(Press-News.org) A significant share of voters see the EU as less democratic than it really is and believe the European Commission can steamroll its member states, a new study shows.
The research shows that key channels of legitimation in the EU are not well known by the citizens of large member states. Whether people see themselves only as citizens of their nation, or simultaneously as a European, is linked to what they believe about the EU.
A substantial share of EU voters who took part in the study believed that the members of the European Parliament are not directly elected. Many assumed the European Parliament is unimportant for decision making in Brussels.
Less than half of those who took part in the research knew which powers the EU has and which it does not have.
Some were aware of their gaps in knowledge about EU institutions, but a large number who had gaps in their knowledge also thought they were informed.
Those who said they did not hold a European identity were more likely to assume that the EU is less democratic than it is.
The research, published in the journal European Union Politics, was carried out by Florian Stoeckel, Jack Thompson and Jason Reifler from the University of Exeter, Vittorio Mérola from Durham University and Benjamin Lyons from the University of Utah.
Professor Stoeckel said: “Not knowing how a complex institution like the EU works is completely understandable but it is problematic when people have the wrong idea about how the institution works and assume the organization is not as democratic as it is or has power over member states that it doesn’t have. Populist parties can mobilize or exploit such misperceptions, or they create them in the first place.”
“Our findings help elucidate the rhetorical value of ‘taking back control’ from Brussels. Indeed, to voters who believe that the European Commission can legislate against the will of a majority of MEPs or member states, European integration is likely to appear like an absolute loss of the sovereignty of the general will, rather than just a transfer of authority to another level.”
Researchers carried out a survey in France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain, and Sweden, with approximately 1,000 respondents per country, in February 2019. Participants were asked three questions - if MEPs are directly elected by voters; to react to the following statement: ‘the European Commission can issue new laws even when a majority of MPs of the European Parliament objects’ and whether the following statement is correct: ‘the European Commission can issue new laws for the EU even when a majority of member states objects’.
While the exact proportions vary by country and issue, the combined share of the uninformed and misinformed made up more than half of respondents.
For instance, a third (35 per cent) of respondents knew the European Commission cannot pass laws against the will of a majority of Member States. In contrast, 40 per cent of respondents wrongly believed the EC could override the will of member states, while another 25 per cent were uninformed.
Respondents who took part in the study who described their identity in a narrow, national way thought of the EU as an organisation with more unrestricted powers. They are more likely to wrongly believe MEPs are not directly elected and the European Commission can rule over the European Parliament and EU member states. They were less likely to know legislation needs to be approved by a majority of MEPs in order for it to become law.
Substantial portions of the public in all six countries were either uninformed or misinformed. Pooling responses across countries showed 19 per cent held the misperception that MEPs are not directly elected and 21 per cent of respondents answered that they ‘don’t know’.
A total of 22 per cent of respondents said the European Commission could pass laws while overriding the objection of the European Parliament, while 27 per cent of the respondents selected the ‘don’t know’ category.
Only 35 per cent of respondents correctly said that the European Commission cannot pass laws against the will of the member states of the EU, whereas 40 per cent of respondents held a misperception and another 25 per cent of respondents chose ‘don’t know’.
END
Eurosceptics more likely to think of the EU as less democratic than it is, study shows
2023-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Poor water, sanitation, and hygiene in low-income countries may help fuel the emergence of deadly pathogens
2023-09-19
A new study suggests that Escherichia coli and other disease-causing microbes are passing easily between humans and animals in Cambodia, a country where clean water, sanitation and hygienic controls are lacking in many regions. The continuous exchange, along with unregulated antibiotic use, leads to the emergence and spread of drug-resistant E. coli, the authors say.
Maya Nadimpalli, a scientific collaborator at the Antibiotic Research Action Center at the George Washington University and her international colleagues, conducted the research in Phnom Penh, an urban area where humans and animals are often living in close proximity without clean water or other ...
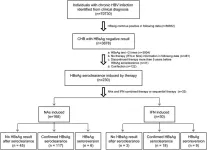
Durability of hepatitis b surface antigen seroclearance studied in real-world data from electronic health records
2023-09-19
In a study published in the journal Genes & Diseases, researchers from The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University analyzed data from an extensive dataset comprising over 70,000 HBsAg-positive individuals at The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. They compared two groups: those achieving HBsAg seroclearance through NAs monotherapy (168 patients) and those through IFN monotherapy (30 patients). NAs monotherapy patients were older, with a higher proportion achieving HBsAg seroclearance during ...
