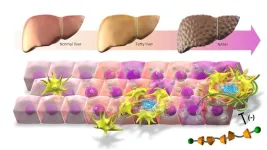
(Press-News.org) A research group from the Graduate School of Medicine and Research Institute of Environmental Medicine at Nagoya University reported that cholesterol accumulation in macrophages promotes liver fibrosis in the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Using a unique supramolecule, they removed cholesterol in a mouse model, stopping the development of the disease. As cholesterol crystals are also found in human patients, this suggests a potential treatment for the disease. Their findings were published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
As the number of patients with obesity increases, so do cases of fatty liver. Fatty liver risks progressing to NASH, a severe disease characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, and the increased death of the functional cells in the liver known as hepatocytes. Although it is known that cholesterol accumulation promotes NASH development, the precise mechanism is unknown.
Macrophages, the body’s immune cells, are also found around the dead hepatocytes, attracted to the inflamed liver tissue by signals released by damaged liver cells. Hepatocytes release cytokines, which amplify the inflammation, leading to tissue damage and fibrosis.
To further understand the mechanism, the group led by Nagoya University doctors Takayoshi Suganami (he, him) and Michiko Itoh (she, her) used a combination of techniques to identify cholesterol crystals in the lipids of the dead hepatocytes and the macrophages that engulf the cells.
To understand whether the cholesterol was involved in NASH, the researchers needed to find out if removing it improved the symptoms. To do this, they synthesized a unique supramolecule that combined the oligosaccharide β-cyclodextrin, which encapsulates free cholesterol, with a polymer to create β-cyclodextrin polyrotaxane (βCD-PRX). When they administered the supramolecule to mice, they found that it accumulated in the liver where it promoted excretion of cholesterol, which effectively stopped the progression of NASH.
“Cholesterol crystals are also observed in human NASH patients, which suggests that βCD-PRX could be a potential therapeutic strategy for human NASH,” Suganami said. “Recent advances in analytical techniques have led us to understand the characteristics of macrophages, which play crucial roles in the development of NASH. This study provides evidence that cholesterol overload triggers macrophage changes and promotes the development of NASH, which could be a novel therapeutic target.”
END
Treating NASH disease by removing cholesterol from macrophages using a unique supramolecule
2023-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers unveil new flexible adhesive with exceptional recovery and adhesion properties for electronic devices
2023-09-19
The rapid advancements in flexible electronic technology have led to the emergence of innovative devices such as foldable displays, wearables, e-skin, and medical devices. These breakthroughs have created a growing demand for flexible adhesives that can quickly recover their shape while effectively connecting various components in these devices. However, conventional pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) often face challenges in achieving a balance between recovery capabilities and adhesive strength. In an extraordinary study conducted at UNIST, researchers have successfully synthesized new types of urethane-based crosslinkers that address this critical challenge.
Led by Professor Dong Woog ...
Grant awarded to University of Louisville law professor will fund climate adaptation project
2023-09-19
The Resilience Justice Project (RJ Project) at the University of Louisville’s Brandeis School of Law has been awarded a one-year multi-institutional grant through a national competitive process to evaluate how climate adaptation planning can be more equitable for low-income communities in eight U.S. coastal areas.
The RJ Project will use the $75,000 award from the National Sea Grant Law Center through NOAA’s National Coastal Resilience Fund to examine coastal urban adaptation in the eight cities: Boston, Cleveland, Miami, New Orleans, San Diego, Savannah, Seattle and Tampa. Principal ...
Technological progress and climate change
2023-09-19
Technological progress can reduce the energy required to achieve the same ends, reducing the use of fossil fuels and the greenhouse gases associated with burning fossil fuels. But technological progress can also make production, consumption, and travel cheaper, stimulating demand and consequently increasing greenhouse gas emissions. Sai Liang and colleagues sought to explore this conundrum by building an environmentally extended general equilibrium model with heterogeneous agent and input-output network covering 141 nations and 65 sectors, ...
Yogurt may be the next go-to garlic breath remedy
2023-09-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – It turns out yogurt may have a previously unknown benefit: eliminating garlic odors.
A new study conducted in a lab – with follow-up human breath tests being planned – showed that whole milk plain yogurt prevented almost all of the volatile compounds responsible for garlic’s pungent scent from escaping into the air.
Researchers tested the garlic deodorizing capacity of yogurt and its individual components of water, fat and protein to see how each stood up to the stink. Both fat and protein were effective at trapping garlic odors, leading the scientists to suggest high-protein ...
Laser-based ice-core sampling for studying climate change
2023-09-19
Researchers led by Yuko Motizuki from the Astro-Glaciology Laboratory at the RIKEN Nishina Center in Japan have developed a new laser-based sampling system for studying the composition of ice cores taken from glaciers. The new system has a 3-mm depth-resolution—about 3 times smaller than what is currently available—meaning that it can detect temperature variations that occurred over much smaller periods of time in the past. The new laser melting sampler, or LMS, is expected to help reconstruct continuous annual temperature changes that occurred thousands to hundreds of thousands of years ago, which will ...
Gene required for root hair growth, nitrate foraging found in grasses
2023-09-19
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Scientists have found a plant gene that drives the growth of root hairs, the tiny structures that help plants find water and nutrients in the soil.
Identified by a team led by Washington State University researcher Karen Sanguinet, the gene, dubbed “BUZZ,” causes faster-growing, denser webs of roots and may also determine how plants find and use nitrates, a prime source of nitrogen essential to plant growth. Nitrates are also used in fertilizers that can pollute the environment as runoff, and this genetic discovery could ultimately help plant scientists find ways to grow crops more sustainably.
“Nitrate ...
Job strain combined with high efforts and low reward doubled men’s heart disease risk
2023-09-19
Research Highlights:
Men exposed to stressful working conditions who also felt that they put forth high effort but received low reward had twice the risk of heart disease compared to men who were free of those psychosocial stressors.
The impact of job strain and effort-reward imbalance combined was similar to the magnitude of the impact of obesity on the risk of coronary heart disease, in the study of nearly 6,500 white-collar workers in Canada.
Results on how work stress affects women’s heart health were inconclusive.
Embargoed ...
Breaking in the black box of pedagogical authority
2023-09-19
How does pedagogical authority operate in the classroom? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the University of Teacher Education, State of Vaud (HEP Vaud) has produced one of the first in-depth field studies on this subject. By filming teachers in training over a period of several months, the researchers identified different ways of exercising teaching authority and assessed their effectiveness. They found that strategies based on double addressing - i.e. addressing several students or groups of students simultaneously, using two different communication channels - were particularly effective. These results ...
Witchcraft accusations an ‘occupational hazard’ for female workers in early modern England
2023-09-19
While both men and women have historically been accused of the malicious use of magic, only around 10–30% of suspected witches were men by the 16th and 17th centuries.*
This bias towards women is often attributed to misogyny as well as economic hard times. Now, a Cambridge historian has added another contributing factor to the mix.
Dr Philippa Carter argues that the types of employment open to women at the time came with a much higher risk of facing allegations of witchcraft, or maleficium.
In a study published in the journal Gender & History, Carter uses the casebooks of Richard ...
China global Merged Surface Temperature dataset (CMST) reveals 2023 on Track to Be Hottest Year Ever
2023-09-19
The climate crisis is reaching unprecedented levels of urgency as global temperatures soar to record-breaking heights, with July 2023 marking another alarming milestone. United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres declared it a "disaster for the whole planet," emphasizing that the era of "global warming" has given way to an era of "global boiling." This alarming assessment is supported by recent findings from Professor Qingxiang Li 's team at the School of Atmospheric ...