size and concentration of nanoparticles. The latest addition to the company’s growing suite of bioprocessing technology, Videodrop can analyze a solution in less than 60 seconds, and requires only a single 5-10 µl drop of sample material for testing.
The technology is capable of collecting a physical titer of viral vectors such as lentivirus, ...
Groundbreaking soft valve technology enabling sensing and control integration in soft robots
2023-09-15
Soft inflatable robots have emerged as a promising paradigm for applications that require inherent safety and adaptability. However, the integration of sensing and control systems in these robots has posed significant challenges without compromising their softness, form factor, or capabilities. Addressing this obstacle, a research team jointly led by Professor Jiyun Kim (Department of New Material Engineering, UNIST) and Professor Jonbum Bae (Department of Mechanical Engineering, UNIST) has developed groundbreaking “soft valve” technology—an all-in-one solution that integrates sensors and control valves while maintaining complete softness.
Traditionally, ...
Living in a disadvantaged neighborhood affects food choices, weight gain and the microstructure of the brain
2023-09-15
You are what you eat, according to the adage. But it’s not just the body that’s impacted. According to research from UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine, living in a disadvantaged neighborhood can affect food choices, weight gain and even the microstructure of the brain.
The study, appearing in Communications Medicine, a Nature journal, finds poor quality of available foods, increased intake of calories from foods high in trans-fatty acids, and environments that do not foster physical activity, all prevalent in disadvantaged neighborhoods, disrupt the flexibility ...
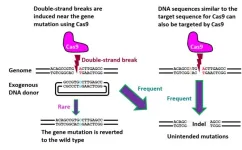
A NICER approach to genome editing
2023-09-15
Osaka, Japan – The gene editing technique CRISPR/Cas9 has allowed researchers to make precise and impactful changes to an organism’s DNA to fix mutations that cause genetic disease. However, the CRISPR/Cas9 method can also result in unintended DNA mutations that may have negative effects. Recently, researchers in Japan have developed a new gene editing technique that is as effective as CRISPR/Cas9 while significantly reducing these unintended mutations.
In a new study published in Nature ...
Learn the intricacies in solving problems related to energy transfer
2023-09-15
Volume 2 of the series on Solved Problems in Transport Phenomena is out. This unique compendium covers energy transfer at the microscopic and macroscopic levels in a format that does not overwhelm students with a large repertoire of problems. It uses clear highlights and easy-to-follow concept presentations to help students grasp the methodology in problem solving.
Solved Problems in Transport Phenomena: Energy Transfer shows the students how to tackle a problem related to heat transfer as if they were going to solve it for the first time in their lives. A balanced approach ...
A quarter of people are undoing the benefits of healthy meals by unhealthy snacking
2023-09-15
A quarter of people are undoing the benefits of healthy meals with unhealthy snacks, which increases the risk of strokes and cardiovascular disease.
The findings, published today in the European Journal of Nutrition by researchers from the School of Life Course & Population Sciences and ZOE, details the snacking habits of 854 people from the ZOE PREDICT study.
Researchers found that half of the participants do not match the healthiness of their meals to their snacks and vice versa. This difference has a negative effect on health measures, such as blood sugar and fat levels, and addressing this could be a simple diet strategy to improve ...
Polar experiments reveal seasonal cycle in Antarctic sea ice algae
2023-09-15
In the frigid waters surrounding Antarctica, an unusual seasonal cycle occurs. During winter, from March to October, the sun barely rises. As seawater freezes it rejects salts, creating pockets of extra-salty brine where microbes live in winter. In summer, the sea ice melts under constant daylight, producing warmer, fresher water at the surface.
This remote ecosystem is home to much of the Southern Ocean’s photosynthetic life. A new University of Washington study provides the first measurements of how sea-ice algae and other single-celled life adjust to these seasonal rhythms, offering clues to what might happen as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Receipt of BNT162b2 vaccine and COVID-19 ambulatory visits in young US childrenJAMA