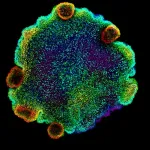
Tiny sea creatures reveal the ancient origins of neurons
2023-09-19
A study in the journal Cell sheds new light on the evolution of neurons, focusing on the placozoans, a millimetre-sized marine animal. Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona find evidence that specialized secretory cells found in these unique and ancient creatures may have given rise to neurons in more complex animals.
Placozoans are tiny animals, around the size of a large grain of sand, which graze on algae and microbes living on the surface of rocks and other substrates found in shallow, warm seas. The blob-like and pancake-shaped creatures are so simple that they live without any body parts or organs. These animals, thought to have ...
Argyle study reveals crucial third clue to finding new diamond deposits
2023-09-19
Curtin University researchers studying diamond-rich rocks from Western Australia’s Argyle volcano have identified the missing third key ingredient needed to bring valuable pink diamonds to the Earth’s surface where they can be mined, which could greatly help in the global hunt for new deposits.
While it is known that for diamonds to form there needs to be carbon deep in the Earth, and for these diamonds to turn pink they must be subjected to forces from colliding tectonic plates, the new study has found the third ingredient needed for the presence of pink diamonds at surface ...
Assessing unintended consequences in AI-based neurosurgical training
2023-09-19
Virtual reality simulators can help learners improve their technical skills faster and with no risk to patients. In the field of neurosurgery, they allow medical students to practice complex operations before using a scalpel on a real patient. When combined with artificial intelligence, these tutoring systems can offer tailored feedback like a human instructor, identifying areas where the students need to improve and making suggestions on how to achieve expert performance.
A new study from the Neurosurgical Simulation and Artificial Intelligence Learning Centre at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University, ...
USPSTF recommendation on screening for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
2023-09-19
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for hypertensive disorders in pregnant persons with blood pressure measurements throughout pregnancy. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are among the leading causes of maternal morbidity and mortality in the U.S. The rate has been increasing from approximately 500 cases per 10,000 deliveries in 1993 to 1,021 cases per 10,000 deliveries in 2016 to 2017. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this recommendation is consistent with its 2017 recommendation statement.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Deep learning reveals valuable clues about kidney cancer in pathology slides
2023-09-19
A team of Dana-Farber researchers has identified a potential new way to assess clinically valuable features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), a form of kidney cancer, using image processing with deep learning. Their AI-based assessment tool evaluates two-dimensional pictures of a tumor sample on a pathology slide and identifies previously underappreciated features, such as tumor microheterogeneity, that could help predict whether a tumor will respond to immunotherapy.
Their results suggest that ...
Poor oral health could lessen survival from head and neck cancer
2023-09-19
An international study has revealed strong associations between oral health and survival among people diagnosed with head and neck cancer. Specifically, better oral health, as evidenced by the number of natural teeth and dental visits prior to the time of diagnosis, was associated with increased survival. Importantly, those who had more frequent dental visits were more likely to have their cancer diagnosed at an earlier, and less deadly, stage of the disease than those who had few or no dental visits.
The study, by researchers at UNC Lineberger ...
Interventions for physical capacity and quality of life in adults with post–COVID-19 condition
2023-09-19
About The Study: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that rehabilitation interventions in adults with post–COVID-19 condition are associated with improvements in functional exercise capacity, dyspnea, and quality of life, with a high probability of improvement compared with the current standard care. The certainty of evidence was moderate for functional exercise capacity and quality of life and low for other outcomes.
Authors: Dimitra V. Pouliopoulou, M.Sc., of Western University in London, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Premenstrual disorders, timing of menopause, and severity of vasomotor symptoms
2023-09-19
About The Study: In this study of 3,635 female participants in the U.S., premenstrual disorders (PMDs) were associated with increased risks of early menopause and moderate or severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS). PMDs may be indicative of underlying physiology linked to early menopause and VMS, suggesting a phenotype observable during the reproductive years that may allow clinicians to target women at risk of earlier menopause and subsequent health risks later in the life course.
Authors: Yihui Yang, M.P.H., and Donghao Lu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden are the corresponding authors.
To ...