(Press-News.org) The amino acid creatine is essential for muscle and brain health, and people commonly use creatine supplements to improve exercise performance and increase muscle mass. Results from a recent clinical trial published in Food Science & Nutrition indicate that dietary creatine may also benefit individuals experiencing post-COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (also known as long COVID).
In the trial, 12 people with post-COVID-19 fatigue syndrome were randomized to take a placebo or 4 grams of creatine monohydrate per day for 6 months. Creatine intake caused a significant increase in creatine levels in leg muscles and across the brain at both 3-month and 6-month follow-ups. Creatine supplementation also led to a significant reduction in general fatigue after 3 months of intake, and it significantly improved scores for several post-COVID-19 fatigue syndrome–related symptoms—including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headaches, and difficulties concentrating—at the 6-month follow up.
“Endorsing creatine might be of great importance in tackling this prevalent condition, but additional studies are warranted to confirm our findings in various post-COVID-19 cohorts,” said corresponding author Sergej M. Ostojic, MD, PhD, of the University of Novi Sad, in Serbia.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/fsn3.3597
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Food Science & Nutrition enables the rapid dissemination of fundamental and applied research related to all aspects of food science and nutrition, as well as interdisciplinary research that spans these two fields. An open access publication, our research is discoverable and accessible to everyone.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Can creatine supplements help people suffering from post-COVID-19 fatigue?
2023-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How will sea level rise affect the health of freshwater mussels and other salt-sensitive species?
2023-09-20
Investigators recently studied several species of freshwater mussels, which are endangered and are especially sensitive to changes in water quality, to explore the ramifications of sea-level rise in coastal rivers. The research published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry determined the concentration of sea salt that would harm the viability of young mussels.
The study focused on the ecosystems along the southeastern US coast, where sea-level measurements have indicated rising waters from 2 to 6mm per year. By detailing the levels in which salt water is toxic to mussels at various life stages, the results can provide guidance for conservation programs ...
Can artificial intelligence predict the risk of dying in the years following a hip fracture?
2023-09-20
A new study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research indicates that an artificial intelligence–based model trained on basic blood and lab test data as well as basic demographic data can predict a patient’s risk of death within 1-, 5-, and 10-years of experiencing a hip fracture.
In the analysis of 3,751 hip fracture patient records from two in‐hospital database systems at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, the 1‐year mortality rate for all patients was 21% and for those aged 80 years and older was 29%. After assessing 10 different machine learning classification ...
Study reveals the most important considerations for grizzly bear conservation
2023-09-20
Humans negatively impact the health of grizzly bear populations through top-down influences like direct mortality associated with forestry roads (from conflict or illegal killings) and displacement from high quality habitats, and through bottom-up influences like reducing availability of food resources. Research published in Wildlife Monographs reveals the relationship between these forces, informing a strategic conservation program.
Investigators radio-collared and followed numerous grizzly bears over multiple years in southeastern British Columbia. They found an interesting interplay between the most important bottom-up factor, ...
Cognitive behavioral therapy eases how fibromyalgia pain is experienced by the brain
2023-09-20
Patients living with fibromyalgia (FM) – a disease that predominantly affects women and is characterized by chronic pain, fatigue and brain fog – often find limited treatment options and a scarcity of explanations for their symptoms. Research led by Mass General Brigham investigators has found that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can significantly reduce the burden of FM by, in part, reducing pain-catastrophizing, a negative cognitive and emotional response that can intensify pain through feelings of helplessness, rumination and intrusive thoughts. This finding is backed by neuroimaging ...
How bats evolved to avoid cancer
2023-09-20
A new paper in Genome Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, shows that rapid evolution in bats may account for the animals’ extraordinary ability to both host and survive infections as well as avoid cancer.
Bats are exceptional among mammals for not only their ability to fly but also their long lives, low cancer rates, and robust immune systems. Bats are also thought to have played a role in the emergence of SARS-CoV-2. The ability of bats to tolerate viral infections may stem from unusual features ...
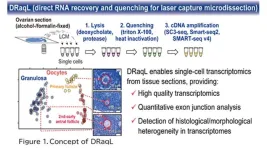
High-quality single-cell transcriptomics from tissue sections reveals histology-associated heterogeneity of mouse follicles
2023-09-20
【Summary】
A research group led by Professor Kazuki Kurimoto and Assistant Professor Hiroki Ikeda from the Department of Embryology at Nara Medical University has developed a highly sensitive method for quantitative single-cell transcriptome analysis, which enables the precise examination of cells extracted from tissue sections using laser capture microdissection (LCM), and named the method DRaqL (Direct RNA recovery and quenching for LCM). Moreover, this method allows quantification of exon-exon junctions of mRNA. In an application of DRaqL to mouse ovarian sections, the research group established a predictive model for oocyte transcriptomes based on their diameter. Remarkably, ...
A hot summer led to more malaria deaths the following year
2023-09-20
As climate change accelerates, it is becoming increasingly important to study the impact of climate change on human health. A new thesis from the University of Gothenburg examines church records and historical weather data in the Nordic countries to show that the risk of dying from malaria was higher if the previous summer was a hot one.
The growing impact of climate change on human health is an acute global threat in the 21st century. The rise in certain types of extreme weather events is not only affecting individuals, but also putting ecosystems that are closely linked to our health under pressure.
“As the climate grows warmer, there is a risk of insect-borne ...
Shading the Great Barrier Reef from the sun might slow bleaching-induced coral decline
2023-09-20
Over the past two decades, coral reefs have declined at unprecedented rates. This is in part because of extreme weather events, which cause wide-spread coral bleaching, a process during which corals lose their color because of stressors, including changes in water temperature, light, or nutrient availability. One of the worst mass bleaching events occurred in 2016 and 2017 on the Great Barrier Reef, causing bleaching on 91% of the system’s reefs.
As frequency and severity of mass bleaching events are expected to increase in the future, researchers are looking for ways to protect corals from excessive radiation and temperatures. As part of the Cooling and Shading ...
New method makes microcombs ten times more efficient
2023-09-20
Microcombs can help us discover planets outside our solar system and track new diseases in our bodies. But current microcombs are inefficient and unable to reach their full potential. Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden have scored a world first with their solution to make microcombs ten times more efficient. Their breakthrough opens the way to new discoveries in space and healthcare and paves the way for high-performance lasers in a range of other technologies.
Laser frequency ...
Over 50s with ADHD ‘overlooked’ for diagnosis and treatment, say experts
2023-09-20
Doctors urgently need better international guidance on treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in the over 50s, conclude world-leading experts reviewing current research on this increasing issue globally.
Published in the peer-reviewed journal Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, the team’s findings highlight a ‘striking’ gap in knowledge about older people as existing guidelines focus on children and young adults.
“Our analysis concludes that better approaches are urgently required to screen and diagnose people aged from around age 50 to 55,” says lead author Dr Maja Dobrosavljevic ...